使用Spring cloud alibaba简单构建微服务项目以及注册中心Nacos与Spirng的整合原理(二)
前言
紧接上文使用Spring cloud alibaba简单构建微服务项目以及注册中心Nacos与Spirng的整合原理(一),咱们来讲一下Nacos作为注册中心与Spring的整合原理。这边小编额外多说一些,上文虽然简单,这边需要注意的是各个jar包版本引起的问题,最好与上文示例的版本一致,才能保证运行启动不出问题。
整合原理
大胆猜测
大家有没有想过假设我们有一个怎样把服务注册到nacos上去?这边小编先启动nacos,然后根据官方文档中不启动任何微服务项目的情况下,注册一个服务上去。通过发送http请求命令
curl -X PUT ‘http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=example&ip=127.0.0.1&port=8080’
这样就发现服务了,当然这是假的,内部nacos会有心跳服务,15秒没收到心跳就会断开服务,说明服务不存在了。那为什么我们发送http请求就可以注册服务了呢?按照小编的理解,nacos里面暴露了请求地址,然后我们发送请求nacos做了一系列逻辑后就注册上去了,所以可以做控制台上看见。又因为nacos是个springboot项目,那里面有个controller,然后@RequestMapping里面有url地址映射。那我们构建的微服务项目也应该做了相应的操作。
根据小编猜测和理解那就去源码中找寻是否真的有这个controller和这个url地址。那小编根据“/instance”全局搜索,当然小编很幸运的找到了。
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.controllers.InstanceController
核心代码为(有兴趣的小伙伴可以去看下,map存储注册信息):
com.alibaba.nacos.naming.core.ServiceManager#registerInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance);
说到这儿,大家是否觉得注册原理就这样了,咱们继续猜测,当启动微服务的时候就可以发送http请求,然后注册到nacos上去了,那谁发了这个http请求,我们看nacos源码的时候可以看到子项目nacos-client,这个主要就是用来发送http请求的。紧接着微服务启动怎么自动让nacos-client发送请求。这就是今天小编要讲的重中之重。
分析
spring-cloud-alibaba构建微服务具体关联哪些框架(列举几个)
- 自己写的业务代码
- spring-boot(简化spring web的配置等)
- spring framework(IOC,AOP)
- spring cloud (微服务)
- nacos server (服务注册)
- nacos client (客户端信息发送)
- mybatis (数据库操作)
说明:spring cloud做的是微服务技术,需要完成自动注册功能,但是他没有具体实现,只提供了规范,咱们需要监听服务,当启动完成后调用nacos client发送http请求到nacos server。
先来看下spring cloud抽象类:
org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AbstractAutoServiceRegistration
实现了ApplicationListener监听器里面监听的事件是WebServerInitializedEvent
监听到这个时间后实现里面的onApplicationEvent方法
最终会调用到register()方法
之后会使用org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.ServiceRegistry#register
ServiceRegistry会有NacosServiceRegistry去做这件事情最终完成服务注册
源码阅读
核心源码阅读,这次小编从内部往外扩展的思路,也就是先注册调用源码,然后是监听事件的发布。
org.springframework.cloud.client.serviceregistry.AbstractAutoServiceRegistration
public abstract class AbstractAutoServiceRegistration<R extends Registration> implements ApplicationListener<WebServerInitializedEvent> {
private final ServiceRegistry<R> serviceRegistry;
//监听事件
public void onApplicationEvent(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
this.bind(event);
}
public void bind(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
ApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext();
if (!(context instanceof ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext) || !"management".equals(((ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext)context).getServerNamespace())) {
this.port.compareAndSet(0, event.getWebServer().getPort());
this.start();
}
}
public void start() {
if (!this.isEnabled()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Discovery Lifecycle disabled. Not starting");
}
} else {
if (!this.running.get()) {
this.context.publishEvent(new InstancePreRegisteredEvent(this, this.getRegistration()));
//服务注册
this.register();
if (this.shouldRegisterManagement()) {
this.registerManagement();
}
this.context.publishEvent(new InstanceRegisteredEvent(this, this.getConfiguration()));
this.running.compareAndSet(false, true);
}
}
}
protected void register() {
//这边spring-cloud没有一个实现ServiceRegistry,交由其他框架扩展
this.serviceRegistry.register(this.getRegistration());
}
}
spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery jar包下的NacosServiceRegistry
@Override
public void register(Registration registration) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(registration.getServiceId())) {
log.warn("No service to register for nacos client...");
return;
}
String serviceId = registration.getServiceId();
String group = nacosDiscoveryProperties.getGroup();
Instance instance = getNacosInstanceFromRegistration(registration);
try {
namingService.registerInstance(serviceId, group, instance);
log.info("nacos registry, {} {} {}:{} register finished", group, serviceId,
instance.getIp(), instance.getPort());
}
catch (Exception e) {
log.error("nacos registry, {} register failed...{},", serviceId,
registration.toString(), e);
// rethrow a RuntimeException if the registration is failed.
// issue : https://github.com/alibaba/spring-cloud-alibaba/issues/1132
rethrowRuntimeException(e);
}
}
最终调到nacos-client类NamingProxy#registerService
public void registerService(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
LogUtils.NAMING_LOGGER.info("[REGISTER-SERVICE] {} registering service {} with instance: {}", new Object[]{
this.namespaceId, serviceName, instance});
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap(9);
params.put("namespaceId", this.namespaceId);
params.put("serviceName", serviceName);
params.put("groupName", groupName);
params.put("clusterName", instance.getClusterName());
params.put("ip", instance.getIp());
params.put("port", String.valueOf(instance.getPort()));
params.put("weight", String.valueOf(instance.getWeight()));
params.put("enable", String.valueOf(instance.isEnabled()));
params.put("healthy", String.valueOf(instance.isHealthy()));
params.put("ephemeral", String.valueOf(instance.isEphemeral()));
params.put("metadata", JSON.toJSONString(instance.getMetadata()));
this.reqAPI(UtilAndComs.NACOS_URL_INSTANCE, params, "POST");
}
接着我们看发布事件中哪个地方
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()中的onRefresh()方法,由于springboot中重写了这个方法ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onRefresh()
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
//创建webServer
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}
finishRefresh()中getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();的时候最终跳到的方法是
org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.WebServerStartStopLifecycle#start方法
public void start() {
//webServer启动
this.webServer.start();
this.running = true;
//发布监听事件
this.applicationContext
//完成事件发布ServletWebServerInitializedEvent为WebServerInitializedEvent的子类
.publishEvent(new ServletWebServerInitializedEvent(this.webServer, this.applicationContext));
}
当然只是springboot对spring做了扩展,然后是spring cloud对这个事件进行了监听,之后有spring cloud alibaba nacos 对spring cloud进行的实现。整体流程就是这样了。
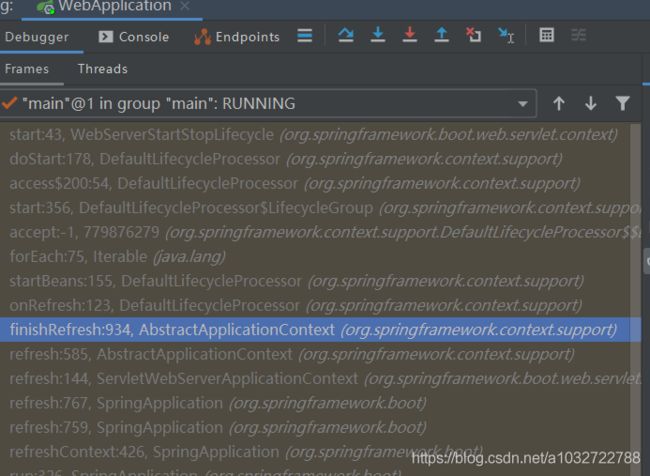
大家可以直接打断点在上面一段代码,然后查看堆栈信息,如下图
总结
今天小编讲了最后重要的spring的扩展点,事件监听的扩展,当然咱们普通人扩展可以对这个ContextRefreshedEvent事件做监听,因为spring的finishRefresh方法就会发布这个监听。整体的流程和扩展的原理,小编觉得应该讲清楚了,虽然这次重点好像侧重中nacos的服务注册上,但他的扩展依旧没变,希望大家自己打断的调试,加油啊。spring后续会依次推出spring mvc和spring boot的讲解。希望大家一如既往的关注小编啊。