点赞再看,养成习惯,公众号搜一搜【一角钱技术】关注更多原创技术文章。本文 GitHub org_hejianhui/JavaStudy 已收录,有我的系列文章。
前言
PriorityBlockingQueue 优先级队列,线程安全(添加、读取都进行了加锁)、无界、读阻塞的队列,底层采用的堆结构实现(二叉树),默认是小根堆,最小的或者最大的元素会一直置顶,每次获取都取最顶端的数据
队列创建
小根堆
PriorityBlockingQueue concurrentLinkedQueue = new PriorityBlockingQueue();
大根堆
PriorityBlockingQueue concurrentLinkedQueue = new PriorityBlockingQueue(10, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
应用场景
有任务要执行,可以对任务加一个优先级的权重,这样队列会识别出来,对该任务优先进行出队。
我们来看一个具体例子,例子中定义了一个将要放入“优先阻塞队列”的任务类,并且定义了一个任务工场类和一个任务执行类,在任务工场类中产生了各种不同优先级的任务,将其添加到队列中,在任务执行类中,任务被一个个取出并执行。
package com.niuh.queue.priority;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
*
* PriorityBlockingQueue使用示例
*
*/
public class PriorityBlockingQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Random random = new Random(47);
ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
PriorityBlockingQueue queue = new PriorityBlockingQueue<>();
exec.execute(new PrioritizedTaskProducer(queue, exec)); // 这里需要注意,往PriorityBlockingQueue中添加任务和取出任务的
exec.execute(new PrioritizedTaskConsumer(queue)); // 步骤是同时进行的,因而输出结果并不一定是有序的
}
}
class PrioritizedTask implements Runnable, Comparable {
private Random random = new Random(47);
private static int counter = 0;
private final int id = counter++;
private final int priority;
protected static List sequence = new ArrayList<>();
public PrioritizedTask(int priority) {
this.priority = priority;
sequence.add(this);
}
@Override
public int compareTo(PrioritizedTask o) {
return priority < o.priority ? 1 : (priority > o.priority ? -1 : 0); // 定义优先级计算方式
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(random.nextInt(250));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println(this);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("[%1$-3d]", priority) + " Task " + id;
}
public String summary() {
return "(" + id + ": " + priority + ")";
}
public static class EndSentinel extends PrioritizedTask {
private ExecutorService exec;
public EndSentinel(ExecutorService exec) {
super(-1);
this.exec = exec;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int count = 0;
for (PrioritizedTask pt : sequence) {
System.out.print(pt.summary());
if (++count % 5 == 0) {
System.out.println();
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(this + " Calling shutdownNow()");
exec.shutdownNow();
}
}
}
class PrioritizedTaskProducer implements Runnable {
private Random random = new Random(47);
private Queue queue;
private ExecutorService exec;
public PrioritizedTaskProducer(Queue queue, ExecutorService exec) {
this.queue = queue;
this.exec = exec;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
queue.add(new PrioritizedTask(random.nextInt(10))); // 往PriorityBlockingQueue中添加随机优先级的任务
Thread.yield();
}
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(250);
queue.add(new PrioritizedTask(10)); // 往PriorityBlockingQueue中添加优先级为10的任务
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
queue.add(new PrioritizedTask(i));// 往PriorityBlockingQueue中添加优先级为1-10的任务
}
queue.add(new PrioritizedTask.EndSentinel(exec));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("Finished PrioritizedTaskProducer");
}
}
class PrioritizedTaskConsumer implements Runnable {
private PriorityBlockingQueue queue;
public PrioritizedTaskConsumer(PriorityBlockingQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
queue.take().run(); // 任务的消费者,从PriorityBlockingQueue中取出任务执行
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
System.out.println("Finished PrioritizedTaskConsumer");
}
}
工作原理
PriorityBlockingQueue 是 JDK1.5 的时候出来的一个阻塞队列。但是该队列入队的时候是不会阻塞的,永远会加到队尾。下面我们介绍下它的几个特点:
- PriorityBlockingQueue 和 ArrayBlockingQueue 一样是基于数组实现的,但后者在初始化时需要指定长度,前者默认长度是 11。
- 该队列可以说是真正的无界队列,它在队列满的时候会进行扩容,而前面说的无界阻塞队列其实都有有界,只是界限太大可以忽略(最大值是 2147483647)
- 该队列属于权重队列,可以理解为它可以进行排序,但是排序不是从小到大排或从大到小排,是基于数组的堆结构(具体如何排下面会进行分析)
- 出队方式和前面的也不同,是根据权重来进行出队,和前面所说队列中那种先进先出或者先进后出方式不同。
- 其存入的元素必须实现Comparator,或者在创建队列的时候自定义Comparator。
注意:
- 堆结构实际上是一种完全二叉树。关于二叉树可以查看 《树、二叉树、二叉搜索树的实现和特性》
- 堆又分为大顶堆和小顶堆 。大顶堆中第一个元素肯定是所有元素中最大的,小顶堆中第一个元素是所有元素中最小的。
源码分析
定义
PriorityBlockingQueue的类继承关系如下:
其包含的方法定义如下:
成员属性
从下面的字段我们可以知道,该队列可以排序,使用显示锁来保证操作的原子性,在空队列时,出队线程会堵塞等。
/**
* 默认数组长度
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
/**
* 最大达容量,分配时超出可能会出现 OutOfMemoryError 异常
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* 队列,存储我们的元素
*/
private transient Object[] queue;
/**
* 队列长度
*/
private transient int size;
/**
* 比较器,入队进行权重的比较
*/
private transient Comparator comparator;
/**
* 显示锁
*/
private final ReentrantLock lock;
/**
* 空队列时进行线程阻塞的 Condition 对象
*/
private final Condition notEmpty;
构造函数
/**
* 默认构造,使用长度为 11 的数组,比较器为空
*/
public PriorityBlockingQueue() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, null);
}
/**
* 自定义数据长度构造,比较器为空
*/
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, null);
}
/**
* 自定义数组长度,可以自定义比较器
*/
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator comparator) {
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.lock = new ReentrantLock();
this.notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
this.comparator = comparator;
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
/**
* 构造函数,带有初始内容的队列
*/
public PriorityBlockingQueue(Collection c) {
this.lock = new ReentrantLock();
this.notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
boolean heapify = true; // true if not known to be in heap order
boolean screen = true; // true if must screen for nulls
if (c instanceof SortedSet) {
SortedSet ss = (SortedSet) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator) ss.comparator();
heapify = false;
}
else if (c instanceof PriorityBlockingQueue) {
PriorityBlockingQueue pq =
(PriorityBlockingQueue) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator) pq.comparator();
screen = false;
if (pq.getClass() == PriorityBlockingQueue.class) // exact match
heapify = false;
}
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int n = a.length;
// If c.toArray incorrectly doesn't return Object[], copy it.
if (a.getClass() != Object[].class)
a = Arrays.copyOf(a, n, Object[].class);
if (screen && (n == 1 || this.comparator != null)) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (a[i] == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
}
this.queue = a;
this.size = n;
if (heapify)
heapify();
}
入队方法
入队方法,下面可以看到 put 方法最终会调用 offer 方法,所以我们只看 offer 方法即可。
offer(E e)
public void put(E e) {
offer(e); // never need to block
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
//判断是否为空
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//显示锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
//定义临时对象
int n, cap;
Object[] array;
//判断数组是否满了
while ((n = size) >= (cap = (array = queue).length))
//数组扩容
tryGrow(array, cap);
try {
//拿到比较器
Comparator cmp = comparator;
//判断是否有自定义比较器
if (cmp == null)
//堆上浮
siftUpComparable(n, e, array);
else
//使用自定义比较器进行堆上浮
siftUpUsingComparator(n, e, array, cmp);
//队列长度 +1
size = n + 1;
//唤醒休眠的出队线程
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array)
上浮调整比较器方法的实现
private static void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array) {
Comparable key = (Comparable) x;
while (k > 0) {
//无符号向左移,目的是找到放入位置的父节点
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
//拿到父节点的值
Object e = array[parent];
//比较是否大于该元素,不大于就没比较交换
if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0)
break;
//以下都是元素位置交换
array[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
array[k] = key;
}
根据上面的代码,可以看出这是完全二叉树在进行上浮调整。调整入队的元素,找出最小的,将元素排列有序化。简单理解就是:父节点元素值一定要比它的子节点得小,如果父节点大于子节点了,那就两者位置进行交换。
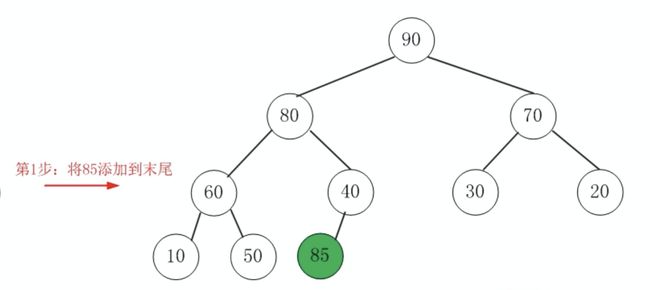
入队图解
例子:85 添加到二叉堆中(大顶堆)
package com.niuh.queue.priority;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue;
/**
*
* PriorityBlockingQueue 简单演示 demo
*
*/
public class TestPriorityBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 大顶堆
PriorityBlockingQueue concurrentLinkedQueue = new PriorityBlockingQueue(10, new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2 - o1;
}
});
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(90);
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(80);
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(70);
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(60);
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(40);
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(30);
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(20);
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(10);
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(50);
concurrentLinkedQueue.offer(85);
//输出元素排列
concurrentLinkedQueue.stream().forEach(e-> System.out.print(e+" "));
//取出元素
Integer take = concurrentLinkedQueue.take();
System.out.println();
concurrentLinkedQueue.stream().forEach(e-> System.out.print(e+" "));
}
}
操作的细节分为两步:
- 第一步:首先把新元素插入到堆的尾部再说;(新的元素可能是特别大或者特别小,那么要做的一件事情就是重新维护一下堆的所有元素,把新元素挪到这个堆的相应的位置)
- 第二步:依次向上调整整个堆的结构,就叫
HeapifyUp
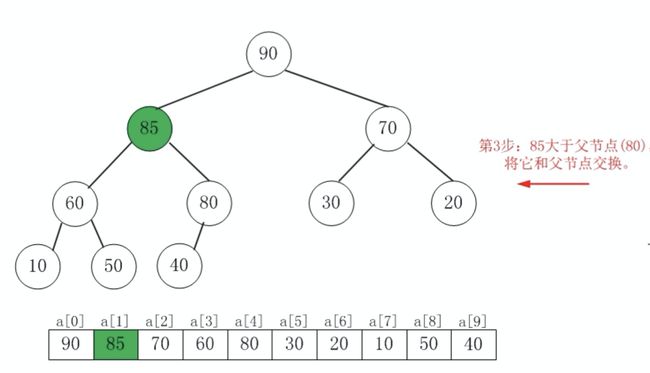
85 按照上面讲的先插入到堆的尾部,也就是一维数组的尾部,一维数组的尾部的话就上图的位置,因为这是一个完全二叉树,所以它的尾部就是50后面这个结点。插进来之后这个时候就破坏了堆,它的每一个结点都要大于它的儿子的这种属性了,接下来要做的事情就是要把 85 依次地向上浮动,怎么浮动?就是 85 大于它的父亲结点,那么就和父亲结点进行交换,直到走到根如果大于根的话,就和根也进行交换。
85 再继续往前走之后,它要和 80 再进行比较,同理可得:也就是说这个结点每次和它的父亲比,如果它大于它的父亲的话就交换,直到它不再大于它的父亲。
出队方法
入队列的方法说完后,我们来说说出队列的方法。PriorityBlockingQueue提供了多种出队操作的实现来满足不同情况下的需求,如下:
- E take();
- E poll();
- E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
- E peek()
poll 和 peek 与上面类似,这里不做说明
take()
出队方法,该方法会阻塞
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
//显示锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
//可中断锁
lock.lockInterruptibly();
//结果接收对象
E result;
try {
//判断队列是否为空
while ( (result = dequeue()) == null)
//线程阻塞
notEmpty.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return result;
}
dequeue()**
我们再来看看具体出队方法的实现,dequeue方法
private E dequeue() {
//长度减少 1
int n = size - 1;
//判断队列中是否有元素
if (n < 0)
return null;
else {
//队列对象
Object[] array = queue;
//取出第一个元素
E result = (E) array[0];
//拿出最后一个元素
E x = (E) array[n];
//置空
array[n] = null;
Comparator cmp = comparator;
if (cmp == null)
//下沉调整
siftDownComparable(0, x, array, n);
else
siftDownUsingComparator(0, x, array, n, cmp);
//成功则减少队列中的元素数量
size = n;
return result;
}
}
总体就是找到父节点与两个子节点中最小的一个节点,然后进行交换位置,不断重复,由上而下的交换。
siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array, int n)
再来看看下沉比较器方法的实现
private static void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array,
int n) {
//判断队列长度
if (n > 0) {
Comparable key = (Comparable)x;
//找到队列最后一个元素的父节点的索引。
int half = n >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) {
//拿到 k 节点下的左子节点
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least
//取得子节点对应的值
Object c = array[child];
//取得 k 右子节点的索引
int right = child + 1;
//比较右节点的索引是否小于队列长度和左右子节点的值进行比较
if (right < n &&
((Comparable) c).compareTo((T) array[right]) > 0)
c = array[child = right];
//比较父节点值是否大于子节点
if (key.compareTo((T) c) <= 0)
break;
//下面都是元素替换
array[k] = c;
k = child;
}
array[k] = key;
}
}
出队图解
- 将堆尾元素替换到顶部(即堆顶被替代删除掉)
- 依次从根部向下调整整个堆的结构(一直到堆尾即可)
HeapifyDown
例子:90 从二叉堆中删除(大顶堆)
完整代码
public class PriorityBlockingQueue extends AbstractQueue
implements BlockingQueue, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5595510919245408276L;
/**
* 默认数组长度 11
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
/**
* 最大达容量,分配时超出可能会出现 OutOfMemoryError 异常
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* 队列,存储我们的元素
*/
private transient Object[] queue;
/**
* 队列长度
*/
private transient int size;
/**
* 比较器,入队进行权重的比较
*/
private transient Comparator comparator;
/**
* 显示锁
*/
private final ReentrantLock lock;
/**
* 空队列时进行线程阻塞的 Condition 对象
*/
private final Condition notEmpty;
/**
* Spinlock for allocation, acquired via CAS.
*/
private transient volatile int allocationSpinLock;
/**
* A plain PriorityQueue used only for serialization,
* to maintain compatibility with previous versions
* of this class. Non-null only during serialization/deserialization.
*/
private PriorityQueue q;
/**
* 默认构造,使用长度为 11 的数组,比较器为空
*/
public PriorityBlockingQueue() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, null);
}
/**
* 自定义数据长度构造,比较器为空
*/
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, null);
}
/**
* 自定义数组长度,可以自定义比较器
*/
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator comparator) {
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.lock = new ReentrantLock();
this.notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
this.comparator = comparator;
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
/**
* 构造函数,带有初始内容的队列
*/
public PriorityBlockingQueue(Collection c) {
this.lock = new ReentrantLock();
this.notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
boolean heapify = true; // true if not known to be in heap order
boolean screen = true; // true if must screen for nulls
if (c instanceof SortedSet) {
SortedSet ss = (SortedSet) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator) ss.comparator();
heapify = false;
}
else if (c instanceof PriorityBlockingQueue) {
PriorityBlockingQueue pq =
(PriorityBlockingQueue) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator) pq.comparator();
screen = false;
if (pq.getClass() == PriorityBlockingQueue.class) // exact match
heapify = false;
}
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int n = a.length;
// If c.toArray incorrectly doesn't return Object[], copy it.
if (a.getClass() != Object[].class)
a = Arrays.copyOf(a, n, Object[].class);
if (screen && (n == 1 || this.comparator != null)) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (a[i] == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
}
this.queue = a;
this.size = n;
if (heapify)
heapify();
}
/**
* Tries to grow array to accommodate at least one more element
* (but normally expand by about 50%), giving up (allowing retry)
* on contention (which we expect to be rare). Call only while
* holding lock.
*
* @param array the heap array
* @param oldCap the length of the array
*/
private void tryGrow(Object[] array, int oldCap) {
lock.unlock(); // must release and then re-acquire main lock
Object[] newArray = null;
if (allocationSpinLock == 0 &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, allocationSpinLockOffset,
0, 1)) {
try {
int newCap = oldCap + ((oldCap < 64) ?
(oldCap + 2) : // grow faster if small
(oldCap >> 1));
if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) { // possible overflow
int minCap = oldCap + 1;
if (minCap < 0 || minCap > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
newCap = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
if (newCap > oldCap && queue == array)
newArray = new Object[newCap];
} finally {
allocationSpinLock = 0;
}
}
if (newArray == null) // back off if another thread is allocating
Thread.yield();
lock.lock();
if (newArray != null && queue == array) {
queue = newArray;
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, oldCap);
}
}
/**
* Mechanics for poll(). Call only while holding lock.
*/
private E dequeue() {
//长度减少 1
int n = size - 1;
//判断队列中是否有元素
if (n < 0)
return null;
else {
//队列对象
Object[] array = queue;
//取出第一个元素
E result = (E) array[0];
//拿出最后一个元素
E x = (E) array[n];
//置空
array[n] = null;
Comparator cmp = comparator;
if (cmp == null)
//下沉调整
siftDownComparable(0, x, array, n);
else
siftDownUsingComparator(0, x, array, n, cmp);
//成功则减少队列中的元素数量
size = n;
return result;
}
}
/**
* Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
* promoting x up the tree until it is greater than or equal to
* its parent, or is the root.
*
* To simplify and speed up coercions and comparisons. the
* Comparable and Comparator versions are separated into different
* methods that are otherwise identical. (Similarly for siftDown.)
* These methods are static, with heap state as arguments, to
* simplify use in light of possible comparator exceptions.
*
* @param k the position to fill
* @param x the item to insert
* @param array the heap array
*/
private static void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array) {
Comparable key = (Comparable) x;
while (k > 0) {
//无符号向左移,目的是找到放入位置的父节点
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
//拿到父节点的值
Object e = array[parent];
//比较是否大于该元素,不大于就没比较交换
if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0)
break;
//以下都是元素位置交换
array[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
array[k] = key;
}
private static void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, T x, Object[] array,
Comparator cmp) {
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = array[parent];
if (cmp.compare(x, (T) e) >= 0)
break;
array[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
array[k] = x;
}
/**
* Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
* demoting x down the tree repeatedly until it is less than or
* equal to its children or is a leaf.
*
* @param k the position to fill
* @param x the item to insert
* @param array the heap array
* @param n heap size
*/
private static void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array,
int n) {
//判断队列长度
if (n > 0) {
Comparable key = (Comparable)x;
//找到队列最后一个元素的父节点的索引。
int half = n >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) {
//拿到 k 节点下的左子节点
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least
//取得子节点对应的值
Object c = array[child];
//取得 k 右子节点的索引
int right = child + 1;
//比较右节点的索引是否小于队列长度和左右子节点的值进行比较
if (right < n &&
((Comparable) c).compareTo((T) array[right]) > 0)
c = array[child = right];
//比较父节点值是否大于子节点
if (key.compareTo((T) c) <= 0)
break;
//下面都是元素替换
array[k] = c;
k = child;
}
array[k] = key;
}
}
private static void siftDownUsingComparator(int k, T x, Object[] array,
int n,
Comparator cmp) {
if (n > 0) {
int half = n >>> 1;
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
Object c = array[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < n && cmp.compare((T) c, (T) array[right]) > 0)
c = array[child = right];
if (cmp.compare(x, (T) c) <= 0)
break;
array[k] = c;
k = child;
}
array[k] = x;
}
}
/**
* Establishes the heap invariant (described above) in the entire tree,
* assuming nothing about the order of the elements prior to the call.
*/
private void heapify() {
Object[] array = queue;
int n = size;
int half = (n >>> 1) - 1;
Comparator cmp = comparator;
if (cmp == null) {
for (int i = half; i >= 0; i--)
siftDownComparable(i, (E) array[i], array, n);
}
else {
for (int i = half; i >= 0; i--)
siftDownUsingComparator(i, (E) array[i], array, n, cmp);
}
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be compared
* with elements currently in the priority queue according to the
* priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
return offer(e);
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
* As the queue is unbounded, this method will never return {@code false}.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be compared
* with elements currently in the priority queue according to the
* priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
//判断是否为空
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//显示锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
//定义临时对象
int n, cap;
Object[] array;
//判断数组是否满了
while ((n = size) >= (cap = (array = queue).length))
//数组扩容
tryGrow(array, cap);
try {
//拿到比较器
Comparator cmp = comparator;
//判断是否有自定义比较器
if (cmp == null)
//堆上浮
siftUpComparable(n, e, array);
else
//使用自定义比较器进行堆上浮
siftUpUsingComparator(n, e, array, cmp);
//队列长度 +1
size = n + 1;
//唤醒休眠的出队线程
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
//释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
* As the queue is unbounded, this method will never block.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be compared
* with elements currently in the priority queue according to the
* priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public void put(E e) {
offer(e); // never need to block
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
* As the queue is unbounded, this method will never block or
* return {@code false}.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @param timeout This parameter is ignored as the method never blocks
* @param unit This parameter is ignored as the method never blocks
* @return {@code true} (as specified by
* {@link BlockingQueue#offer(Object,long,TimeUnit) BlockingQueue.offer})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be compared
* with elements currently in the priority queue according to the
* priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
return offer(e); // never need to block
}
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
//显示锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
//可中断锁
lock.lockInterruptibly();
//结果接收对象
E result;
try {
//判断队列是否为空
while ( (result = dequeue()) == null)
//线程阻塞
notEmpty.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return result;
}
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
E result;
try {
while ( (result = dequeue()) == null && nanos > 0)
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return result;
}
public E peek() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (size == 0) ? null : (E) queue[0];
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns the comparator used to order the elements in this queue,
* or {@code null} if this queue uses the {@linkplain Comparable
* natural ordering} of its elements.
*
* @return the comparator used to order the elements in this queue,
* or {@code null} if this queue uses the natural
* ordering of its elements
*/
public Comparator comparator() {
return comparator;
}
public int size() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return size;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Always returns {@code Integer.MAX_VALUE} because
* a {@code PriorityBlockingQueue} is not capacity constrained.
* @return {@code Integer.MAX_VALUE} always
*/
public int remainingCapacity() {
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
private int indexOf(Object o) {
if (o != null) {
Object[] array = queue;
int n = size;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (o.equals(array[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Removes the ith element from queue.
*/
private void removeAt(int i) {
Object[] array = queue;
int n = size - 1;
if (n == i) // removed last element
array[i] = null;
else {
E moved = (E) array[n];
array[n] = null;
Comparator cmp = comparator;
if (cmp == null)
siftDownComparable(i, moved, array, n);
else
siftDownUsingComparator(i, moved, array, n, cmp);
if (array[i] == moved) {
if (cmp == null)
siftUpComparable(i, moved, array);
else
siftUpUsingComparator(i, moved, array, cmp);
}
}
size = n;
}
/**
* Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue,
* if it is present. More formally, removes an element {@code e} such
* that {@code o.equals(e)}, if this queue contains one or more such
* elements. Returns {@code true} if and only if this queue contained
* the specified element (or equivalently, if this queue changed as a
* result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this queue, if present
* @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = indexOf(o);
if (i == -1)
return false;
removeAt(i);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Identity-based version for use in Itr.remove
*/
void removeEQ(Object o) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] array = queue;
for (int i = 0, n = size; i < n; i++) {
if (o == array[i]) {
removeAt(i);
break;
}
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this queue contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that {@code o.equals(e)}.
*
* @param o object to be checked for containment in this queue
* @return {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue.
* The returned array elements are in no particular order.
*
* The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this queue. (In other words, this method must allocate
* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
*
This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this queue
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return Arrays.copyOf(queue, size);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public String toString() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int n = size;
if (n == 0)
return "[]";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
Object e = queue[i];
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
if (i != n - 1)
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
return sb.append(']').toString();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int drainTo(Collection c) {
return drainTo(c, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
/**
* @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public int drainTo(Collection c, int maxElements) {
if (c == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (c == this)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (maxElements <= 0)
return 0;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int n = Math.min(size, maxElements);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
c.add((E) queue[0]); // In this order, in case add() throws.
dequeue();
}
return n;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Atomically removes all of the elements from this queue.
* The queue will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
Object[] array = queue;
int n = size;
size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
array[i] = null;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue; the
* runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array.
* The returned array elements are in no particular order.
* If the queue fits in the specified array, it is returned therein.
* Otherwise, a new array is allocated with the runtime type of the
* specified array and the size of this queue.
*
*
If this queue fits in the specified array with room to spare
* (i.e., the array has more elements than this queue), the element in
* the array immediately following the end of the queue is set to
* {@code null}.
*
*
Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between
* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows
* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,
* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.
*
*
Suppose {@code x} is a queue known to contain only strings.
* The following code can be used to dump the queue into a newly
* allocated array of {@code String}:
*
*
{@code String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);}
*
* Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to
* {@code toArray()}.
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the queue are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this queue
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this queue
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
public T[] toArray(T[] a) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int n = size;
if (a.length < n)
// Make a new array of a's runtime type, but my contents:
return (T[]) Arrays.copyOf(queue, size, a.getClass());
System.arraycopy(queue, 0, a, 0, n);
if (a.length > n)
a[n] = null;
return a;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue. The
* iterator does not return the elements in any particular order.
*
* The returned iterator is
* weakly consistent.
*
* @return an iterator over the elements in this queue
*/
public Iterator iterator() {
return new Itr(toArray());
}
/**
* Snapshot iterator that works off copy of underlying q array.
*/
final class Itr implements Iterator {
final Object[] array; // Array of all elements
int cursor; // index of next element to return
int lastRet; // index of last element, or -1 if no such
Itr(Object[] array) {
lastRet = -1;
this.array = array;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor < array.length;
}
public E next() {
if (cursor >= array.length)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastRet = cursor;
return (E)array[cursor++];
}
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
removeEQ(array[lastRet]);
lastRet = -1;
}
}
/**
* Saves this queue to a stream (that is, serializes it).
*
* For compatibility with previous version of this class, elements
* are first copied to a java.util.PriorityQueue, which is then
* serialized.
*
* @param s the stream
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
lock.lock();
try {
// avoid zero capacity argument
q = new PriorityQueue(Math.max(size, 1), comparator);
q.addAll(this);
s.defaultWriteObject();
} finally {
q = null;
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* Reconstitutes this queue from a stream (that is, deserializes it).
* @param s the stream
* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the class of a serialized object
* could not be found
* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs
*/
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
try {
s.defaultReadObject();
int sz = q.size();
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, sz);
this.queue = new Object[sz];
comparator = q.comparator();
addAll(q);
} finally {
q = null;
}
}
// Similar to Collections.ArraySnapshotSpliterator but avoids
// commitment to toArray until needed
static final class PBQSpliterator implements Spliterator {
final PriorityBlockingQueue queue;
Object[] array;
int index;
int fence;
PBQSpliterator(PriorityBlockingQueue queue, Object[] array,
int index, int fence) {
this.queue = queue;
this.array = array;
this.index = index;
this.fence = fence;
}
final int getFence() {
int hi;
if ((hi = fence) < 0)
hi = fence = (array = queue.toArray()).length;
return hi;
}
public Spliterator trySplit() {
int hi = getFence(), lo = index, mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
return (lo >= mid) ? null :
new PBQSpliterator(queue, array, lo, index = mid);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer action) {
Object[] a; int i, hi; // hoist accesses and checks from loop
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if ((a = array) == null)
fence = (a = queue.toArray()).length;
if ((hi = fence) <= a.length &&
(i = index) >= 0 && i < (index = hi)) {
do { action.accept((E)a[i]); } while (++i < hi);
}
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer action) {
if (action == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (getFence() > index && index >= 0) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) array[index++];
action.accept(e);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public long estimateSize() { return (long)(getFence() - index); }
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.NONNULL | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
/**
* Returns a {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this queue.
*
* The returned spliterator is
* weakly consistent.
*
*
The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED} and
* {@link Spliterator#NONNULL}.
*
* @implNote
* The {@code Spliterator} additionally reports {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}.
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this queue
* @since 1.8
*/
public Spliterator spliterator() {
return new PBQSpliterator(this, null, 0, -1);
}
// Unsafe mechanics
private static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE;
private static final long allocationSpinLockOffset;
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
Class k = PriorityBlockingQueue.class;
allocationSpinLockOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("allocationSpinLock"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
}
总结
PriorityBlockingQueue 真的是个神奇的队列,可以实现优先出队。最特别的是它只有一个锁,入队操作永远成功,而出队只有在空队列的时候才会进行线程阻塞。可以说有一定的应用场景吧,比如:有任务要执行,可以对任务加一个优先级的权重,这样队列会识别出来,对该任务优先进行出队。
PS:以上代码提交在 Github :https://github.com/Niuh-Study/niuh-juc-final.git
文章持续更新,可以公众号搜一搜「 一角钱技术 」第一时间阅读, 本文 GitHub org_hejianhui/JavaStudy 已经收录,欢迎 Star。