2021 蓝桥杯省赛第一场 C++ 大学 B 组
目录
A. 空间
B. 卡片
C. 直线
D. 货物摆放
E. 路径
F. 时间显示
G. 砝码称重
H. 杨辉三角形
I. 双向排序
J. 括号序列
前言
今年的省赛题型和风格大变,没了模拟和搜索码量少了很多,侧重考察数学、思维还有DP,对ACMer来说越来越友好了。
A. 空间
1 M B = 2 10 K B = 2 20 B 1MB = 2^{10} KB = 2^{20}B 1MB=210KB=220B, 1 B = 8 b i t 1B = 8~bit 1B=8 bit,实际上就是求 256 M B 256MB 256MB有多少个 32 b i t 32~bit 32 bit。
答案:67108864
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENDL "\n"
typedef long long ll;
const int Mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
// ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cout << (1 << 26) << endl;
return 0;
}
B. 卡片
模拟即可
答案:3181
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENDL "\n"
typedef long long ll;
const int Mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int a[10];
bool cal(int x) {
while (x) {
int y = x % 10;
if (a[y])
a[y]--;
else
return 0;
x /= 10;
}
return 1;
}
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
// ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++) a[i] = 2021;
for (int i = 1;; i++) {
if (!cal(i)) {
cout << i - 1 << endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
C. 直线
根据两点确定直线,得到直线的方程 x − x 1 x 1 − x 2 = y − y 1 y 1 − y 2 \frac{x - x_1}{x_1 - x_2} = \frac{y - y_1}{y_1 - y_2} x1−x2x−x1=y1−y2y−y1,然后将两点式方程化成一般式 a x + b y + c = 0 ax + by + c = 0 ax+by+c=0,求出所有的三元组 { a , b , c } \{a, b, c\} { a,b,c}然后去重即可。注意对于 { 1 , 2 , 1 } \{1,2,1\} { 1,2,1}和 { 2 , 4 , 2 } \{2,4,2\} { 2,4,2}是本质相同的直线,因此要对所有的这样三元组化为最简的,即除以三个数的 g c d gcd gcd。
PS:
- 0和任何非0数求最大公因数都是那个数本身,比赛时还纠结了一下0,且求 g c d gcd gcd时要取绝对值。
- 如果使用点斜式, k k k的精度会带来误差。
答案:40257
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENDL "\n"
typedef long long ll;
const int Mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
struct node {
int a, b, c;
bool operator<(const node &p) const {
if (a == p.a) return b == p.b ? c < p.c : b < p.b;
return a < p.a;
}
bool operator==(const node &p) const {
return a == p.a && b == p.b && c == p.c;
}
};
struct Point {
int x, y;
} p[maxn];
set<node> s;
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
// ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n = 20, m = 21, cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) p[++cnt] = {
i, j};
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= cnt; j++) {
int a = p[i].y - p[j].y;
int b = p[j].x - p[i].x;
int c = p[i].y * (p[i].x - p[j].x) - p[i].x * (p[i].y - p[j].y);
int g = __gcd(abs(a), __gcd(abs(b), abs(c)));
a /= g, b /= g, c /= g;
s.insert({
a, b, c});
}
}
cout << s.size() << endl;
return 0;
}
D. 货物摆放
解题思路
考虑固定 L L L,那么显然只需要看有多少种 W ∗ H W*H W∗H的情况即可,又因为三个数相乘等于 n n n,那么 L L L一定是 n n n的因数。故先对 n n n因数分解,然后拿每个因数作为 L L L,再计算 n / L n/L n/L的因数个数,累加贡献即可。
比赛时数组开成int了,算出来的是2512,哭了…
答案:2430
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENDL "\n"
typedef long long ll;
const int Mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
ll fac[1005];
int cal(ll n) {
int ans = 0;
for (ll i = 1; i * i <= n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
if (i * i == n)
ans++;
else
ans += 2;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
// ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
ll n = 2021041820210418LL;
int cnt = 0;
for (ll i = 1; i * i <= n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
if (i * i == n)
fac[++cnt] = i;
else
fac[++cnt] = i, fac[++cnt] = n / i;
}
}
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
ans += cal(n / fac[i]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
E. 路径
解题思路
比赛时也没想太多,就跑最短路算法就就行了,迪杰斯特拉写着太麻烦,还不如安心跑弗洛伊德,差不多二十多秒出答案也挺爽的(主要是写的快)
答案:10266837
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENDL "\n"
typedef long long ll;
const int Mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b); }
int lcm(int a, int b) {
return a / gcd(a, b) * b; }
int g[2050][2050];
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
// ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n = 2021;
memset(g, 0x3f, sizeof g);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
g[i][i] = 0;
for (int j = i + 1; j <= i + 21; j++) g[i][j] = g[j][i] = lcm(i, j);
}
for (int k = 1; k <= n; k++)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (g[i][k] + g[k][j] < g[i][j]) {
g[i][j] = g[i][k] + g[k][j];
}
cout << g[1][n] << endl;
return 0;
}
F. 时间显示
解题思路
注意一秒等于一千毫秒即可,其他模拟。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENDL "\n"
typedef long long ll;
const int Mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 10;
const int del = 24 * 60 * 60;
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
// ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
ll n;
cin >> n;
n /= 1000;
int res = n % del;
int h = res / 3600;
res %= 3600;
int m = res / 60;
res %= 60;
printf("%02d:%02d:%02d", h, m, res);
return 0;
}
G. 砝码称重
不难看出本题是01背包的变形,我采取的做法是,先背包求出所有求和可能的结果,然后将所有物品的权值看做负数,在前面的基础上再做一次01背包。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENDL "\n"
typedef long long ll;
const int Mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
int w[205];
bool d[205][maxn];
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n, sum = 0;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> w[i];
w[n + i] = w[i];
sum += w[i];
}
d[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= sum; j++) {
d[i][j] = d[i - 1][j];
if (j >= w[i]) d[i][j] |= d[i - 1][j - w[i]];
}
}
for (int i = n + 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= sum; j++) {
d[i][j] = d[i - 1][j];
if (j + w[i] <= sum) d[i][j] |= d[i - 1][j + w[i]];
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= sum; i++)
if (d[2 * n][sum]) ans++;
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
H. 杨辉三角形
本题的切入点为 n n n的范围—— n n n一定是一个小于 1 e 9 1e9 1e9的数,对杨辉三角大概前五十项打表:
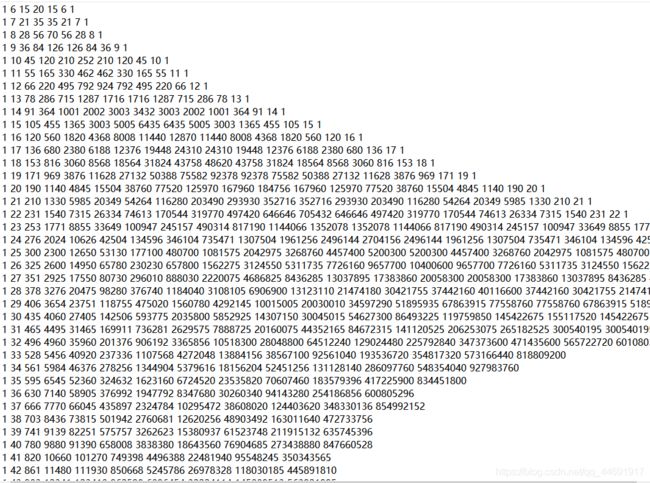
实际上到三十几项时,中间的数已经超过了 1 e 9 1e9 1e9,然后再次联想到 C 10000 2 C_{10000}^{2} C100002大概也就到 1 e 9 1e9 1e9,因此我们只需要保存杨辉三角表中小于 1 e 9 1e9 1e9的数,这些数的个数是很少的完全存的下,而且不难证明第 n n n行的数的个数一定小于等于第 n − 1 n-1 n−1行,那么递推时大于 1 e 9 1e9 1e9的数不保存也不会影响下面的递推。对于表里面找不到的数,一定是 C n 1 C_{n}^1 Cn1第一次出现,那么答案就是 1 + 2 + 3 + . . . + n + 2 1 +2 +3+...+n + 2 1+2+3+...+n+2
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENDL "\n"
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 2e4 + 10;
const int limit = 1e9;
ll c[maxn][50];
int len[maxn];
void init() {
c[0][0] = c[1][0] = c[1][1] = 1;
len[0] = 1, len[1] = 2;
for (int i = 2, k; i < maxn; i++) {
c[i][0] = 1, k = i + 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
c[i][j] = c[i - 1][j - 1] + c[i - 1][j];
if (c[i][j] > limit) {
k = j;
break;
}
}
len[i] = k;
}
// for (int i = 0; i < maxn; i++) {
// for (int j = 0; j < len[i]; j++) cout << c[i][j] << " ";
// cout << endl;
// }
}
ll cal(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < maxn; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < len[i]; j++) {
if (c[i][j] == n) {
return 1LL * i * (i + 1) / 2 + j + 1;
}
}
}
return 1LL * n * (n + 1) / 2 + 2;
}
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
// ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
init();
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << cal(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
I. 双向排序
解题思路
暂时不会完全的做法,暴力骗分。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ENDL "\n"
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
int a[maxn];
int main() {
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) a[i] = i + 1;
for (int i = 0, op, x; i < m; i++) {
cin >> op >> x;
if (op == 0)
sort(a, a + x, greater<int>());
else
sort(a + x - 1, a + n);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << a[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}













