【插件开发】—— 5 SWT控件以及布局使用
前文回顾:
1 插件学习篇
4 SWT编程须知
经过前几篇的介绍,多少对SWT又有了一些认识,那么这篇继续来看一下一些控件的组合使用。
首先是几种简单的控件,Label,Text,Button,Combo这些都是些常用的简单框架,但是为了能够构造出整齐的布局,还是要多花些心思的。
除了这些简单的控件外,还有点复杂的控件,比如Table和树、选项卡和菜单等等,这里就先不做介绍了。
为了整个这些控件,经常要使用两个组合控件以及多种布局。
1 【Group 组】,这个组可以为我们生成一个带有线的框,这样可以把杂乱的控件放到一个规整的容器内。
2 【Composite 组合控件】,它是为了拼接一些简单的控件,形成具有复杂功能的整合控件。
比如文件路径的浏览,往往就需要一个文件浏览的按钮,和一个文本框。
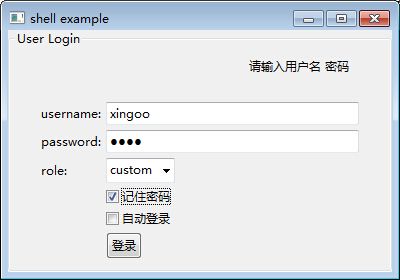
这里先放出一段代码,代码中使用到了简单的布局模型GridLayout(),以及组和组合控件,还有一些简单的控件。形成一个登陆界面,并且单击按钮可以出发响应事件。效果图如下:
登录前:
登陆后:
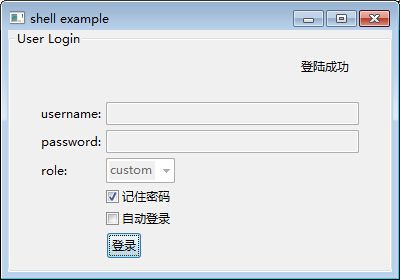
实现代码如下:
1 package com.xingoo.plugin.swttest.test; 2 3 import org.eclipse.swt.SWT; 4 import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionAdapter; 5 import org.eclipse.swt.events.SelectionEvent; 6 import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout; 7 import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridData; 8 import org.eclipse.swt.layout.GridLayout; 9 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Button; 10 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Combo; 11 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Composite; 12 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Group; 13 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Label; 14 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.MessageBox; 15 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell; 16 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Text; 17 18 import com.xingoo.plugin.swttest.Abstract.AbstractExample; 19 20 public class Test extends AbstractExample{ 21 private Label infoLabel; 22 private Text usernameText; 23 private Text passwordText; 24 private Combo roleCombo; 25 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 new Test().run(); 28 } 29 public void todo(Shell shell) { 30 Group testGroup = new Group(shell,SWT.NONE); 31 testGroup.setText("User Login"); 32 GridLayout layout = new GridLayout(); 33 layout.numColumns = 2; 34 layout.marginWidth = 30; 35 layout.marginHeight = 10; 36 testGroup.setLayout(layout); 37 testGroup.setLayoutData(new GridData(GridData.FILL_HORIZONTAL)); 38 { 39 Composite composite = new Composite(testGroup,SWT.NONE); 40 GridLayout layoutComposite = new GridLayout(); 41 layoutComposite.numColumns = 2; 42 layoutComposite.marginHeight = 1; 43 composite.setLayout(layoutComposite); 44 composite.setLayoutData(new GridData(SWT.FILL,SWT.FILL,true,true,2,2)); 45 46 infoLabel = new Label(composite,SWT.NONE); 47 infoLabel.setText("请输入用户名 密码"); 48 infoLabel.setLayoutData(new GridData(GridData.FILL_BOTH)); 49 infoLabel.setAlignment(SWT.RIGHT); 50 } 51 { 52 Label usernameLabel = new Label(testGroup,SWT.NONE); 53 usernameLabel.setText("username:"); 54 55 usernameText = new Text(testGroup,SWT.BORDER); 56 usernameText.setLayoutData(new GridData(GridData.FILL_HORIZONTAL)); 57 } 58 { 59 Label passwordLabel = new Label(testGroup,SWT.NONE); 60 passwordLabel.setText("password:"); 61 62 passwordText = new Text(testGroup,SWT.BORDER | SWT.PASSWORD); 63 passwordText.setLayoutData(new GridData(GridData.FILL_HORIZONTAL)); 64 } 65 { 66 Label roleLabel = new Label(testGroup,SWT.NONE); 67 roleLabel.setText("role:"); 68 69 roleCombo = new Combo(testGroup,SWT.DROP_DOWN); 70 roleCombo.setItems(new String[]{"Admin","custom"}); 71 roleCombo.select(1); 72 } 73 { 74 new Label(testGroup,SWT.NONE); 75 76 Button rememberPWBtn = new Button(testGroup,SWT.CHECK); 77 rememberPWBtn.setText("记住密码"); 78 } 79 { 80 new Label(testGroup,SWT.NONE); 81 82 Button autoLoginBtn = new Button(testGroup,SWT.CHECK); 83 autoLoginBtn.setText("自动登录"); 84 } 85 { 86 new Label(testGroup,SWT.NONE); 87 88 Button loginBtn = new Button(testGroup,SWT.PUSH); 89 loginBtn.setText("登录"); 90 91 loginBtn.addSelectionListener(new SelectionAdapter() { 92 public void widgetSelected(SelectionEvent evt){ 93 infoLabel.setText("登陆成功"); 94 95 usernameText.setText(""); 96 usernameText.setEnabled(false); 97 98 passwordText.setText(""); 99 passwordText.setEnabled(false); 100 101 roleCombo.setEnabled(false); 102 } 103 }); 104 } 105 } 106 }
注意其中的一些技巧:
30-36行:我们创建了一个组控件,并且使用了网格布局,设置每行有两列。并且设置了组内填充边界,marginWidth以及marginHeight。
39-49行:我们创建了一个组合对象,使他占有了两个列元素。并且设置组内为两列的网格布局。
关于事件的监听,之后也会搜集整理出一些常用的事件。
剩下的就比较好理解了,当没有空间元素填补的时候,为了防止布局错乱,创建了一个空的Label对象用来占位。
new Label(testGroup,SWT.NONE);
这里面使用到了一个前文提到的抽象类,这里再贴出来一次。
1 package com.xingoo.plugin.swttest.Abstract; 2 3 import org.eclipse.swt.layout.FillLayout; 4 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Display; 5 import org.eclipse.swt.widgets.Shell; 6 7 public abstract class AbstractExample{ 8 public void run(){ 9 Display display = new Display(); 10 Shell shell = new Shell(display); 11 shell.setText("shell example"); 12 shell.setBounds(200,200,400,280); 13 shell.setLayout(new FillLayout()); 14 todo(shell); 15 shell.open(); 16 17 while(!shell.isDisposed()){ 18 if(!display.readAndDispatch()) 19 display.sleep(); 20 } 21 //dispose the resource 22 display.beep(); 23 display.dispose(); 24 } 25 public abstract void todo(Shell shell);//extension something here 26 }
后续将会更新,复杂控件以及布局模型的介绍。