自定义ioc/aop(一)
自定义ioc
-
- 什么是ioc
- Ioc实现原理
- 手动实现ioc
-
- 转账的demo
-
- Service
- ServiceImpl
- Dao
- Model
- DruidUtils
- ConnectionUtils
- Test
- 实现ioc
-
- 编写beans.xml
- 修改类
-
- Dao
- Impl
- BeanFactory 工厂方法
- 测试
什么是ioc
ioc:Inversion of Control 控制反转,它是一种技术思想,而不是一种技术实现,主要的目的在于解除类与类之间的耦合。
在传统的开发模式下,A类依赖于B类,往往要在A类里面去new一个B类。
在Ioc模式下,我们不用自己去new实例化对象,我们将实例化和控制类的权利交给ioc容器去帮我们实现,在我们需要的时候和ioc容器去要就可以了,所以我们将原本我们自己控制类的权利交给ioc容器,所以叫做控制反转。
Ioc实现原理
配置文件+工厂+反射
手动实现ioc
我们根据ioc的实现原理,手动自己利用配置文件+工厂+反射实现一个简单的ioc的demo
转账的demo
首先我们先写一个不使用ioc的demo
Service
public interface BankService {
public Boolean transfer(String fromCardNo,String toCardNo,int money) throws SQLException;
}
ServiceImpl
public class BankServiceImpl implements BankService {
@Override
public Boolean transfer(String fromCardNo, String toCardNo, int money) throws SQLException {
BankDao bankDao = new BankDao();
User fromUser = bankDao.query(fromCardNo);
User toUser = bankDao.query(toCardNo);
int i = fromUser.getMoney() - money;
fromUser.setMoney(i);
int i1 = toUser.getMoney() + money;
toUser.setMoney(i1);
Boolean transfer = bankDao.transfer(fromUser.getCardNo(), fromUser.getMoney());
Boolean transfer1 = bankDao.transfer(toUser.getCardNo(), toUser.getMoney());
if(transfer && transfer1){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
Dao
public class BankDao {
public User query(String cardNo) throws SQLException {
ConnectionUtils connectionUtils = new ConnectionUtils();
Connection currentConnection = connectionUtils.getCurrentConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = currentConnection.prepareStatement("select * from account where cardNo=?");
preparedStatement.setString(1,cardNo);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
User user = new User();
while (resultSet.next()){
user.setCardNo(resultSet.getString("cardNo"));
user.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
user.setMoney(resultSet.getInt("money"));
}
preparedStatement.close();
return user;
}
public Boolean transfer(String cardNo,int money) throws SQLException {
ConnectionUtils connectionUtils = new ConnectionUtils();
Connection currentConnection = connectionUtils.getCurrentConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = currentConnection.prepareStatement("update account set money=? where cardNo=?");
preparedStatement.setInt(1,money);
preparedStatement.setString(2,cardNo);
boolean execute = preparedStatement.execute();
preparedStatement.close();
return execute;
};
}
Model
public class User {
private String name;
private String cardNo;
private int money;
}
DruidUtils
public class DruidUtils {
private static DruidDataSource druidDataSource=new DruidDataSource();
static {
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
druidDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/bank");
druidDataSource.setUsername("root");
druidDataSource.setPassword("123456");
}
public static DruidDataSource getInstance(){
return druidDataSource;
}
}
ConnectionUtils
public class ConnectionUtils {
private ThreadLocal threadLocal=new ThreadLocal<>();
public Connection getCurrentConnection() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
if (connection == null) {
connection = DruidUtils.getInstance().getConnection();
threadLocal.set(connection);
}
return connection;
}
}
Test
@Test
public void druidUserTest() throws SQLException {
BankServiceImpl bankService = new BankServiceImpl();
Boolean transfer = bankService.transfer("6029621011001", "6029621011000", 100);
}
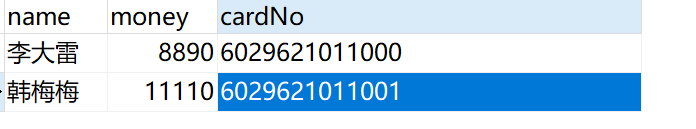
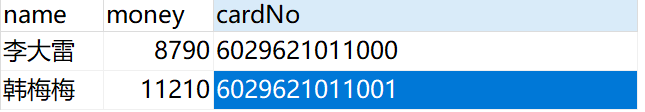
账户余额:
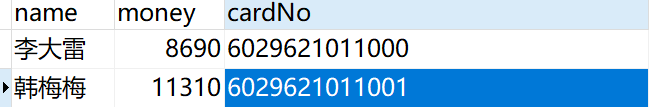
然后我们执行一下方法
执行成功demo可用
接着我们尝试去改造一下demo,使用ioc思想,实现转账功能
实现ioc
首先我们确定哪些对象实例是要交由ioc容器去管理的
那ioc容器是为了将我们需要手动去new的对象,交由ioc去管理,所以我们去将demo里面的所有自己new的对象找出来
通过对上面demo的分析,我们就可以找出在以下几个类里面分别new了哪些对象
DAO:ConnectionUtils
BankServiceImpl:Dao
Test:BankServiceImpl
所以我们可以将上面的几个使用配置文件去管理
编写beans.xml
修改类
Dao
删掉dao方法中的ConnectionUtils connectionUtils=new ConnectionUtils();
添加setConnectionUtils方法,通过set方法来构造对象
ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils){
this.connectionUtils=connectionUtils;
}
其他类同理
Impl
BankDao bankDao;
public void setBankDao(BankDao bankDao){
this.bankDao=bankDao;
}
BeanFactory 工厂方法
public class BeanFactory {
public static Map map=new HashMap<>();
static {
// 读取beans.xml文件
InputStream resourceAsStream = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("beans.XML");
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
try {
// 获取document
Document read = saxReader.read(resourceAsStream);
// 获得根标签
Element rootElement = read.getRootElement();
// 获取所有bean标签对应的属性 包括id、class等等
List beanList = rootElement.selectNodes("//bean");
beanList.forEach(b->{
String id = b.attributeValue("id");
String aClass = b.attributeValue("class");
try {
// 通过反射获取类
Class forName = Class.forName(aClass);
// 实例化对象
Object o = forName.newInstance();
// 放入map中备用
map.put(id,o);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
// 获取所有property标签,并读取其属性name,ref 等
List propertyList = rootElement.selectNodes("//property");
propertyList.forEach(po->{
String name = po.attributeValue("name");
String ref = po.attributeValue("ref");
// 获取该标签对应的父标签,也就是获取该property代表的属性所属于的类
// 例如 ConnectonUtils 是Dao的熟悉
Element parent = po.getParent();
String id = parent.attributeValue("id");
// 从map中获取该类的对象
Object o = map.get(id);
// 获取该类所有的方法
Method[] methods = o.getClass().getMethods();
for (int i = 0; i 测试
@Test
public void beanFactoryTest() throws SQLException {
BankService bankService = (BankService) BeanFactory.getBean("bankService");
Boolean transfer = bankService.transfer("6029621011001", "6029621011000", 100);
}