指数平滑方法(一次指数平滑、二次指数平滑、三次指数平滑):理论、代码、参数 介绍(全)
@创建于:20210324
@修改于:20210324
文章目录
-
-
- 特别说明
-
- 参考来源
- 包版本号
- 1、简介
- 2、一次指数平滑
-
- 2.1 理论介绍
- 2.2 代码展示
- 2.3 参数介绍
- 3、 二次指数平滑
-
- 3.1 理论介绍
-
- 3.1.1 Holt’s linear trend method
- 3.1.2 Damped trend methods
- 3.2 代码展示
- 3.3 参数介绍
- 4、 三次指数平滑
-
- 4.1 理论介绍
-
- 4.1.1 Holt-Winters’ additive method
- 4.1.2 Holt-Winters’ multiplicative method
- 4.1.3 Holt-Winters’ damped method
- 4.2 代码展示
- 4.3 参数介绍
- 5、参数优化和模型选择理论——AIC BIC
- 6、 与 ARIMA 的关系
-
特别说明
参考来源
本文理论内容转自下面三个博客,它们为同一位作者。代码部分我做了改动。
- 指数平滑方法简介 个人博客
- 指数平滑方法简介 简书
- 指数平滑方法简介 CSDN
包版本号
本文测试所用的版本号:
- python 3.8.5
- statsmodels 0.12.2
- pandas 1.2.2
1、简介
指数平滑(Exponential smoothing)是除了 ARIMA 之外的另一种被广泛使用的时间序列预测方法。 指数平滑即指数移动平均(exponential moving average),是以指数式递减加权的移动平均。各数值的权重随时间指数式递减,越近期的数据权重越高。常用的指数平滑方法有一次指数平滑、二次指数平滑和三次指数平滑。
2、一次指数平滑
2.1 理论介绍
一次指数平滑又叫简单指数平滑(simple exponential smoothing, SES),适合用来预测没有明显趋势和季节性的时间序列。其预测结果是一条水平的直线。模型形如:

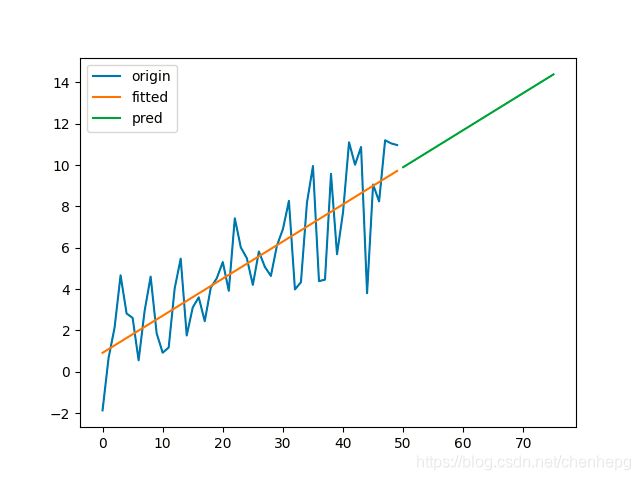
2.2 代码展示
使用 python 的 statsmodels 可以方便地应用该模型:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def ses():
from statsmodels.tsa.holtwinters import SimpleExpSmoothing
number = 30
x1 = np.round(np.linspace(0, 1, number), 4)
y1 = pd.Series(np.multiply(x1, (x1 - 0.5)) + np.random.randn(number))
# fitted部分是直线或者是曲线,受到原始数据影响。
# 多次测试显示,直线的概率高。
# ets1 = SimpleExpSmoothing(endog=y1, initialization_method='estimated')
ets1 = SimpleExpSmoothing(endog=y1, initialization_method='heuristic')
r1 = ets1.fit()
pred1 = r1.predict(start=len(y1), end=len(y1) + len(y1)//2)
pd.DataFrame({
'origin': y1,
'fitted': r1.fittedvalues,
'pred': pred1
}).plot()
plt.savefig('ses.png')
ses()
2.3 参数介绍
Simple Exponential Smoothing
Parameters
----------
endog : array_like
The time series to model.
initialization_method : str, optional
Method for initialize the recursions. One of:
* None
* 'estimated'
* 'heuristic'
* 'legacy-heuristic'
* 'known'
None defaults to the pre-0.12 behavior where initial values
are passed as part of ``fit``. If any of the other values are
passed, then the initial values must also be set when constructing
the model. If 'known' initialization is used, then `initial_level`
must be passed, as well as `initial_trend` and `initial_seasonal` if
applicable. Default is 'estimated'. "legacy-heuristic" uses the same
values that were used in statsmodels 0.11 and earlier.
initial_level : float, optional
The initial level component. Required if estimation method is "known".
If set using either "estimated" or "heuristic" this value is used.
This allows one or more of the initial values to be set while
deferring to the heuristic for others or estimating the unset
parameters.
Fit the model
Parameters
----------
smoothing_level : float, optional
The smoothing_level value of the simple exponential smoothing, if
the value is set then this value will be used as the value.
optimized : bool, optional
Estimate model parameters by maximizing the log-likelihood.
start_params : ndarray, optional
Starting values to used when optimizing the fit. If not provided,
starting values are determined using a combination of grid search
and reasonable values based on the initial values of the data.
initial_level : float, optional
Value to use when initializing the fitted level.
use_brute : bool, optional
Search for good starting values using a brute force (grid)
optimizer. If False, a naive set of starting values is used.
use_boxcox : {
True, False, 'log', float}, optional
Should the Box-Cox transform be applied to the data first? If 'log'
then apply the log. If float then use the value as lambda.
remove_bias : bool, optional
Remove bias from forecast values and fitted values by enforcing
that the average residual is equal to zero.
method : str, default "L-BFGS-B"
The minimizer used. Valid options are "L-BFGS-B" (default), "TNC",
"SLSQP", "Powell", "trust-constr", "basinhopping" (also "bh") and
"least_squares" (also "ls"). basinhopping tries multiple starting
values in an attempt to find a global minimizer in non-convex
problems, and so is slower than the others.
minimize_kwargs : dict[str, Any]
A dictionary of keyword arguments passed to SciPy's minimize
function if method is one of "L-BFGS-B" (default), "TNC",
"SLSQP", "Powell", or "trust-constr", or SciPy's basinhopping
or least_squares. The valid keywords are optimizer specific.
Consult SciPy's documentation for the full set of options.
Returns
-------
HoltWintersResults
See statsmodels.tsa.holtwinters.HoltWintersResults.
3、 二次指数平滑
3.1 理论介绍
3.1.1 Holt’s linear trend method
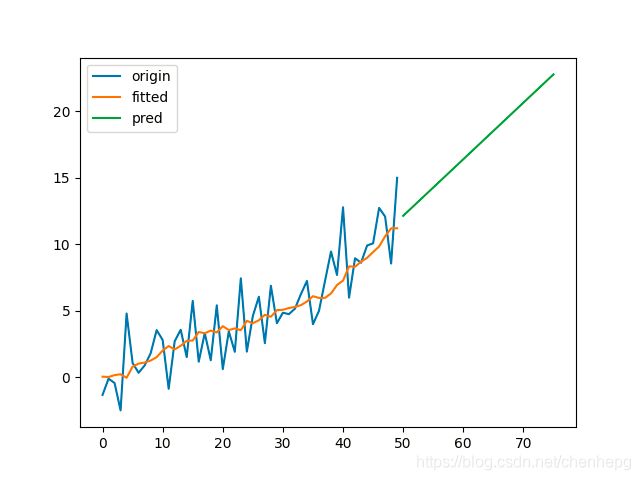
Holt 扩展了简单指数平滑,使其可以用来预测带有趋势的时间序列。直观地看,就是对平滑值的一阶差分(可以理解为斜率)也作一次平滑。模型的预测结果是一条斜率不为0的直线。模型形如:
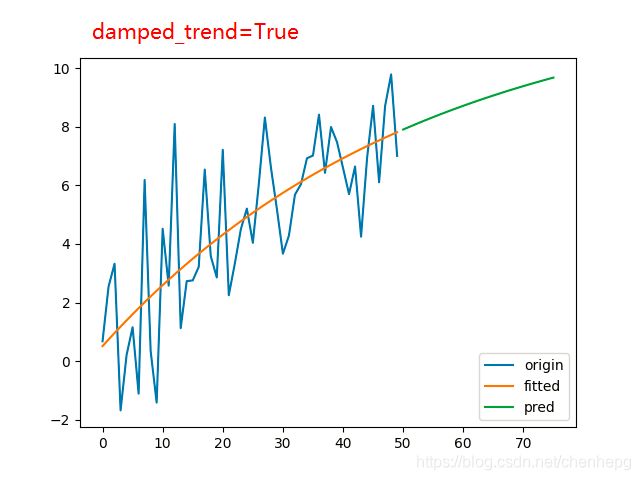
3.1.2 Damped trend methods
Holt’s linear trend method 得到的预测结果是一条直线,即认为未来的趋势是固定的。对于短期有趋势、长期趋于稳定的序列,可以引入一个阻尼系数 0<ϕ<1,将模型改写为:

3.2 代码展示
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from statsmodels.tsa.holtwinters import Holt
number = 50
x2 = np.round(np.linspace(0, 99, number))
y2 = pd.Series(0.1 * x2 + 2 * np.random.randn(number))
# fitted部分是直线或者是曲线,受到原始数据影响。
# 多次测试显示,直线的概率高。
ets2 = Holt(endog=y2, initialization_method='estimated')
# ets2 = Holt(endog=y2, initialization_method='heuristic')
# ets2 = Holt(endog=y2, initialization_method='estimated', damped_trend=True)
r2 = ets2.fit()
pred2 = r2.predict(start=len(y2), end=len(y2) + len(y2) // 2)
pd.DataFrame({
'origin': y2,
'fitted': r2.fittedvalues,
'pred': pred2
}).plot(legend=True)
plt.savefig('holt2.png')
holt()
3.3 参数介绍
Holt's Exponential Smoothing
Parameters
----------
endog : array_like
The time series to model.
exponential : bool, optional
Type of trend component.
damped_trend : bool, optional
Should the trend component be damped.
initialization_method : str, optional
Method for initialize the recursions. One of:
* None
* 'estimated'
* 'heuristic'
* 'legacy-heuristic'
* 'known'
None defaults to the pre-0.12 behavior where initial values
are passed as part of ``fit``. If any of the other values are
passed, then the initial values must also be set when constructing
the model. If 'known' initialization is used, then `initial_level`
must be passed, as well as `initial_trend` and `initial_seasonal` if
applicable. Default is 'estimated'. "legacy-heuristic" uses the same
values that were used in statsmodels 0.11 and earlier.
initial_level : float, optional
The initial level component. Required if estimation method is "known".
If set using either "estimated" or "heuristic" this value is used.
This allows one or more of the initial values to be set while
deferring to the heuristic for others or estimating the unset
parameters.
initial_trend : float, optional
The initial trend component. Required if estimation method is "known".
If set using either "estimated" or "heuristic" this value is used.
This allows one or more of the initial values to be set while
deferring to the heuristic for others or estimating the unset
parameters.
Fit the model
Parameters
----------
smoothing_level : float, optional
The alpha value of the simple exponential smoothing, if the value
is set then this value will be used as the value.
smoothing_trend : float, optional
The beta value of the Holt's trend method, if the value is
set then this value will be used as the value.
damping_trend : float, optional
The phi value of the damped method, if the value is
set then this value will be used as the value.
optimized : bool, optional
Estimate model parameters by maximizing the log-likelihood.
start_params : ndarray, optional
Starting values to used when optimizing the fit. If not provided,
starting values are determined using a combination of grid search
and reasonable values based on the initial values of the data.
initial_level : float, optional
Value to use when initializing the fitted level.
.. deprecated:: 0.12
Set initial_level when constructing the model
initial_trend : float, optional
Value to use when initializing the fitted trend.
.. deprecated:: 0.12
Set initial_trend when constructing the model
use_brute : bool, optional
Search for good starting values using a brute force (grid)
optimizer. If False, a naive set of starting values is used.
use_boxcox : {
True, False, 'log', float}, optional
Should the Box-Cox transform be applied to the data first? If 'log'
then apply the log. If float then use the value as lambda.
remove_bias : bool, optional
Remove bias from forecast values and fitted values by enforcing
that the average residual is equal to zero.
method : str, default "L-BFGS-B"
The minimizer used. Valid options are "L-BFGS-B" (default), "TNC",
"SLSQP", "Powell", "trust-constr", "basinhopping" (also "bh") and
"least_squares" (also "ls"). basinhopping tries multiple starting
values in an attempt to find a global minimizer in non-convex
problems, and so is slower than the others.
minimize_kwargs : dict[str, Any]
A dictionary of keyword arguments passed to SciPy's minimize
function if method is one of "L-BFGS-B" (default), "TNC",
"SLSQP", "Powell", or "trust-constr", or SciPy's basinhopping
or least_squares. The valid keywords are optimizer specific.
Consult SciPy's documentation for the full set of options.
Returns
-------
HoltWintersResults
See statsmodels.tsa.holtwinters.HoltWintersResults.
4、 三次指数平滑
4.1 理论介绍
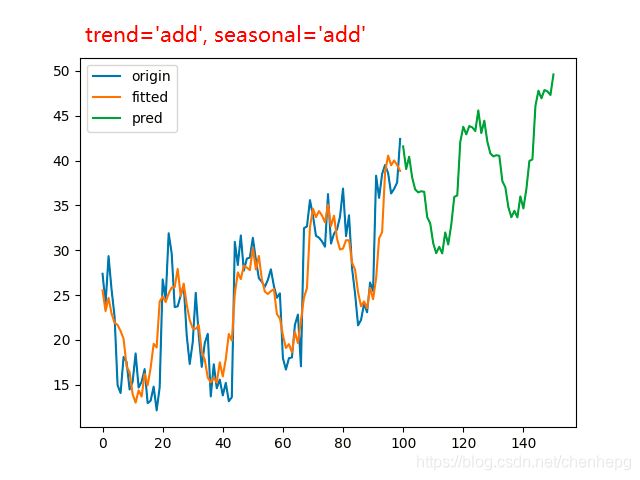
为了描述时间序列的季节性,Holt 和 Winters 进一步扩展了 Holt’s linear trend method,得到了三次指数平滑模型,也就是通常说的 Holt-Winters’ 模型。我们用 mmm 表示“季节”的周期。根据季节部分和非季节部分的组合方式不同,Holt-Winters’ 又可以分为加法模型和乘法模型。
4.1.1 Holt-Winters’ additive method
4.1.2 Holt-Winters’ multiplicative method
4.1.3 Holt-Winters’ damped method
Holt-Winters’ 模型的趋势部分同样可以引入阻尼系数 ϕ\phiϕ,这里不再赘述。
4.2 代码展示
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def holtwinters():
from statsmodels.tsa.holtwinters import ExponentialSmoothing
number = 100
x3 = np.round(np.linspace(0, 4 * np.pi, number))
y3 = pd.Series(20 + 0.1 * np.multiply(x3, x3) + 8 * np.cos(2 * x3) + 2 * np.random.randn(number))
# ets3 = ExponentialSmoothing(y3, trend='add', seasonal='add', seasonal_periods=25)
# ets3 = ExponentialSmoothing(y3, trend='mul', seasonal='mul', seasonal_periods=25)
ets3 = ExponentialSmoothing(y3, trend='mul', seasonal='mul', damped_trend=True, seasonal_periods=25)
r3 = ets3.fit()
pred3 = r3.predict(start=len(y3), end=len(y3) + len(y3) // 2)
pd.DataFrame({
'origin': y3,
'fitted': r3.fittedvalues,
'pred': pred3
}).plot(legend=True)
plt.savefig('holtwinters_mul_damped.png')
holtwinters()
4.3 参数介绍
Holt Winter's Exponential Smoothing
Parameters
----------
endog : array_like
The time series to model.
trend : {
"add", "mul", "additive", "multiplicative", None}, optional
Type of trend component.
damped_trend : bool, optional
Should the trend component be damped.
seasonal : {
"add", "mul", "additive", "multiplicative", None}, optional
Type of seasonal component.
seasonal_periods : int, optional
The number of periods in a complete seasonal cycle, e.g., 4 for
quarterly data or 7 for daily data with a weekly cycle.
initialization_method : str, optional
Method for initialize the recursions. One of:
* None
* 'estimated'
* 'heuristic'
* 'legacy-heuristic'
* 'known'
None defaults to the pre-0.12 behavior where initial values
are passed as part of ``fit``. If any of the other values are
passed, then the initial values must also be set when constructing
the model. If 'known' initialization is used, then `initial_level`
must be passed, as well as `initial_trend` and `initial_seasonal` if
applicable. Default is 'estimated'. "legacy-heuristic" uses the same
values that were used in statsmodels 0.11 and earlier.
initial_level : float, optional
The initial level component. Required if estimation method is "known".
If set using either "estimated" or "heuristic" this value is used.
This allows one or more of the initial values to be set while
deferring to the heuristic for others or estimating the unset
parameters.
initial_trend : float, optional
The initial trend component. Required if estimation method is "known".
If set using either "estimated" or "heuristic" this value is used.
This allows one or more of the initial values to be set while
deferring to the heuristic for others or estimating the unset
parameters.
initial_seasonal : array_like, optional
The initial seasonal component. An array of length `seasonal`
or length `seasonal - 1` (in which case the last initial value
is computed to make the average effect zero). Only used if
initialization is 'known'. Required if estimation method is "known".
If set using either "estimated" or "heuristic" this value is used.
This allows one or more of the initial values to be set while
deferring to the heuristic for others or estimating the unset
parameters.
use_boxcox : {
True, False, 'log', float}, optional
Should the Box-Cox transform be applied to the data first? If 'log'
then apply the log. If float then use the value as lambda.
bounds : dict[str, tuple[float, float]], optional
An dictionary containing bounds for the parameters in the model,
excluding the initial values if estimated. The keys of the dictionary
are the variable names, e.g., smoothing_level or initial_slope.
The initial seasonal variables are labeled initial_seasonal.<j>
for j=0,...,m-1 where m is the number of period in a full season.
Use None to indicate a non-binding constraint, e.g., (0, None)
constrains a parameter to be non-negative.
dates : array_like of datetime, optional
An array-like object of datetime objects. If a Pandas object is given
for endog, it is assumed to have a DateIndex.
freq : str, optional
The frequency of the time-series. A Pandas offset or 'B', 'D', 'W',
'M', 'A', or 'Q'. This is optional if dates are given.
missing : str
Available options are 'none', 'drop', and 'raise'. If 'none', no nan
checking is done. If 'drop', any observations with nans are dropped.
If 'raise', an error is raised. Default is 'none'.
霍尔特-温特指数平滑
参数
----------
endog:数组类型
要建模的时间序列。
trend:{
“add”,“mul”,“additive”,“乘法”,None},可选
趋势组件的类型。
阻尼趋势:bool,可选
趋势成分应该被抑制。
季节:{
“add”,“mul”,“additive”,“multiplicative”,None},可选
季节性成分的类型。
季节性周期:int,可选
一个完整的季节性周期中的周期数,例如,季度数据为4,周周期的日数据为7。
初始化方法:str,可选
方法初始化递归。什么之中的一个:
*没有
*'估计'
*“启发式”
*'传统启发式'
*'已知'
None默认为0.12之前的行为,其中初始值作为“fit”的一部分传递。如果传递了任何其他值,那么在构建模型时也必须设置初始值。如果使用“known”初始化,则必须传递“initial_level”,以及“initial_trend”和“initial_seasional”(如果适用)。默认值为“估计”“遗留启发式”使用与statsmodels 0.11和更早版本中使用的值相同的值。
initial_level : float, optional 可选
初始级别组件。如果估算方法为“已知”,则需要。如果使用“估计”或“启发式”设置,则使用此值。这允许设置一个或多个初始值,同时遵从其他启发式或估计未设置的参数。
initial_trend : float, optional
初始趋势成分。如果估算方法为“已知”,则需要。如果使用“估计”或“启发式”设置,则使用此值。这允许设置一个或多个初始值,同时遵从其他启发式或估计未设置的参数。
initial_seasonal : array_like, optional
最初的季节性成分。长度为“seasional”或长度为“seasional-1”的数组(在这种情况下,计算最后一个初始值以使平均效果为零)。仅在初始化为“已知”时使用。如果估算方法为“已知”,则需要。如果使用“估计”或“启发式”设置,则使用此值。这允许设置一个或多个初始值,同时遵从其他启发式或估计未设置的参数。
use_boxcox : {
True, False, 'log', float}, optional
是否应该首先对数据应用Box-Cox变换?如果是'log',则应用日志。如果是float,则使用lambda值。
bounds : dict[str, tuple[float, float]], optional
一个字典,包含模型中参数的界限,如果估计,则不包括初始值。字典的键是变量名,例如,smoothing_level 或 initial_slope。初始季节变量被标记为initial_seasonal。<j> for j=0,...,m-1,其中m是整个季节的周期数。使用None表示非绑定约束,例如,(0,None)将参数约束为非负。
dates : array_like of datetime, optional
datetime对象的类似数组的对象。如果为endog指定了Pandas对象,则假定该对象具有DateIndex。
freq : str, optional
时间序列的频率。A或“B”、“D”、“W”、“M”、“A”或“Q”。如果给出了日期,这是可选的。
missing : str
可用选项有 'none', 'drop', and 'raise' 。如果'none',则不进行nan检查。如果是“drop”,则任何与nan有关的观测都将被丢弃。如果“raise”,则会引发错误。默认值为'none'。
Fit the model
Parameters
----------
smoothing_level : float, optional
The alpha value of the simple exponential smoothing, if the value
is set then this value will be used as the value.
smoothing_trend : float, optional
The beta value of the Holt's trend method, if the value is
set then this value will be used as the value.
smoothing_seasonal : float, optional
The gamma value of the holt winters seasonal method, if the value
is set then this value will be used as the value.
damping_trend : float, optional
The phi value of the damped method, if the value is
set then this value will be used as the value.
optimized : bool, optional
Estimate model parameters by maximizing the log-likelihood.
remove_bias : bool, optional
Remove bias from forecast values and fitted values by enforcing
that the average residual is equal to zero.
start_params : array_like, optional
Starting values to used when optimizing the fit. If not provided,
starting values are determined using a combination of grid search
and reasonable values based on the initial values of the data. See
the notes for the structure of the model parameters.
method : str, default "L-BFGS-B"
The minimizer used. Valid options are "L-BFGS-B" , "TNC",
"SLSQP" (default), "Powell", "trust-constr", "basinhopping" (also
"bh") and "least_squares" (also "ls"). basinhopping tries multiple
starting values in an attempt to find a global minimizer in
non-convex problems, and so is slower than the others.
minimize_kwargs : dict[str, Any]
A dictionary of keyword arguments passed to SciPy's minimize
function if method is one of "L-BFGS-B", "TNC",
"SLSQP", "Powell", or "trust-constr", or SciPy's basinhopping
or least_squares functions. The valid keywords are optimizer
specific. Consult SciPy's documentation for the full set of
options.
use_brute : bool, optional
Search for good starting values using a brute force (grid)
optimizer. If False, a naive set of starting values is used.
use_boxcox : {
True, False, 'log', float}, optional
Should the Box-Cox transform be applied to the data first? If 'log'
then apply the log. If float then use the value as lambda.
.. deprecated:: 0.12
Set use_boxcox when constructing the model
use_basinhopping : bool, optional
Deprecated. Using Basin Hopping optimizer to find optimal values.
Use ``method`` instead.
.. deprecated:: 0.12
Use ``method`` instead.
initial_level : float, optional
Value to use when initializing the fitted level.
.. deprecated:: 0.12
Set initial_level when constructing the model
initial_trend : float, optional
Value to use when initializing the fitted trend.
.. deprecated:: 0.12
Set initial_trend when constructing the model
or set initialization_method.
Returns
-------
HoltWintersResults
See statsmodels.tsa.holtwinters.HoltWintersResults.
5、参数优化和模型选择理论——AIC BIC
参数优化的方法是最小化误差平方和或最大化似然函数。模型选择可以根据信息量准则,常用的有 AIC 和 BIC等。
(1)AIC 即 Akaike information criterion, 定义为
A I C = 2 k − 2 l n L ( θ ) AIC = 2k-2lnL(\theta) AIC=2k−2lnL(θ)
其中 L(θ) 是似然函数, k是参数数量。用 AIC 选择模型时要求似然函数大,同时对参数数量作了惩罚,在似然函数相近的情况下选择复杂度低的模型。
(2)BIC 即 Bayesian information criterion,定义为
B I C = k l n k − 2 l n L ( θ ) BIC = klnk-2lnL(\theta) BIC=klnk−2lnL(θ)
其中 n n n 是样本数量。当 n > e 2 ≈ 7.4 n>e^2≈7.4 n>e2≈7.4 时, k l n n > 2 k klnn>2k klnn>2k,因此当样本量较大时 BIC 对模型复杂度的惩罚比 AIC 更严厉。
6、 与 ARIMA 的关系
线性的指数平滑方法可以看作是 ARIMA 的特例。例如简单指数平滑等价于 ARIMA(0, 1, 1),Holt’s linear trend method 等价于 ARIMA(0, 2, 2),而 Damped trend methods 等价于 ARIMA(1, 1, 2) 等。
数学推理过程如下:
非线性的指数平滑方法则没有对应的 ARIMA 表示。【这句话的含义还未理解。】