1. Foundational practice: Always use strict mode
"use strict";
使用严格模式,可以使得浏览器运行js代码更加规范。例如
`"use strict";
city = "shenzhen";
console.log(city);` 在严格模式下运行,浏览器会检查出错误。Uncaught ReferenceError: city is not defined
`"use strict";
module.exports = {
env:{
es6:true
},
rules:{
"strict":["error","global"]
}
};` 2.Declaring Variables
Prefer const, then let. 优先使用const再是let, 不使用var
规则:no-var
相对var,let 声明的对象作用域不会泄露。 变量名不能多次声明,例如:
`let type = "testType";
//再次声明
let type = "testAgain";` 规则:no-redeclare , prefer-const
使用const可以防止变量被意外修改。
Use individual states to create variables; 一个声明创建一个变量
最佳实践表明,这样有利于代码调试且方便阅读代码。
`"use strict";
let color,
background,
size;
const rate = 65.9,
markup = 0.1;
//对比代码====================================
let color;
let background;
let size;
const rate = 65.9;
const markup = 0.1;` 规则:one-var
Create descriptive variable names 创建具有描述意义的变量名
`//snake Case
let sz_inventory_ratio = 0.2;
//camel Case
let szInventoryRatio = 0.2;` 使用驼峰命名规则,规则:camelcase
Standardize acronym case 标准化字母缩写体
`const cogs = 12.7; //COGS: cost of goods sold
const YtdSales = 15.3; //YTD: year to date
const NOP = YtdSales - cogs; //NOP: net operating profit
//===========修改后===========
const COGS = 12.7;
const YTDSales = 15.3;
const NOP = YTDSales - COGS;` Remove unused variables 去除没有使用的变量
规则:no-unused-vars
参考 .eslintrc.js
`"use strict";
module.exports = {
env:{
es6:true
},
rules:{
"strict":["error","global"],
"no-var":"error",
"prefer-const":"error",
"one-var": ["error", "never"],
"camelcase": "error",
"no-unused-vars": "error"
}
};` 3.Assigning Values
Don't assign variables in chains 不允许链式赋值
`let subTotal;
let shipping;
let netTotal;
subTotal = shipping = netTotal = 0; //链式赋值
//=====修改后======
subTotal = 0;
shipping = 0;
netTotal = 0;` 规则:no-multi-assign
Standardize qutoes 标准化引号
js定义字符串对象,默认对双引号",单引号‘都支持。Es6支持backtick ` 。但是在项目要求统一。json文件只支持双引号。要求项目中默认统一使用双引号
规则:quotes
Create arrays and objects using Literals 使用文本创建数组和对象,不允许使用构造函数
new Array()初始化数组令人困惑
因此,为了得到一致的结果,也为了代码简洁。要求初始化数组和对象统一使用文本。例如:
let arr2 = [2];
let arr3 = [2,3,2];
规则:no-array-constructor , no-new-object
Quote object property names consistently 对象属性名使用引号
定义对象,其属性名,也就是key,如果中间有特殊字符(-,_ )就需要用双引号包围。
`const sessions = {
plenary: "The latest buzz in beekeeping",
"morning-beginner": "Hive management 101",
"morning-expert": "Advances in mite control"
};` 通常定义属性名要求驼峰命名,这样约束可以方便检查哪些属性没有这样命名。
规则:quote-props
参考 .eslintrc.js
`"use strict";
module.exports = {
env: {
es6: true,
},
rules: {
strict: ["error", "global"],
"no-var": "error",
"prefer-const": "error",
"one-var": ["error", "never"],
"camelcase": "error",
"no-unused-vars": "error",
"no-multi-assign": "error",
"quotes": ["error", "single"],
"no-array-constructor": "error",
"no-new-object": "error",
"quote-props": ["error","as-needed"]
}
};` 4.Type Casting
Type cast strings with the String wrapper 使用String()转换字符串类型
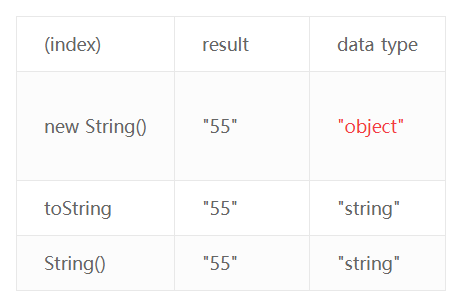
字符串类型转换,使用new String(el), el.toString(), 会有歧义。参考如下:
``"use strict";
const formData = [55];
formData.forEach((el) => {
console.log(`n${el}:`);
console.table({
"new String()": {
result: `${new String(el)}`,
"data type": `${typeof new String(el)}`,
},
toString: {
result: `${el.toString()}`,
"data type": `${typeof el.toString()}`,
},
"String()": {
result: `${String(el)}`,
"data type": `${typeof String(el)}`,
},
});
});`` 字符类型转换对比结果
如果变量是undefined, 使用toString方法会抛错。
因此字符串变量转换最好的方式就是使用String(). 规则:no-new-wrappers
Type cast numbers with the Number wrapper 使用Number()转换数字类型
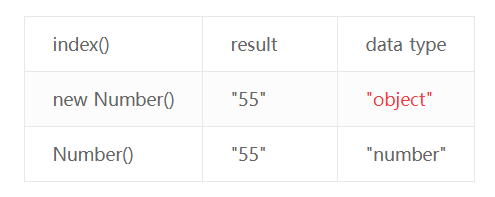
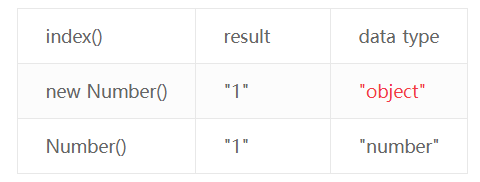
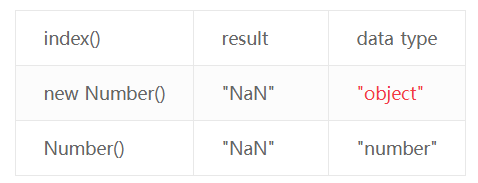
使用new Number()转换数字类型有歧义,参考如下:
``"use strict";
const formData = ["55", true, undefined];
formData.forEach((el) => {
console.log(`n${el}:`);
console.table({
"new Number()": {
result: `${new Number(el)}`,
"data type": `${typeof new Number(el)}`,
},
"Number()": {
result: `${Number(el)}`,
"data type": `${typeof Number(el)}`,
},
});
});`` 运行结果:
55:
true:
undefined:
规则同上:no-new-wrappers
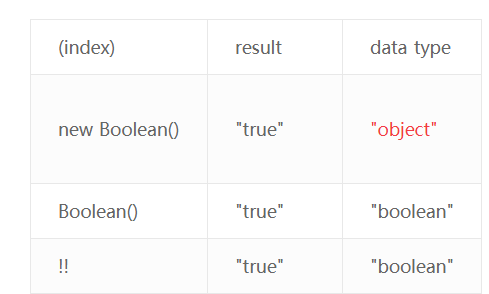
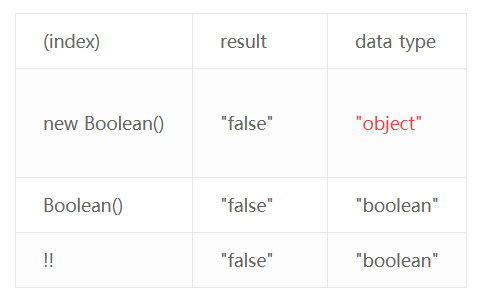
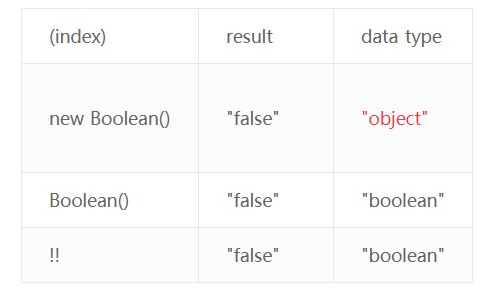
Type cast Booleans using double negation 使用两次非运算 !! 转换布尔类型
使用new Boolean()转换布尔类型有歧义,参考如下:
``"use strict";
const formData = ["flower", 0, undefined];
formData.forEach((el) => {
console.log(`n${el}:`);
console.table({
"new Boolean()": {
result: `${new Boolean(el)}`,
"data type": `${typeof new Boolean(el)}`,
},
"Boolean()": {
result: `${Boolean(el)}`,
"data type": `${typeof Boolean(el)}`,
},
"!!": {
result: `${!!el}`,
"data type": `${typeof !!el}`,
}
});
});`` 运行结果:
0:
underfined:
使用Boolean(), !! 都能得到正确的数据类型,但是为了代码简洁,通常使用!!
规则同上:no-new-wrappers
Rely on implicit Boolean values in conditionsals 在条件中使用隐式布尔类型
`let logged = true;
if(!!logged){ //多余的转换
//do something...
}
if(logged === true){ //多余的判断
//do something...
}
//正确的姿势
if(logged){
//do something...
}` 规则: no-extra-boolean-cast
5.Comparing Values
Use triple-character equality operators 使用===作为相等操作符
js有两个比较符号 "==", "===", 双等号做比较判断会有歧义,参考代码:
``"use strict";
const data = [0, "", false, null];
data.forEach((el) => {
if (el == "0") {
console.log(`${el} == "0"`);
}
if (el == undefined) {
console.log(`${el} == undefined`);
}
});`` 运行结果:
0 == "0"
false == "0"
null == undefined
更为详细的对比参考:https://dorey.github.io/JavaS...
规则: eqeqeq
Don't use Yoda conditions 不使用Yoda条件判断
Yoda特指条件比较时,先列出条件再写出变量的这种倒装式的写法:
`if ("1" === data.alert) { //Yoda
//...
}
if ( 3 < value){ //Yoda
//...
}
//正确的写法
if (data.alert === "1"){
//...
}
if (value > 3){
//...
}` 规则:yoda
Compare appropriately for the data type 数据类型恰当的比较
``"use strict";
const data = {
warning: true,
warningText: "Solar flare may disrupt communications",
notes: "",
alert: 2,
obj: { o1: "hello", o2: 222}
};
if (data.warning) {
console.log(data.warningText);
}
if (data.notes) {
console.log(data.notes);
}
if (data.alert) {
if (data.alert === 1) {
console.log("Winter storm");
} else if (data.alert === 2) {
console.log("High wind");
} else if (data.alert === 3) {
console.log("Hurricane");
} else if (data.alert === 4) {
console.log("Heat advisory");
}
}
if(data.obj){
console.log(`data.obj.o1=${data.obj.o1}`)
}
//============推荐写法==========
if (data.warning) {
console.log(data.warningText);
}
if (data.notes !== "") {
console.log(data.notes);
}
if (data.alert > 0) {
if (data.alert === 1) {
console.log("Winter storm");
} else if (data.alert === 2) {
console.log("High wind");
} else if (data.alert === 3) {
console.log("Hurricane");
} else if (data.alert === 4) {
console.log("Heat advisory");
}
}
if(!!data.obj){
console.log(`data.obj.o1=${data.obj.o1}`)
}`` Use ternary statements judiciously 明智的使用三目比较符
``"use strict";
const data = {
warning: true,
warningText: "Solar flare may disrupt communications",
};
const warning = data.warning ? true : false;
console.log(`Warning: ${(warning) ? data.warningText : "No warning message at this time"}`);
//==========干净的写法=============
const nullWarning = 'No warning message at this time';
const warning = data.warning;
const text = data.warningText;
console.log(`Warning: ${(warning) ? text : nullWarning}`);`` Add parentheses to clarify logic 加()使逻辑清晰
while (thirdChoice === firstChoice || thirdChoice === secondChoice) {
thirdChoice = choose();
}
//清晰的写法
while ((thirdChoice === firstChoice) ||
(thirdChoice === secondChoice)) {
thirdChoice = choose();
}原文链接https://www.sdk.cn/details/emdvzb3PQRem8jqQPA
SDK社区是一个中立的社区,这里有多样的前端知识,有丰富的api,有爱学习的人工智能开发者,有风趣幽默的开发者带你学python,还有未来火热的鸿蒙,当各种元素组合在一起,让我们一起脑洞大开共同打造专业、好玩、有价值的开发者社区,帮助开发者实现自我价值!