迷宫求解----更新迭代
迷宫求解
问题:
1.为什么要使用栈
2.什么是回溯法
栈的原理:
栈也是一种线性表,只不过它是操作受限的线性 表,只能在一端操作。 进出的一端称为栈顶(top),另一端称为栈底(base)。栈可以用顺序存储,也可以用链式存储。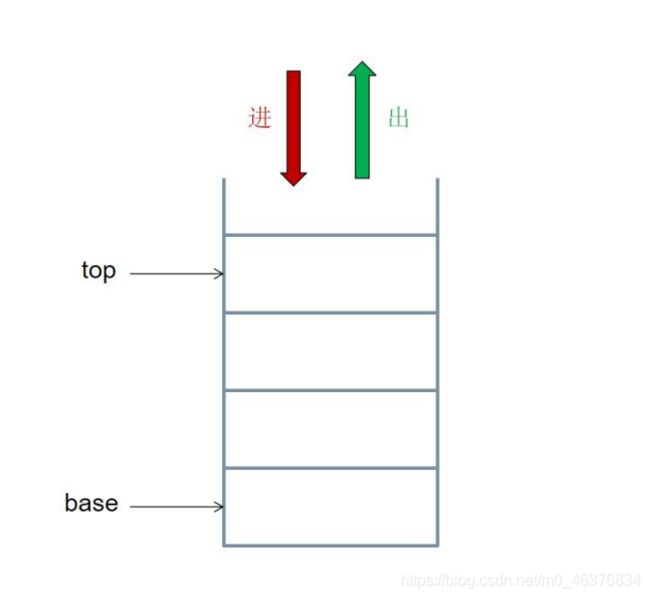
- 找迷宫通路需要使用回溯法,找迷宫通路是对回溯法的一个很好的应用,实现回溯的过程用到数据结构
- 回溯法:对一个包括有很多个结点,每个结点有若干个搜索分支的问题,把原问题分解为若干个子问题求解的 算法。
- 当搜索到某个结点发现无法再继续搜索下去时,就让搜索过程回溯(回退)到该节点的前一个结点,继续 搜索该节点外的其他尚未搜索的分支。
- 如果发现该结点无法再搜索下去,就让搜索过程回溯到这个结点的前一 结点继续这样的搜索过程;这样的搜索过程一直进行到搜索到问题的解或者搜索完了全部可搜索分支没有解存 在为止。
世界上最大的迷宫


使用栈可以实现先进入先出的特点,所以当小人在迷宫中错误了,可以进行后面进入位置的依次退出到原来的位置。
二次更新
- 迷宫坐标结构体
typedef struct _Position{
//迷宫坐标
int _x;
int _y;
}Position;
- 栈结构体的定义
typedef struct _SqStack{
ElemType *base;//栈底指针
ElemType *top;//栈顶指针
}SqStack;
3.构造一个空栈S
bool InitStack(SqStack &S){
S.base=new ElemType[MaxSize];//为顺序表分配一个最大容量为Maxsize的空间
if(!S.base) return false;//空间分配失败
S.top=S.base;//top初始化为base,空栈
return true;
}
4.插入元素e为新的栈顶元素
bool PushStack(SqStack &S,ElemType e){
if(S.top -S.base==MaxSize) return false;//栈满
*(S.top++)=e;
return true;
}
- 删除S的栈顶元素,暂存在变量e中
bool PopStack(SqStack &S,ElemType &e){
if(S.base==S.top) return false;
e=*(--S.top);
return true;
}
6.返回S的栈顶元素,栈顶指针不变
ElemType* GetTop(SqStack &S){
if(S.top!=S.base){
//栈非空
return S.top-1;//返回栈顶的值,栈顶元素不变
}else{
return NULL;
}
}
7.返回栈中元素的个数
int GetSize(SqStack &S){
return (S.top-S.base);
}
8.判断栈是否为空
bool IsEmpty(SqStack &S){
if(S.top==S.base){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
9.摧毁栈
void DestoryStack(SqStack &S){
if(S.base){
free(S.base);
S.base=NULL;
S.top=NULL;
}
}
10.迷宫的初始化
void InitMaze(Maze* m,int map[ROW][COL]){
for(int i=0;i<ROW;++i){
for(int j=0;j<COL;++j){
m->map[i][j]=map[i][j];
}
}
}
11.打印迷宫
void PrintMaze(Maze* m){
for(int i=0;i<ROW;++i){
for(int j=0;j<COL;++j){
printf("%d",m->map[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
12.判断是否为有效入口
int IsValidEnter(Maze* m,Position cur){
assert(m);
if((cur._x==0||cur._x==ROW-1)||(cur._y==0||cur._y==COL-1)&&(m->map[cur._x][cur._y]==1)){
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
13.判断当前节点的下一个结点能否走通
int IsNextPass(Maze* m,Position cur,Position next){
assert(m);
//判断next结点是否为cur 的下一节点
if(((next._x == cur._x) && ((next._y == cur._y+1)||(next._y == cur._y-1))) //在同一行上并且相邻
||((next._y == cur._y) && ( (next._x == cur._x+1)||(next._x == cur._x-1)))){
//或在同一列上并且相邻
//判断下一个节点是否在迷宫里面
if (((next._x >= 0 && next._x < ROW) || (next._y >= 0 && next._y < COL))&&(m->map[next._x][next._y] == 1)){
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
14.判断当前节点是不是有效的迷宫出口
int IsValidExit(Maze* m, Position cur,Position enter){
assert(m);
//这里首先得保证该节点不是入口点,其次只要它处在迷宫的边界即可
if ((cur._x != enter._x || cur._y != enter._y) && ((cur._x == 0 || cur._x == ROW - 1) || (cur._y == 0 || cur._y == COL - 1)))
{
return 1;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
15.找出迷宫通路
int PassMaze(Maze* m,Position enter,SqStack* s){
assert(m && IsValidEnter(m,enter) == 1); //对给的迷宫的入口进行合法 性判断
Position cur = enter;
Position next;
PushStack(*s, cur); //首先将迷宫的入口压入栈中
m->map[cur._x][cur._y] = 2; //将入口值改为 2
//PrintMaze(m);
while (!IsEmpty(*s)) {
cur = *GetTop(*s);
//printf("cur: %d %d\n",cur._x, cur._y);
if (IsValidExit(m,cur,enter) == 1) //判断当前位置是否出口
return 1;
//尝试向左一步:看当前节点的左一个节点能不能走通
next = cur;
next._y = cur._y - 1;
if (IsNextPass(m, cur, next) == 1) {
PushStack(*s, next);
m->map[next._x][next._y] = m->map[cur._x][cur._y] + 1;
//PrintMaze(m);
continue;
}
//尝试向上一步:看当前节点的上一个节点能不能走通
next = cur;
next._x = cur._x - 1;
if (IsNextPass(m,cur,next) == 1) //next 节点能够走通时,将其压入 栈中
{
PushStack(*s,next);
m->map[next._x][next._y] = m->map[cur._x][cur._y]+1;
//将 next 节点的值等于 cur 节点的值加 1
//PrintMaze(m);
continue;
}
//右:看当前节点的向右的一个节点能不能走通
next = cur;
next._y = cur._y + 1;
if (IsNextPass(m, cur,next) == 1){
PushStack(*s, next);
m->map[next._x][next._y] = m->map[cur._x][cur._y] + 1;
//PrintMaze(m);
continue;
}
//下:看当前节点的下一个节点能不能走通
next = cur;
next._x = cur._x + 1;
if (IsNextPass(m, cur,next) == 1){
PushStack(*s, next);
m->map[next._x][next._y] = m->map[cur._x][cur._y] + 1;
//PrintMaze(m);
continue;
}
//走到这里说明当前节点的四个方向都走不通,进行回溯,看前一个节点 未被遍历的方向是否还能走通
Position tmp;
PopStack(*s, tmp);
}
return 0;
}
16.main函数
int main() {
int map[ROW][COL] = {
//用二维数组描绘迷宫:1 代表通路,0 代表墙
0,0,1,0,0,0,
0,0,1,1,1,0,
0,0,1,0,0,0,
0,1,1,1,1,0,
0,0,1,0,1,0,
0,0,0,0,1,0
};
Maze m; Position enter; //迷宫入口
enter._x = 0;
enter._y = 2;
InitMaze(&m, map);
PrintMaze(&m);
//system("pause");
//exit(0);
SqStack s; //定义栈,保存已走过的坐标轨迹,便于回溯
InitStack(s); //栈的初始
int ret = PassMaze(&m,enter,&s); //使用栈和回溯法解开迷宫
if(ret){
printf("恭喜你!终于找到了出口~\n");
}else {
printf("不是我笨!实在没有出口~\n");
}
PrintMaze(&m);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
源码:
maze.h
#pragma once
#include main.cpp
#include