jdk源码分析之 ConcurrentHashMap
整体架构:
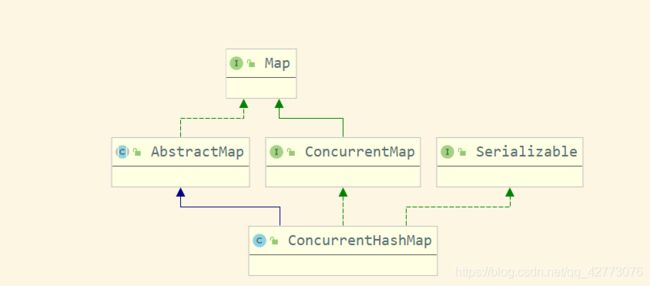
ConcurrentHashMap 继承了AbstractMap及实现了ConcurrentMap。
从类注解获得的信息
- 所有的操作都是线程安全的,可以放心使用,无需再加锁;
- 多个线程同时进行 put、remove 等操作时并不会阻塞,可以同时进行,和 HashTable 不同,HashTable 在操作时,会锁住整个 Map;(所以有些时候要求数据是强一致性时,要使用HashTable,ConcurentHashMap只是弱一致性)。
- 迭代过程中,即使 Map 结构被修改,也不会抛 ConcurrentModificationException 异常;(线程安全)
- 除了数组 + 链表 + 红黑树的基本结构外,新增了转移节点,是为了保证扩容时的线程安全的节点;
- 提供了很多 Stream 流式方法,比如说:forEach、search、reduce 等等。
与hashMap区别
从类注解和类的继承结构图可知,ConcurrentHashMap与hashMa功能和实现思想大体相同,但是直接继承HashMap,主要是因为ConcurrentHashMap的一些方法在中间加锁的方式,通过继承很难在中间加锁的操作。
相同点
- 数组、链表结构几乎相同,所以底层对数据结构的操作思路是相同的
- 都实现了 Map 接口,继承了 AbstractMap 抽象类,所以大多数的方法也都是相同的,HashMap 有的方法,ConcurrentHashMap 几乎都有,所以当我们需要从 HashMap 切换到 ConcurrentHashMap 时,无需关心两者之间的兼容问题。
不同
- 红黑树结构略有不同,HashMap 的红黑树中的节点叫做 TreeNode,TreeNode 不仅仅有属性,还维护着红黑树的结构,比如说查找,新增等等;ConcurrentHashMap 中红黑树被拆分成两块,TreeNode 仅仅维护的属性和查找功能,新增了 TreeBin,来维护红黑树结构,并负责根节点的加锁和解锁;
- 新增 ForwardingNode (转移)节点,扩容的时候会使用到,通过使用该节点,来保证扩容时的线程安全。
put方法
与hashMap实现思路大致相同的,
put的流程如:
- 如果数组为空,初始化,初始化完成之后,走 2。
- 计算当前槽点有没有值,没有的话,cas创建,创建失败后继承cas(for为死循环)知道完成,若当前槽点有值的话,走3.
- 如果当前槽点是转移节点的话(ConcurrentHashMap正在扩容),就会自旋等待扩容完成后再新增。不是转移节点走4.
- 槽点有值的,先锁定当前槽点,保证其余线程不能操作,如果是链表,新增值到链表的尾部,如果是红黑树,使用红黑树新增的方法新增;
- 新增完成之后 check 需不需要扩容,需要的话去扩容。
源码如下:
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
// 如传入的key 为空直接抛空指针异常。
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 计算key的hash值
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
// 数组是空则进行初始操作
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
// 如果当前槽点没有值,则使用casTabAt创建,cas进行创建
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
// 如果是转移节点,则进行自旋等待,完成后则
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
// 如果当前槽点有值,则锁住,防住其他线程修改(排他锁),
else {
V oldVal = null;
// 锁住
synchronized (f) {
//这里再次判断 i 索引位置的数据没有被修改
//binCount 被赋值的话,说明走到了修改表的过程里面
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
// 为链表
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
// 有旧值,根据onlyIfAbsent属性是否选择覆盖,退出自旋
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
// 不存在的话,则放在链表的尾结点,然后退出自旋操作。
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
// 如果是TreeBin 则调用TreeBin新增方法,进行新增。
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
// binCount不为空,并且 oldVal 有值的情况,说明已经新增成功了
if (binCount != 0) {
// 链表是否需要转化成红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
//这一步几乎走不到。槽点已经上锁,只有在红黑树或者链表新增失败的时候
//才会走到这里,这两者新增都是自旋的,几乎不会失败
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
//check 容器是否需要扩容,如果需要去扩容,调用 transfer 方法去扩容
//如果已经在扩容中了,check有无完成
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
ConcurrentHashMap如何确保数组初始化线程安全
数组初始化时,首先通过自旋的方式确保数组的一定初始化成功,然后通过cas算法设置sizectl变量的值,确保只有一个线程对数组进行初始化,再次判断数组是否已经完成初始化,如果已经完成则不进行初始化操作,通过自旋、cas与双重检测机制确保数组初始化的线程安全。
源码如下:
/**
* 使用在sizeCtl中记录的大小初始化表。
*/
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
// 自旋,如果数组为空,一直自旋确保数组初始化成功。
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
// 如果sizectl < 0 时代表正在有线程初始化数组,放弃cpud的调度权,重新竞争。
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
Thread.yield(); // 失去了初始化竞赛;只是自旋
// cas赋值,保障当前只有一个线程进行赋值,-1表示只有一个线程进行初始化操作,从而确保数组初始化安全。
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
// 再次检查数组是否为空,为空则进行初始化操作,不为空直接返回
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
// 数组进行初始化
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
// 将sizectl 赋给sc
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
ConcurrentHashMap扩容的线程安全性
ConcurrentHashMap是通过putVal方法中的addCount方法进去,统计其的个数,然后检查是否需要扩容操作。源码如下:
// 分两步走:新建数组,并将老数组的元素拷贝到
// 扩容主要分 2 步,第一新建新的空数组,第二移动拷贝每个元素到新数组中去
// tab:原数组,nextTab:新数组
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
// 老数组的长度
int n = tab.length, stride;
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
// 如果新数组为空,初始化,大小为原数组的两倍,n << 1
if (nextTab == null) {
// initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n;
}
// 新数组的长度
int nextn = nextTab.length;
// 代表转移节点,如果原数组上是转移节点,说明该节点正在被扩容
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
boolean advance = true;
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
// 无限自旋,i 的值会从原数组的最大值开始,慢慢递减到 0
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
// 结束循环的标志
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
// 已经拷贝完成
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
// 每次减少 i 的值
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
// if 任意条件满足说明拷贝结束了
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
// 拷贝结束,直接赋值,因为每次拷贝完一个节点,都在原数组上放转移节点,所以拷贝完成的节点的数据一定不会再发生变化。
// 原数组发现是转移节点,是不会操作的,会一直等待转移节点消失之后在进行操作。
// 也就是说数组节点一旦被标记为转移节点,是不会再发生任何变动的,所以不会有任何线程安全的问题
// 所以此处直接赋值,没有任何问题。
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // already processed
else {
synchronized (f) {
// 进行节点的拷贝
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
if (fh >= 0) {
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
// 如果节点只有单个数据,直接拷贝,如果是链表,循环多次组成链表拷贝
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
// 在新数组位置上放置拷贝的值
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
// 在老数组位置上放上 ForwardingNode 节点
// put 时,发现是 ForwardingNode 节点,就不会再动这个节点的数据了
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
// 红黑树的拷贝
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
// 红黑树的拷贝工作,同 HashMap 的内容,代码忽略
…………
// 在老数组位置上放上 ForwardingNode 节点
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
get方法
先获取数组的下标,然后通过判断数组下标的 key 是否和我们的 key 相等,相等的话直接返回,如果下标的槽点是链表或红黑树的话,分别调用相应的查找数据的方法,整体思路和 HashMap 很像,源码如下:
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
//计算hashcode
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
//不是空的数组 && 并且当前索引的槽点数据不是空的
//否则该key对应的值不存在,返回null
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
//槽点第一个值和key相等,直接返回
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
//如果是红黑树或者转移节点,使用对应的find方法
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
//如果是链表,遍历查找
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}