Skip List的工作原理
Skip List(跳跃表)是一种支持快速查找的数据结构,插入、查找和删除操作都仅仅只需要O(log n)对数级别的时间复杂度,它的效率甚至可以与红黑树等二叉平衡树相提并论,而且实现的难度要比红黑树简单多了。
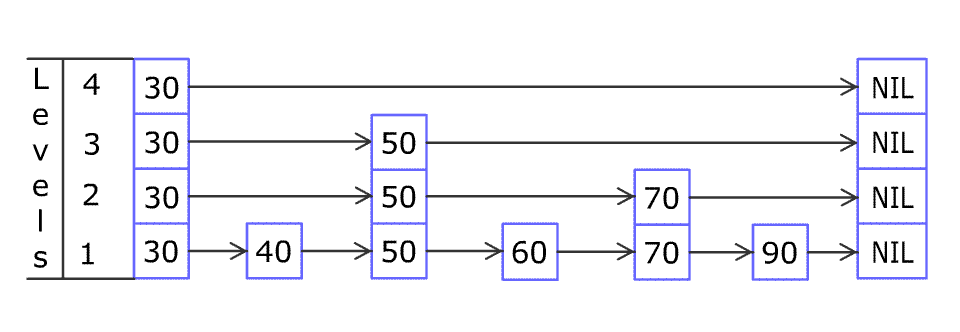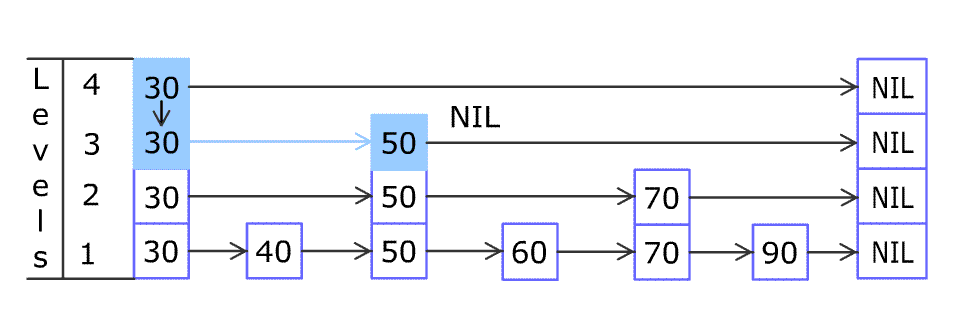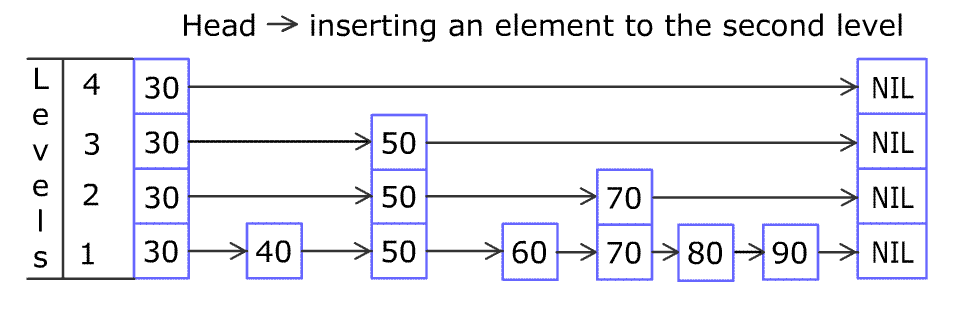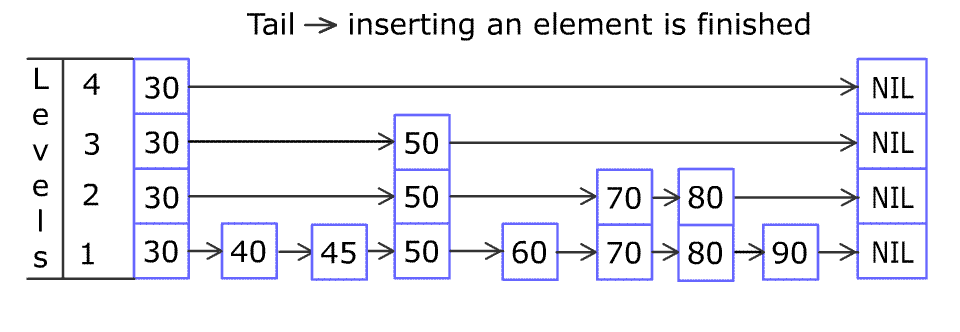
Skip List主要思想是将链表与二分查找相结合,它维护了一个多层级的链表结构(用空间换取时间),可以把Skip List看作一个含有多个行的链表集合,每一行就是一条链表,这样的一行链表被称为一层,每一层都是下一层的"快速通道",即如果x层和y层都含有元素a,那么x层的a会与y层的a相互连接(垂直)。最底层的链表是含有所有节点的普通序列,而越接近顶层的链表,含有的节点则越少。
[图片上传失败...(image-1a72d5-1514724423133)]
对一个目标元素的搜索会从顶层链表的头部元素开始,然后遍历该链表,直到找到元素大于或等于目标元素的节点,如果当前元素正好等于目标,那么就直接返回它。如果当前元素小于目标元素,那么就垂直下降到下一层继续搜索,如果当前元素大于目标或到达链表尾部,则移动到前一个节点的位置,然后垂直下降到下一层。正因为Skip List的搜索过程会不断地从一层跳跃到下一层的,所以被称为跳跃表。
Skip List还有一个明显的特征,即它是一个不准确的概率性结构,这是因为Skip List在决定是否将节点冗余复制到上一层的时候(而在到达或超过顶层时,需要构建新的顶层)依赖于一个概率函数,举个栗子,我们使用一个最简单的概率函数:丢硬币,即概率P为0.5,那么依赖于该概率函数实现的Skip List会不断地"丢硬币",如果硬币为正面就将节点复制到上一层,直到硬币为反。
理解Skip List的原理并不困难,下面我们将使用Java来动手实现一个支持基本需求(查找,插入和删除)的Skip List。
本文作者为SylvanasSun([email protected]),首发于SylvanasSun’s Blog。
原文链接:https://sylvanassun.github.io/2017/12/31/2017-12-31-skip_list/
(转载请务必保留本段声明,并且保留超链接。)
节点与基本实现
对于一个普通的链表节点一般只含有一个指向后续节点的指针(双向链表的节点含有两个指针,一个指向前节点,一个指向后节点),由于Skip List是一个多层级的链表结构,我们的设计要让节点拥有四个指针,分别对应该节点的前后左右,为了方便地将头链表永远置于顶层,还需要设置一个int属性表示该链表所处的层级。
protected static class Node, V> {
private K key;
private V value;
private int level; // 该节点所处的层级
private Node up, down, next, previous;
public Node(K key, V value, int level) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.level = level;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("Node[")
.append("key:");
if (this.key == null)
sb.append("None");
else
sb.append(this.key.toString());
sb.append(" value:");
if (this.value == null)
sb.append("None");
else
sb.append(this.value.toString());
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
// 余下都是get,set方法, 这里省略
.....
}
接下来是SkipList的基本实现,为了能够让Key进行比较,我们规定Key的类型必须实现了Comparable接口,同时为了支持ForEach循环,该类还实现了Iterable接口。
public class SkipList, V> implements Iterable {
// 一个随机数生成器
protected static final Random randomGenerator = new Random();
// 默认的概率
protected static final double DEFAULT_PROBABILITY = 0.5;
// 头节点
private Node head;
private double probability;
// SkipList中的元素数量(不计算多个层级中的冗余元素)
private int size;
public SkipList() {
this(DEFAULT_PROBABILITY);
}
public SkipList(double probability) {
this.head = new Node(null, null, 0);
this.probability = probability;
this.size = 0;
}
.....
}
我们还需要定义几个辅助方法,如下所示(都很简单):
// 对key进行检查
// 因为每条链表的头节点就是一个key为null的节点,所以不允许其他节点的key也为null
protected void checkKeyValidity(K key) {
if (key == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Key must be not null!");
}
// a是否小于等于b
protected boolean lessThanOrEqual(K a, K b) {
return a.compareTo(b) <= 0;
}
// 概率函数
protected boolean isBuildLevel() {
return randomGenerator.nextDouble() < probability;
}
// 将y水平插入到x的后面
protected void horizontalInsert(Node x, Node y) {
y.setPrevious(x);
y.setNext(x.getNext());
if (x.getNext() != null)
x.getNext().setPrevious(y);
x.setNext(y);
}
// x与y进行垂直连接
protected void verticalLink(Node x, Node y) {
x.setDown(y);
y.setUp(x);
}
查找
查找一个节点的过程如下:
从顶层链表的头部开始进行遍历,比较每一个节点的元素与目标元素的大小。
如果当前元素小于目标元素,则继续遍历。
如果当前元素等于目标元素,返回该节点。
如果当前元素大于目标元素,移动到前一个节点(必须小于等于目标元素),然后跳跃到下一层继续遍历。
如果遍历至链表尾部,跳跃到下一层继续遍历。
protected Node findNode(K key) {
Node node = head;
Node next = null;
Node down = null;
K nodeKey = null;
while (true) {
// 不断遍历直到遇见大于目标元素的节点
next = node.getNext();
while (next != null && lessThanOrEqual(next.getKey(), key)) {
node = next;
next = node.getNext();
}
// 当前元素等于目标元素,中断循环
nodeKey = node.getKey();
if (nodeKey != null && nodeKey.compareTo(key) == 0)
break;
// 否则,跳跃到下一层级
down = node.getDown();
if (down != null) {
node = down;
} else {
break;
}
}
return node;
}
public V get(K key) {
checkKeyValidity(key);
Node node = findNode(key);
// 如果找到的节点并不等于目标元素,则目标元素不存在于SkipList中
if (node.getKey().compareTo(key) == 0)
return node.getValue();
else
return null;
}
插入
插入操作的过程要稍微复杂些,主要在于复制节点到上一层与构建新层的操作上。
public void add(K key, V value) {
checkKeyValidity(key);
// 直接找到key,然后修改对应的value即可
Node node = findNode(key);
if (node.getKey() != null && node.getKey().compareTo(key) == 0) {
node.setValue(value);
return;
}
// 将newNode水平插入到node之后
Node newNode = new Node(key, value, node.getLevel());
horizontalInsert(node, newNode);
int currentLevel = node.getLevel();
int headLevel = head.getLevel();
while (isBuildLevel()) {
// 如果当前层级已经到达或超越顶层
// 那么需要构建一个新的顶层
if (currentLevel >= headLevel) {
Node newHead = new Node(null, null, headLevel + 1);
verticalLink(newHead, head);
head = newHead;
headLevel = head.getLevel();
}
// 找到node对应的上一层节点
while (node.getUp() == null) {
node = node.getPrevious();
}
node = node.getUp();
// 将newNode复制到上一层
Node tmp = new Node(key, value, node.getLevel());
horizontalInsert(node, tmp);
verticalLink(tmp, newNode);
newNode = tmp;
currentLevel++;
}
size++;
}
删除
对于删除一个节点,需要先找到节点所在的位置(位于最底层链表中的位置),之后再自底向上地删除该节点在每一行中的冗余复制。
public void remove(K key) {
checkKeyValidity(key);
Node node = findNode(key);
if (node == null || node.getKey().compareTo(key) != 0)
throw new NoSuchElementException("The key is not exist!");
// 移动到最底层
while (node.getDown() != null)
node = node.getDown();
// 自底向上地进行删除
Node prev = null;
Node next = null;
for (; node != null; node = node.getUp()) {
prev = node.getPrevious();
next = node.getNext();
if (prev != null)
prev.setNext(next);
if (next != null)
next.setPrevious(prev);
}
// 对顶层链表进行调整,去除无效的顶层链表
while (head.getNext() == null && head.getDown() != null) {
head = head.getDown();
head.setUp(null);
}
size--;
}
迭代器
由于我们的SkipList实现了Iterable接口,所以还需要实现一个迭代器。对于迭代一个Skip List,只需要找到最底层的链表并且移动到它的首节点,然后进行遍历即可。
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Node node = head;
// 移动到最底层
while (node.getDown() != null)
node = node.getDown();
while (node.getPrevious() != null)
node = node.getPrevious();
// 第一个节点是头部节点,没有任何意义,所以需要移动到后一个节点
if (node.getNext() != null)
node = node.getNext();
// 遍历
while (node != null) {
sb.append(node.toString()).append("\n");
node = node.getNext();
}
return sb.toString();
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator() {
return new SkipListIterator(head);
}
protected static class SkipListIterator, V> implements Iterator {
private Node node;
public SkipListIterator(Node node) {
while (node.getDown() != null)
node = node.getDown();
while (node.getPrevious() != null)
node = node.getPrevious();
if (node.getNext() != null)
node = node.getNext();
this.node = node;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return this.node != null;
}
@Override
public K next() {
K result = node.getKey();
node = node.getNext();
return result;
}
@Override
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
本文中实现的SkipList完整代码地址
参考文献
- Skip list - Wikipedia