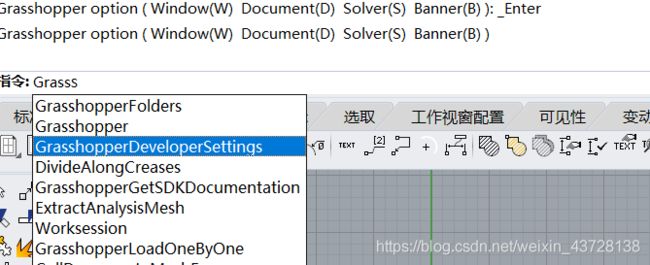
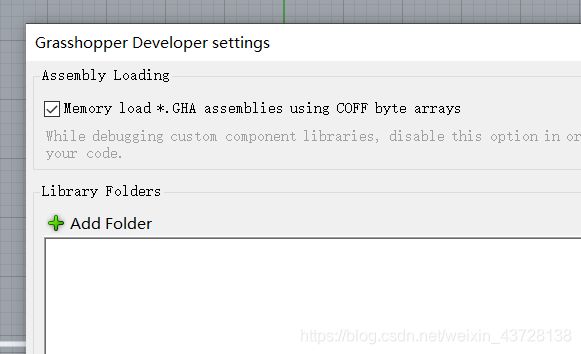
Grasshopper 二次开发 (C#) Part 3 - Write Simple Plug-in for Grasshopper in Visual Studio
本博客内容正在持续更新,最后一次更新时间:2020.08.09
【本文重点】
1.查文档:(1) RhinoCommon SDK (2) Grasshopper API
2.专栏地址:专栏:Rhino (Grasshopper) 二次开发 (C#)
推荐阅读:
【C#】:本文以介绍 Rhino, Grasshopper 的二次开发为主,具体有关 C# 语法的知识点欢迎参考 专栏:C#
【Grasshopper】:有关 Grasshopper 部分知识点和操作欢迎参考 专栏:Rhino (Grasshopper) 二次开发 (C#) 内的 Grasshopper 学习笔记
【视频教程】:本文部分内容来自油管教程 C# Scripting and Plugin Development for Grasshopper
1 Preparations
1.IDE
Visual Studio 2019 (2017 也完全ok,再往前版本不推荐,可能存在不兼容的问题)。
2.Template
To write plug-in for Grasshopper,需要先下载 Grasshopper templates for v6,安装完成后再次打开 VS2019 的新建项目界面,就能找到相应的项目模板

输入项目名以及项目地址并点击创建后,还出弹出一个设置窗口,这个窗口不需要进行任何修改,直接选择确定即可
3 Rhino
作者用的是 Rhino6,不太清楚 Rhino5 是否可行
2 Get Started
2.1 初始类
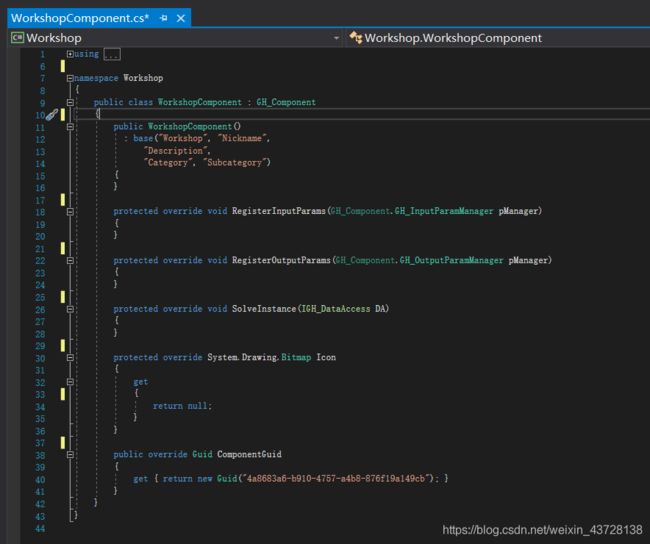
成功创建 Plug-in 项目后,右侧的资源管理器中会显示两个 .cs 文件,我们主要编辑的的是 XXXComponent.cs 文件,作者创建的项目名为 Workshop,因此显示的是 WorkshopComponents.cs

该文件在创建之初就会包含一些代码以注释,为了简洁起见作者直接删去了所有注释。删完之后的代码界面如下,可以看到初始类包含一个构造函数以及五个类方法,下边将依次介绍
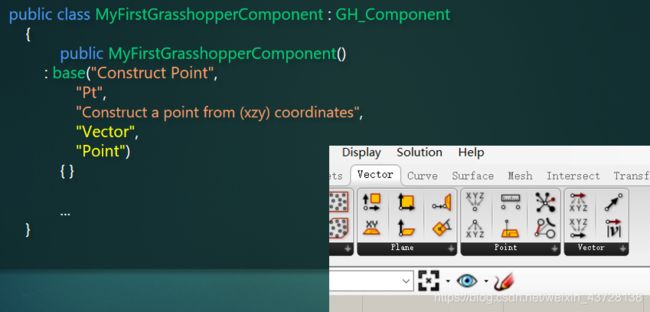
2.1.1 构造函数:public XXXComponent() {}
public MyFirstGhComponent()
: base("类名",
"Nickname",
"Description",
"Category",
"Subcategory")
{
}
base() 中的前三个字符串将直接在鼠标移至电池上时显示:Component:电池名称,Nickname:电池简称,Discription:对电池功能的描述

后两个字符串 Category 和 Subcategory 显示的是该电池在电池菜单栏中的位置
2.1.2 类方法1、2:输入、输出
类方法1、2 用于声明输入和输出变量
protected override void RegisterInputParams(GH_Component.GH_InputParamManager pManager)
{
pManager.AddXXXParameter("Name", "Nickname", "Description", GH_ParamAccess.item, "默认值(可以不写)");
}
protected override void RegisterOutputParams(GH_Component.GH_InputParamManager pManager)
{
pManager.AddXXXParameter("Name", "Nickname", "Description", GH_ParamAccess.item);
}
- 这个 pManager 可以把它看成一个对象,之后的输入或输出操作都要通过这个对象来实现。
- XXX 表示输入或输出的变量类型,涵盖几乎所有类型的变量,比如数字、点线面、几何体等等,只要打出
pManager.Add就可以找到

- AddXXXParameter 方法中的
GH_ParamAccess.item表示该变量是单个 item(list 则为GH_ParamAccess.list)
代码示例
pManager.AddNumberParameter("First Number", "First Number", "First Number", GH_ParamAccess.item, 0.0);
2.1.3 类方法3:主体
类方法3 为 Plug-in 的核心,用于实现 Plug-in 的功能。以下代码的功能为计算两个输入变量的平均值
protected override void SolveInstance(IGH_DataAccess DA)
{
double a = double.NaN; // double.NaN 表示一个没有意义的 double 类型变量
double b = double.NaN;
// 将输入中 Name = "Fisrt Number" 的变量赋值给变量 a
// success1 表示 GetData() 方法是否成功调用
bool success1 = DA.GetData("First Number", ref a);
bool success2 = DA.GetData("Second Number", ref b);
if (success1 && success2) // 如果都调用成功
{
double average = 0.5 * (a + b);
// 将变量 average 赋值给输出中 Name = "Average" 的变量
DA.SetData("Average", average);
}
else
{
AddRuntimeMessage(GH_RuntimeMessageLevel.Error, "Please check the inputs.");
}
}
2.1.4 类方法4:图标
类方法4 用于定义电池的图标
在对这个类进行操作之前,首先需要把图标导入项目中(关于具体图标的绘制请参考本博客的 Appendix - 1):
- 双击 Properties - 资源 - 添加资源 - 添加现有资源,然后选择 png 文件导入

- 重命名文件:作者习惯将文件命名为
name + icon,例如将名为 Average 的电池图标命名为 Averageicon

导入后回到类方法4,在 return 后添加如下代码
protected override System.Drawing.Bitmap Icon
{
get
{
return Properties.Resources.Averageicon;
}
}
2.2 生成并导入 Plug-in 文件
2.2.1 方法1
这是最基础的方法,如果需要频繁修改以及调试话会非常麻烦
(1) 生成

点击生成解决方案按钮,生成成功后,可以在 项目所在的文件夹/bin/ 内找到对应的 .gha 文件
(2) 导入
点击 File - Special Folders - Components Folder,会打开一个文件夹

然后把之前生成的 .gha 文件放进去即可
重启之后就能在电池菜单栏上找到我们的 plug-in 啦
2.2.2 方法2 (recommended)
(1) 设置 VS2019
- 双击右侧资源管理器中的 Properties
- 左侧栏目中的生成事件
- 将下图中间的第二个方框内的蓝色字段替换为,方法1第二步打开的文件夹的地址

修改后第二个方框的内容大致长这样
Copy "$(TargetPath)""C:\Users\Administrator\AppData\Roaming\Grasshopper\Libraries\$(ProjectName).gha"
Erase "$(TargetPath)"
(2) 设置 Rhino6
(3) 重新载入所有 Plug-in
在确保 Grasshopper 所有打开的文件全都关闭之后,在 Rhino6 的菜单栏下的指令栏中输入 GrasshopperReloadAssemblies,即可完成重载(为了方便起见,作者一般会给这个命令设置快捷键 Ctrl + R,设置方法:工具 - 选项 - 键盘)
3 Examples
3.1 Get average
实现功能:计算两个输入变量的平均值
input 1: a number (a)
input 2: a number (b)
output: a number ((a + b) / 2)
1.创建类
右键单击 Workshop - 添加 - 添加新项 - 左侧栏选择 Rhinoceros,创建一个名为 GhcAverage.cs 的文件
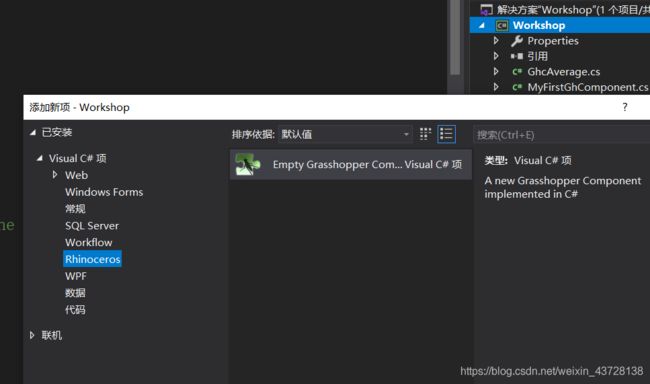
2.全部代码
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Grasshopper.Kernel;
using Rhino.Geometry;
namespace Workshop
{
public class GhcAverage : GH_Component
{
public GhcAverage()
: base("GhcAverage", "Average",
"Galculate the average of two numbers",
"Workshop", "Utilities")
{
}
protected override void RegisterInputParams(GH_Component.GH_InputParamManager pManager)
{
pManager.AddNumberParameter("First Number", "First Number", "First Number", GH_ParamAccess.item, 0.0);
pManager.AddNumberParameter("Second Number", "Second Number", "Second Number", GH_ParamAccess.item, 0.0);
}
protected override void RegisterOutputParams(GH_Component.GH_OutputParamManager pManager)
{
pManager.AddNumberParameter("Average", "Average", "Average", GH_ParamAccess.item);
}
protected override void SolveInstance(IGH_DataAccess DA)
{
double a = double.NaN;
double b = double.NaN;
bool success1 = DA.GetData("First Number", ref a);
bool success2 = DA.GetData("Second Number", ref b);
if (success1 && success2)
{
double average = 0.5 * (a + b);
DA.SetData("Average", average);
}
else
{
AddRuntimeMessage(GH_RuntimeMessageLevel.Error, "Please check the inputs.");
}
}
protected override System.Drawing.Bitmap Icon
{
get
{
return Properties.Resources.Averageicon;
}
}
public override Guid ComponentGuid
{
get {
return new Guid("624cc2f9-5838-4067-85c3-19d06fcc213c"); }
}
}
}
3.2 Get centroid
实现功能:计算多个输入点的形心(centroid),并同时输出形心所在点与其他点之间的距离
input: a list of points
output 1: a point (centroid)
output 2: a list of numbers (distances)
1.效果图
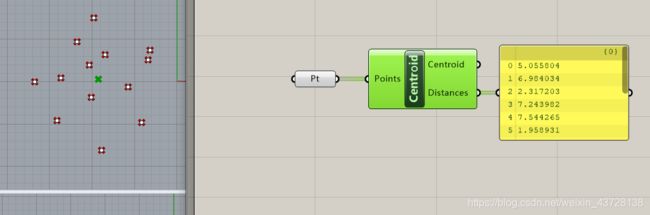
2.全部代码
// using 部分同 Section 3.1
namespace Workshop
{
public class GhcCentroid : GH_Component
{
public GhcCentroid()
: base("GhcCentroid", "Centroid",
"Find the centroid of a set of points, and compute the distance from the centroid to each point.",
"Workshop", "Utilities")
{
}
protected override void RegisterInputParams(GH_Component.GH_InputParamManager pManager)
{
pManager.AddPointParameter("Points", "Points", "Points", GH_ParamAccess.list);
}
protected override void RegisterOutputParams(GH_Component.GH_OutputParamManager pManager)
{
pManager.AddPointParameter("Centroid", "Centroid", "Centroid", GH_ParamAccess.item);
pManager.AddNumberParameter("Distances", "Distances", "Distances", GH_ParamAccess.list);
}
protected override void SolveInstance(IGH_DataAccess DA)
{
List<Point3d> iPoints = new List<Point3d>();
DA.GetDataList("Points", iPoints);
// get the centroid
Point3d centroid = new Point3d(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
foreach (Point3d point in iPoints)
centroid += point;
centroid = centroid / iPoints.Count;
DA.SetData("Centroid", centroid);
// get the distances
List<double> distances = new List<double>();
foreach (Point3d point in iPoints)
distances.Add(centroid.DistanceTo(point));
DA.SetDataList("Distances", distances);
}
protected override System.Drawing.Bitmap Icon
{
get
{
return Properties.Resources.Centroidicon;
}
}
public override Guid ComponentGuid
{
get {
return new Guid("830d40a0-f7fe-4054-965b-c0d1906c4c12"); }
}
}
}
3.3 Move particle
实现功能:以一定的速度移动点
input 1: a boolean (是否从原点重新开始移动)
input 2: a vector (移动速度)
output: a point
在这个例子中,作者在类方法3,即 SolveInstance() 前声明了一个变量 currentPosition。这里声明但不赋值,目的是为了使得程序在运行完一次之后保留这个变量的值以供下次运行使用(体现在例子中:每运行一次 particle 都在上一次的移动的基础上再移动一次 )
1.效果图

2.全部代码
// using 部分同 Section 3.1
namespace Workshop
{
public class GhcMovingParticle : GH_Component
{
public GhcMovingParticle()
: base("GhcMovingParticle", "Moving Particle",
"Create a moving point in the direction specified by the user.",
"Workshop", "Utilities")
{
}
protected override void RegisterInputParams(GH_Component.GH_InputParamManager pManager)
{
pManager.AddBooleanParameter("ifReset", "ifRest", "ifRest", GH_ParamAccess.item);
pManager.AddVectorParameter("Velocity", "Velocity", "Velocity", GH_ParamAccess.item);
}
protected override void RegisterOutputParams(GH_Component.GH_OutputParamManager pManager)
{
pManager.AddPointParameter("Particle", "Particle", "Particle", GH_ParamAccess.item);
}
Point3d currentPosition;
protected override void SolveInstance(IGH_DataAccess DA)
{
bool ifReset = false;
Vector3d v = new Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
bool success1 = DA.GetData("ifReset", ref ifReset);
bool success2 = DA.GetData("Velocity", ref v);
if (success1 && success2)
{
if (ifReset)
currentPosition = new Point3d(0, 0, 0);
currentPosition += v;
DA.SetData("Particle", currentPosition);
}
}
protected override System.Drawing.Bitmap Icon
{
get
{
return Properties.Resources.MovingParticleicon;
}
}
public override Guid ComponentGuid
{
get {
return new Guid("810f88e6-c5ef-419d-8285-39dfa638dbd4"); }
}
}
}