https://github.com/wangcy6/leetcode/blob/master/c%2B%2B/264.UglyNumberII.cpp
题目 ugly-number-ii
编写一个程序,找出第 n 个丑数。
丑数就是只包含质因数 2, 3, 5 的正整数。
Write a program to find the n-th ugly number.
Ugly numbers are positive numbers whose prime factors only include 2, 3, 5.
Example:
Input: n = 10
Output: 12
Explanation: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12 is the sequence of the first 10 ugly numbers.
Note:
1 is typically treated as an ugly number.
n does not exceed 1690.
理解
方法1
时间复杂度:o(n3)
MAX最大的整数
i [1--MAX] i2
j[ i--MAX] j3
k[j--MAX] k*5
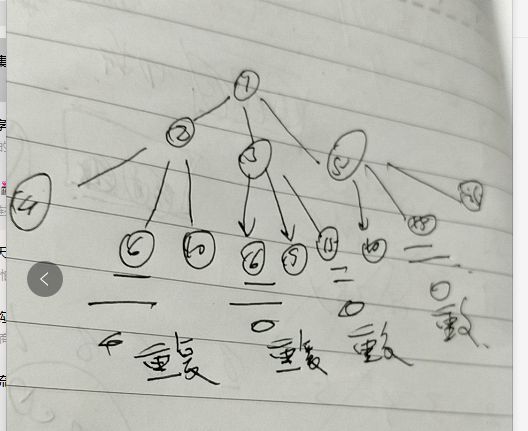
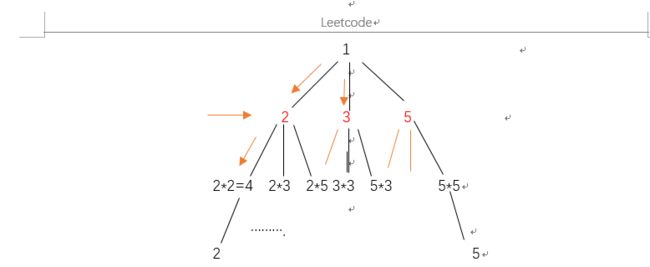
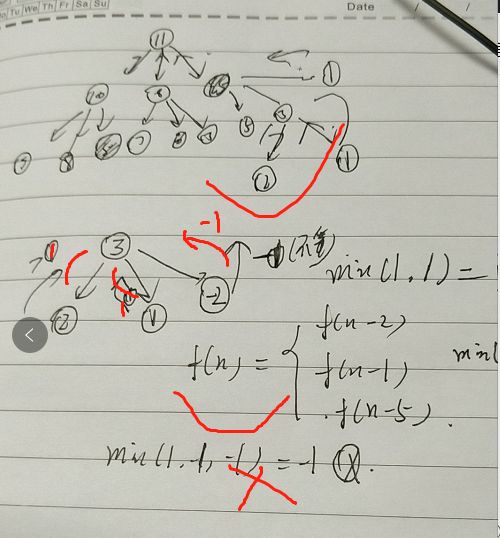
方法2 bfs 树的层次遍历
- 输出结果:
[1 ,2 ,3 ,5, 4,6,10,6,9,15,10,15, 25,8,12,20]
- 期望结果:
【 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12】 - 问题1:顺序不对
10=2*5
9=3×3
但是按照顺序 9,10
【 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12】
- 问题2 重复数据
6=2×3
6=3*2
- 解决办法:
需要2个结构队列完成遍历,
- 保证完成层次遍历
priority_queue - 判断是否重复元素:()
std::map :时间复杂度 log(n)
std::set : 时间复杂度 log(n),不能通过下标访问
unordered_map:时间复杂度理想情况下 o(1)
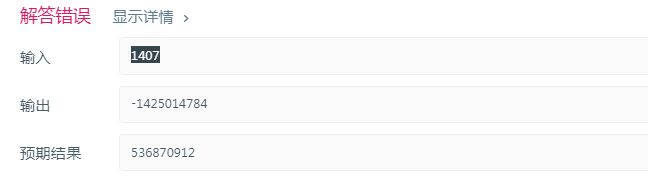
性能测试
long 2147483648~2147483647
long long的最大值:9223372036854775807
long long的最小值:-9223372036854775808
实现
我的实现c++
https://github.com/wangcy6/leetcode/blob/master/c%2B%2B/264.UglyNumberII.cpp
class Solution {
public:
int nthUglyNumber(int n)
{
priority_queue,greater > queue;
unordered_map repeat;
queue.push(1);
repeat[1]=true;
int array[3]={2,3,5};
long long number=1;
int i=0;
while(!queue.empty()&&i++ 别人的实现 golang
func nthUglyNumber(n int) int {
var ugly []int
ugly = append(ugly, 1)
t2, t3, t5 := 0, 0, 0
for n > len(ugly) {
for ugly[t2]*2 <= ugly[len(ugly)-1] {
t2 += 1
}
for ugly[t3]*3 <= ugly[len(ugly)-1] {
t3 += 1
}
for ugly[t5]*5 <= ugly[len(ugly)-1] {
t5 += 1
}
ugly = append(ugly, min(ugly[t2]*2, ugly[t3]*3, ugly[t5]*5))
}
return ugly[n-1]
}
func min(a, b, c int) int{
if a <= b {
b = a
}
if b <= c {
return b
}
return c
}
4 类似题目
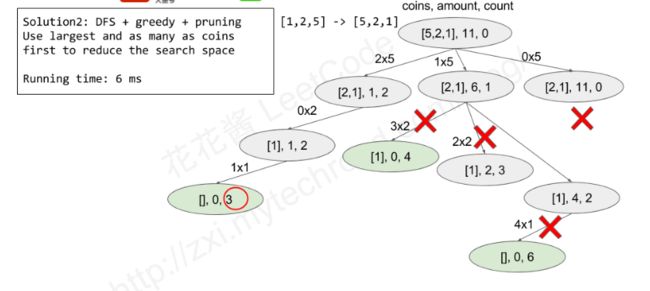
4.1 322. Coin Change
给定不同面额的硬币 coins 和一个总金额 amount。编写一个函数来计算可以凑成总金额所需的最少的硬币个数。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1。
4.2 测试
输入: coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11
输出: 3
解释: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1
4.2 分析
4.3 测试
知识补充
/***************************************************************************
* @file main.cpp
* @author MISAYAONE
* @date 25 March 2017
* @remark 25 March 2017
* @theme Heap Sort
***************************************************************************/
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
//辅助交换函数
void Swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
//堆排序的核心是建堆,传入参数为数组,根节点位置,数组长度
void Heap_build(int a[],int root,int length)
{
int lchild = root*2+1;//根节点的左子结点下标
if (lchild < length)//左子结点下标不能超出数组的长度
{
int flag = lchild;//flag保存左右节点中最大值的下标
int rchild = lchild+1;//根节点的右子结点下标
if (rchild < length)//右子结点下标不能超出数组的长度(如果有的话)
{
if (a[rchild] > a[flag])//找出左右子结点中的最大值
{
flag = rchild;
}
}
if (a[root] < a[flag])
{
//交换父结点和比父结点大的最大子节点
Swap(a[root],a[flag]);
//从此次最大子节点的那个位置开始递归建堆
Heap_build(a,flag,length);
}
}
}
/**
* 调整大顶堆(仅是调整过程,建立在大顶堆已构建的基础上)
* @param arr
* @param i
* @param length
*/
public static void adjustHeap(int []arr,int i,int length){
int temp = arr[i];//先取出当前元素i
for(int k=i*2+1;ktemp){//如果子节点大于父节点,将子节点值赋给父节点(不用进行交换)
arr[i] = arr[k];
i = k;
}else{
break;
}
}
arr[i] = temp;//将temp值放到最终的位置
}
void Heap_sort(int a[],int len)
{ //make_heap() 建堆
for (int i = len/2; i >= 0; --i)//从最后一个非叶子节点的父结点开始建堆
{
Heap_build(a,i,len);
}
for (int j = len-1; j > 0; --j)//j表示数组此时的长度,因为len长度已经建过了,从len-1开始
{ // pop_heap() 从堆中取出一个元素
Swap(a[0],a[j]);//交换首尾元素,将最大值交换到数组的最后位置保存
// push_heap() 将一个元素推进堆内
Heap_build(a,0,j);//去除最后位置的元素重新建堆,此处j表示数组的长度,最后一个位置下标变为len-2
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
clock_t Start_time = clock();
int a[10] = {12,45,748,12,56,3,89,4,48,2};
Heap_sort(a,10);
for (size_t i = 0; i != 10; ++i)
{
cout<(End_time-Start_time)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC*1000<<" ms"<