向 XPath 中添加自定义函数
在 Web 应用程序中处理数据库更新的两种方法
Microsoft Corporation
Prajakta Joshi
2002 年 10 月 8 日
摘要:特邀作家 Prajakta Joshi 讨论了如何使用 .NET 框架 SDK 中的 System.Xml API 为 XPath 创建自定义函数。主题涉及向 XPath 1.0 中添加扩展函数、展望 XPath 2.0 以及使用 XSLT 中的扩展函数。(14 页打印页)
在 XML和XSL公共新闻组中,对扩展函数 的请求是一个经常讨论的主题。撰写本文的动机是因为我注意到有大量的用户帖子涉及该主题。 XPath 1.0中的 XPath 表达式能够返回以下四个基本 XPath 数据类型之一:
| • | 字符串 |
| • | 数值 |
| • | 布尔值 |
| • | 节点集 |
XSLT 变量向表达式语言中引入了一个附加类型 — result tree fragment(结果树片段)。
XPath 中的核心函数库和其他几个 XSLT 特定的附加函数提供了几个用来操作 XPath 数据类型的基本工具。纵观这些函数,您会发现这不是一个能够满足所有用户需要的完善集合。
| XPath 类型 | 函数 |
| 节点集 |
last()、position()、count()、id()、local-name()、namespace-uri()、name() |
| 字符串 |
string()、concat()、starts-with()、contains()、substring-before()、substring-after()、substring()、string-length()、normalize-space()、translate() |
| 布尔值 |
boolean()、not()、true()、false()、lang() |
| 数值 |
number()、sum()、floor()、ceiling()、round() |
| XSLT 1.0 中的新增函数 |
document()、key()、format-number()、current()、unparsed-entity-uri()、generate-id()、system-property() |
需要操作非 XPath 数据类型(例如,日期)或者用 XPath 数据类型执行功能强大的/自定义数据操作的 XML 开发人员通常需要额外的函数。本文旨在概述如何使用 Microsoft .NET 框架 SDK 中的 System.XmlAPI 来为 XPath 实现自定义函数。
两个字符串的比较
在编写我的第一个 XPath 查询时,我需要对两个字符串执行不区分大小写的比较。我编写的 books.xml 如下所示:
<bookstore xmlns:my="urn:http//mycompany.com/">
<book style="young adult">
<title>Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire</title>
<author>
<first-name>Mary</first-name>
<last-name>Gradpre</last-name>
</author>
<my:price>8.99</my:price>
</book>
<book style="young fiction">
<title>Lord of the Rings</title>
<author>
<first-name>J.</first-name>
<last-name>Tolkien</last-name>
</author>
<my:price>22.50</my:price>
</book>
</bookstore>
我寻找到一个类似于 XPath 1.0 字符串函数 中的 String.Compare()的函数。可用在我的解决方案中的最接近的函数是 translate()。我通过以下代码片段使用 System.Xml.XPath命名空间中的 XPath 类解决了该问题:
using System;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.XPath;
public class sample
{
public static void Main(string []args)
{
// Load source XML into XPathDocument.
XPathDocument xd = new XPathDocument(args[0], XmlSpace.Preserve);
// Create XPathNavigator from XPathDocument.
XPathNavigator nav = xd.CreateNavigator();
XPathExpression expr;
expr =
nav.Compile("/bookstore/book/title[translate(.,'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz',
'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ') = 'HARRY POTTER AND THE GOBLET OF FIRE']");
XPathNodeIterator iterator = nav.Select(expr);
// Iterate through selected nodes.
while (iterator.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine("Book title: {0}", iterator.Current.Value);
}
}
}
此代码生成如下输出结果:
Book title: Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire
尽管此解决方案有点长,但我还是解决了我的问题。在几天之后编写 XPath 查询时,我要在由正则表达式匹配定义的位置将字符串拆分成子字符串的数组。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<Books>
<Book>
<Title>Stephen Hawking's Universe: The Cosmos Explained</Title>
<Authors>David Filkin, Stephen Hawking</Authors>
</Book>
<Book>
<Title>Writing Secure code</Title>
<Authors>Michael Howard, David LeBlanc</Authors>
</Book>
</Books>
我要从 <Authors> 元素的逗号分隔列表中找出第 n 个作者的姓名 — 一个有点复杂的字符串操作问题。我认为这是一个学习如何实现 XPath 自定义扩展函数的好机会。
实现 XPath 中的扩展函数
我发现 XPath 1.0 建议没有为扩展函数定义机制。但好消息是,我可以为 XPath 处理器提供一个自定义执行上下文,以便解析 XPath 表达式中用户定义的函数和变量。
下图解释了我的解决方案内 System.Xml.Xsl 命名空间中 XsltContext 类、IXsltContextFunction 接口和 IXsltContextVariable接口的角色。
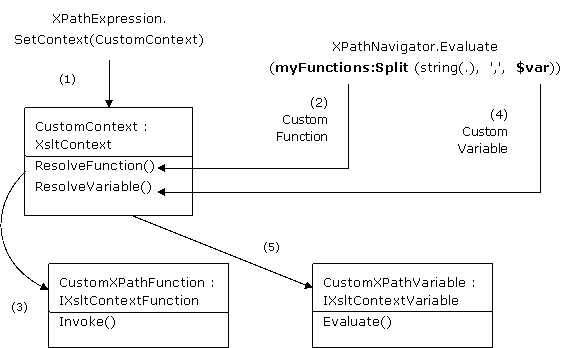
图 1. XsltContext 的角色
解决方案中的关键步骤
| • | 1.XPathExpression.SetContext(CustomContext) 提供一个 XPath 处理器 (XPathNavigator),它具有用来解析用户定义的函数和变量的自定义上下文。CustomContext(从抽象类 XsltContext 派生)实现两个关键方法:ResolveFunction() 和 ResolveVariable()。 |
| • | 2.当 XPathNavigator 在 XPathExpression 中遇到用户定义的函数时,它会针对自定义上下文调用 ResolveFunction() 方法。ResolveFunction() 返回从 IXsltContextFunction 派生的适当自定义函数。 |
| • | 3.XPathNavigator 在运行时使用所提供的参数针对这个自定义函数调用 Invoke() 方法。 |
| • | 4.当 XPathNavigator 在 XPathExpression 中检测到用户定义的变量时,它会针对自定义上下文调用 ResolveVariable() 方法。ResolveVariable() 返回从 IXsltContextVariable 派生的适当的自定义变量。 |
| • | 5.XPathNavigator 在运行时针对这个自定义变量调用 Evaluate() 方法。 |
我决定编写一个自定义的 XPath 函数 — Split(),使该函数的行为类似于 .NET SDK 中的 RegEx.Split()方法。下面介绍如何将所有这些代码片段合并在一起。
XsltContext 类的角色
首先,我实现了我的自定义 XsltContext,以便给 XPath 处理器提供有关解析用户定义的函数所需的信息。ResolveFunction和ResolveVariable是 XsltContext 类的两个关键方法,用户必须重写它们才能实现自定义解析。这些方法在运行时由 XPathNavigator调用,以便解析对 XPath 查询表达式中用户定义的函数和变量的引用。
请注意,我在 CustomContext 类中封装了一个 ResolveVariable对象。此对象是 XPath 表达式中的变量的容器。
public class CustomContext : XsltContext
{
// XsltArgumentList to store my user defined variables
private XsltArgumentList m_ArgList;
// Constructors
public CustomContext()
{}
public CustomContext(NameTable nt) : base(nt)
{
}
public CustomContext(NameTable nt, XsltArgumentList argList) : base(nt)
{
m_ArgList = argList;
}
// Returns the XsltArgumentList that contains custom variable definitions.
public XsltArgumentList ArgList
{
get
{
return m_ArgList;
}
}
// Function to resolve references to my custom functions.
public override IXsltContextFunction ResolveFunction(string prefix,
string name, XPathResultType[] ArgTypes)
{
XPathRegExExtensionFunction func = null;
// Create an instance of appropriate extension function class.
switch (name)
{
case "Split":
// Usage
// myFunctions:Split(string source, string Regex_pattern, int n) returns string
func = new XPathRegExExtensionFunction("Split", 3, 3, new
XPathResultType[] {XPathResultType.String, XPathResultType.String,
XPathResultType.Number}, XPathResultType.String);
break;
case "Replace":
// Usage
// myFunctions:Replace(string source, string Regex_pattern,
string replacement_string) returns string
func = new XPathRegExExtensionFunction("Replace", 3, 3, new
XPathResultType[] {XPathResultType.String, XPathResultType.String,
XPathResultType.String}, XPathResultType.String);
break;
}
return func;
}
// Function to resolve references to my custom variables.
public override IXsltContextVariable ResolveVariable(string prefix, string name)
{
// Create an instance of an XPathExtensionVariable.
XPathExtensionVariable Var;
var = new XPathExtensionVariable(name);
return Var;
}
public override int CompareDocument(string baseUri, string nextbaseUri)
{
return 0;
}
public override bool PreserveWhitespace(XPathNavigator node)
{
return true;
}
public override bool Whitespace
{
get
{
return true;
}
}
}
IXsltContextFunction 接口的角色
下一步是实现供 CustomContext 类使用的
接口。此对象的
方法在运行时由 XPathNavigator利用所提供的参数进行调用。
public class XPathRegExExtensionFunction : IXsltContextFunction
{
private XPathResultType[] m_ArgTypes;
private XPathResultType m_ReturnType;
private string m_FunctionName;
private int m_MinArgs;
private int m_MaxArgs;
// Methods to access the private fields.
public int Minargs
{
get
{
return m_MinArgs;
}
}
public int Maxargs
{
get
{
return m_MaxArgs;
}
}
public XPathResultType[] ArgTypes
{
get
{
return m_ArgTypes;
}
}
public XPathResultType ReturnType
{
get
{
return m_ReturnType;
}
}
// Constructor
public XPathRegExExtensionFunction(string name, int minArgs, int
maxArgs, XPathResultType[] argTypes, XPathResultType returnType)
{
m_FunctionName = name;
m_MinArgs = minArgs;
m_MaxArgs = maxArgs;
m_ArgTypes = argTypes;
m_ReturnType = returnType;
}
// This method is invoked at run time to execute the user defined function.
public object Invoke(XsltContext xsltContext, object[] args,
XPathNavigator docContext)
{
Regex r;
string str = null;
// The two custom XPath extension functions
switch (m_FunctionName)
{
case "Split":
r = new Regex(args[1].ToString());
string [] s1 = r.Split(args[0].ToString());
int n = Convert.ToInt32(args[2]);
if (s1.Length < n)
str = "";
else
str = s1[n - 1];
break;
case "Replace":
r = new Regex(args[1].ToString());
string s2 = r.Replace(args[0].ToString(), args[2].ToString());
str = s2;
break;
}
return (object) str;
}
}
IXsltContextVariable 接口的角色
XPath 表达式中可以包含用户定义的变量引用,例如:
XPathExpression expr1 = nav.Compile("myFunctions:Split(string(.), ',',
$var
)");
我需要实现 IXsltContextVariable接口并重写 Evaluate()方法(此方法在运行时
public class XPathExtensionVariable : IXsltContextVariable
{
// The name of the user-defined variable to resolve
private string m_VarName;
public XPathExtensionVariable(string VarName)
{
m_VarName = VarName;
}
// This method is invoked at run time to find the value of the user defined variable.
public object Evaluate(XsltContext xsltContext)
{
XsltArgumentList vars = ((CustomContext) xsltContext).ArgList;
return vars.GetParam(m_VarName, null);
}
public bool IsLocal
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
public bool IsParam
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
public XPathResultType VariableType
{
get
{
return XPathResultType.Any;
}
}
}
把代码合并在一起
最后,我使用了 XPathExpression.SetContext()方法,将它传入我的自定义上下文对象。图 1 汇总了该解决方案中的所有步骤。请注意,XsltContext 类是从 XmlNamespaceManager中继承而来的,而且通过使用 AddNamespace()向集合中添加了我的自定义命名空间。
using System;
using System.Xml;
using System.Xml.Xsl;
using System.Xml.XPath;
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
public class sample
{
public static void Main(string []argc)
{
// Load source XML into XPathDocument.
XPathDocument doc = new XPathDocument("books.xml", XmlSpace.Preserve);
// Create XPathNavigator from XPathDocument.
XPathNavigator nav = doc.CreateNavigator();
// Add user-defined variable to the XsltArgumentList.
XsltArgumentList varList = new XsltArgumentList();
varList.AddParam("var", "", 2);
// Compile the XPathExpression.
// Note that the compilation step only checks the query expression
// for correct XPath syntax.
// User defined functions and variables are not resolved.
XPathExpression expr1 = nav.Compile("myFunctions:Split(string(.), ',', $var)");
// Create an instance of a custom XsltContext object.
CustomContext cntxt = new CustomContext(new NameTable(), varList);
// Add a namespace definition for myFunctions prefix.
cntxt.AddNamespace("myFunctions", "http://myXPathExtensionFunctions");
// Associate the custom context with the XPathExpression object.
expr1.SetContext(cntxt);
XPathNodeIterator it = nav.Select("/Books/Book/Authors");
while (it.MoveNext())
{
Console.WriteLine("Authors: {0}", it.Current.Value);
Console.WriteLine("Second author: {0}", it.Current.Evaluate(expr1));
}
}
}
运行此代码会生成如下输出结果:
Authors: David Filkin, Stephen Hawking Second author: Stephen Hawking Authors: Michael Howard, David LeBlanc Second author: David LeBlanc
扩展函数的其他用法
在我发现了使用扩展函数的机制之后,在用 XPath编程时,我在其他许多数据操作的情况下都使用了扩展函数。一些其他情况包括:
| • | 操作日期:对两个日期字符串进行比较是常见的操作。为了实现此目的,我使用了 System.DateTime.Compare()方法。 |
| • | 操作数值:Math方法。 类为常见的数学运算提供一组详尽的方法。我将 Abs() 方法用作自定义函数。 |
| • | 操作日期:对两个日期字符串进行比较是常见的操作。为了实现此目的,我使用了 System.DateTime.Compare()方法。 |
| • | 操作字符串:String类为常见的字符串操作提供一组详尽的方法。我发现 ToUpper() 和 ToLower() 方法在被用作为自定义函数时非常有用。 |
这种情况数不胜数。根据您的具体情况,可以在您的自定义函数中使用任何 .NET 类。
未来的方向:XPath 2.0
由于 W3C XML 架构数据类型日益与 XPath 2.0集成,因此,Xquery 1.0 和 XPath 2.0 函数和运算符将为 XML 开发人员提供一个比当前存在于 XPath 1.0 中的函数更为丰富的函数库。这不会完全消除 XPath 2.0 对用户定义的函数的需要。对于 XML 的功能强大、可扩展的查询语言来说,扩展的机制将是不可或缺的。
XSLT 中的扩展函数
XSLT 1.0 的XslTransform实现将命名空间 urn:schemas-microsoft-com:xslt 用作扩展命名空间。它具有对 <msxsl:node-set>扩展函数和 <msxsl:script>扩展元素的内置支持。
在 XSLT 中,可通过两种方法来实现用户定义的函数:
| • | 1.样式表脚本 |
| • | 2.向 XsltArgumentList中添加扩展对象 |