HBase--JavaAPI数据增删改查
HBase--JavaAPI数据增删改查
- 导入依赖以及创建连接对象和admin对象
- 添加数据(更新)
-
- 添加多条记录
- 查询
-
- 查询单条方式一(NavigableMap)
- 查询单条方式二(CellScanner)
- 查询所有一
- 查询所有二
- 删除
hbase版本:2.3.4
学习记录
增删改查的操作相对比较麻烦
导入依赖以及创建连接对象和admin对象
参考这篇文章
HBase–Namespace JavaAPI基本操作
添加数据(更新)
先创建表对象,再创建put对象,将put对象配置好属性之后使用table对象调用put方法将put对象添加到表中,行键相同的数据会覆盖原数据从而达到更新的效果。
/**
* 添加数据
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void put() throws IOException {
//创建table对象
Table t2 = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t2"));
//创建put对象, 参数为行键
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("1001"));
//配置put对象
put.addColumn(
Bytes.toBytes("f1"), //列簇
Bytes.toBytes("name"), //列名
Bytes.toBytes("cxk") //值
);
//向表中插入数据
t2.put(put);
t2.close();
}

与添加一条记录不同点在于需要将多个put对象放到List中。
put对象支持链式调用
添加多条记录
/**
* 批量添加记录
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void putMany() throws IOException {
//创建table对象
Table t2 = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t2"));
//创建多个put对象
Put put1 = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("1001"));
Put put2 = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("1002"));
Put put3 = new Put(Bytes.toBytes("1003"));
//配置put对象
put1.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("cxk1"))
.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes("11"));
put2.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("cxk2"))
.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes("32"));
put3.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("f1"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("cxk3"));
//创建puts列表
List<Put> puts = Arrays.asList(put1, put2, put3);
//批量添加对象
t2.put(puts);
t2.close();
}
此时可以看出行键为1001的记录的name从cxk变为了cxk1,而且新增了age属性。
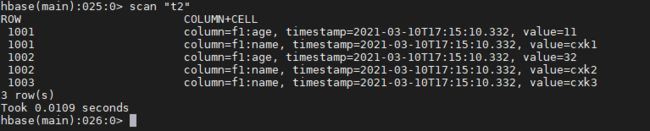
查询
查询记录比较麻烦,需要依次扫描每个表格读取数据。
查询单条方式一(NavigableMap)
通过传入的行键获取到的结果返回列簇键值对。
/**
* 查询单条
* 方式一
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void query1() throws IOException {
//创建table对象
Table t2 = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t2"));
//创建get对象,传入行键
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("1002"));
//获取查询结果
Result result = t2.get(get);
//根据列簇获取键值对
NavigableMap<byte[], byte[]> f1 = result.getFamilyMap(Bytes.toBytes("f1"));
//遍历结果集
f1.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(new String(key) + " === " + new String(value)));
}
查询单条方式二(CellScanner)
通过表格扫描器扫描指定行键的所有属性。
/**
* 查询单条
* 方式二
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void query2() throws IOException {
//创建table对象
Table t2 = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t2"));
//创建get对象,传入行键
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("1002"));
//获取查询结果
Result result = t2.get(get);
//创建表格扫描器
CellScanner cellScanner = result.cellScanner();
//扫描每个表格
while (cellScanner.advance()){
// 每一次扫描获取到当前扫描的表格
Cell current = cellScanner.current();
//列簇
System.out.print(new String(CellUtil.cloneFamily(current)) + "\t");
//列名
System.out.print(new String(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(current)) + "\t");
//值
System.out.println(new String(CellUtil.cloneValue(current)));
}
}
查询所有一
直接把上面查询单条的代码搞过来添加点东西。
/**
* 查询所有一
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void queryAll() throws IOException {
//创建table对象
Table t2 = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t2"));
//获取结果扫描器
ResultScanner scanner = t2.getScanner(new Scan());
//获取结果迭代器
Iterator<Result> iterator = scanner.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Result result = iterator.next();
//获取列簇名集合
Set<byte[]> columnFamilyNames = t2.getDescriptor().getColumnFamilyNames();
for (byte[] columnFamilyName : columnFamilyNames) {
NavigableMap<byte[], byte[]> familyMap = result.getFamilyMap(columnFamilyName);
familyMap.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.print(new String(key) + "===" + new String(value) + "\t"));
}
System.out.println();
}
}
查询所有二
/**
* 查询所有二
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void queryAll2() throws IOException {
//创建table对象
Table t2 = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t2"));
//获取结果扫描器
ResultScanner scanner = t2.getScanner(new Scan());
//获取结果迭代器
Iterator<Result> iterator = scanner.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Result result = iterator.next();
CellScanner cellScanner = result.cellScanner();
while(cellScanner.advance()){
Cell current = cellScanner.current();
System.out.print(new String(CellUtil.cloneRow(current)) + "\t"); //行键
System.out.print(new String(CellUtil.cloneFamily(current)) + "\t"); //列簇
System.out.print(new String(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(current)) + "\t"); //列名
System.out.println(new String(CellUtil.cloneValue(current))); //值
}
}
t2.close();
}
删除
/**
* 删除表
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void delete() throws IOException {
Table t2 = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("t2"));
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes("1003"));
t2.delete(delete);
t2.close();
}




