nest学习:数据验证
文章问题导向
如何 限制 和 验证 前端传递过来的数据?
如果你都有了答案,可以忽略本文章,或去nest学习导图寻找更多答案
验证方式
常用:dto(data transfer object数据传输对象) + class-validator,自定义提示内容,还能集成swagger
其他:@hapi/joi,不常用,提示不友好
这里主要使用dto的方式
class-validator的验证项装饰器
更多请查阅官网,github官网地址
@IsOptional() //可选的
@IsNotEmpty({ message: ‘不能为空’ })
@MinLength(6, {message: ‘密码长度不能小于6位’})
@MaxLength(20, {message: ‘密码长度不能超过20位’})
@IsEmail({}, { message: ‘邮箱格式错误’ }) //邮箱
@IsMobilePhone(‘zh-CN’, {}, { message: ‘手机号码格式错误’ }) //手机号码
@IsEnum([0, 1], {message: ‘只能传入数字0或1’}) //枚举
@ValidateIf(o => o.username === ‘admin’) //条件判断,条件满足才验证,如:这里是传入的username是admin才验证
第一步:安装
yarn add class-validator class-transformer
第二步:全局使用内置管道ValidationPipe ,不然会报错,无法起作用
import {
NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import {
Logger, ValidationPipe } from '@nestjs/common';
import {
AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe()); //全局内置管道
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();
第三步:编写dto,使用class-validator的校验项验证
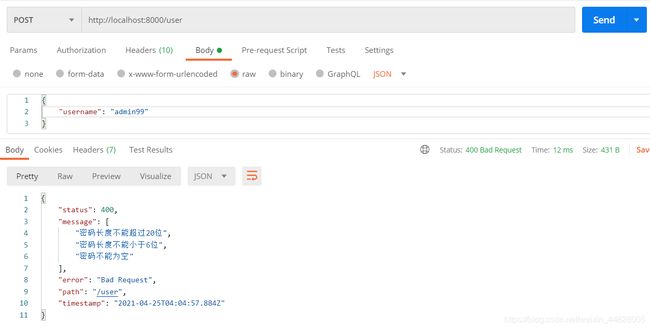
创建:只需要用户名,密码即可,两种都不能为空
import {
IsNotEmpty, MinLength, MaxLength } from 'class-validator';
export class CreateUserDto {
@IsNotEmpty({
message: '用户名不能为空' })
username: string;
@IsNotEmpty({
message: '密码不能为空' })
@MinLength(6, {
message: '密码长度不能小于6位',
})
@MaxLength(20, {
message: '密码长度不能超过20位',
})
password: string;
}
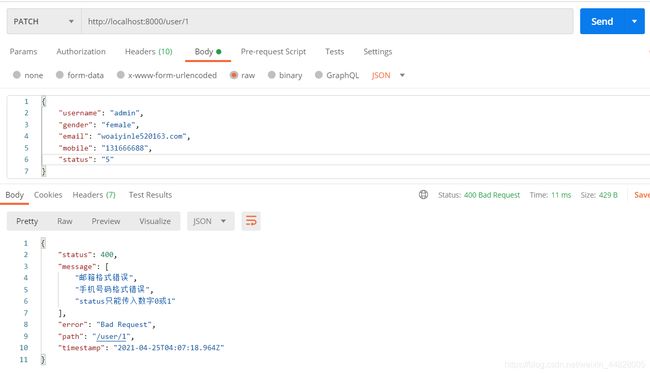
修改:用户名,密码,手机号码,邮箱,性别,状态,都是可选的
import {
IsEnum,
MinLength,
MaxLength,
IsOptional,
IsEmail,
IsMobilePhone,
} from 'class-validator';
import {
Type } from 'class-transformer';
export class UpdateUserDto {
@IsOptional()
username: string;
@IsOptional()
@MinLength(6, {
message: '密码长度不能小于6位',
})
@MaxLength(20, {
message: '密码长度不能超过20位',
})
password: string;
@IsOptional()
@IsEmail({
}, {
message: '邮箱格式错误' })
email: string;
@IsOptional()
@IsMobilePhone('zh-CN', {
}, {
message: '手机号码格式错误' })
mobile: string;
@IsOptional()
@IsEnum(['male', 'female'], {
message: 'gender只能传入字符串male或female',
})
gender: string;
@IsOptional()
@IsEnum({
禁用: 0, 可用: 1 },{
message: 'status只能传入数字0或1',
})
@Type(() => Number) //如果传递的是string类型,不报错,自动转成number类型
status: number;
}
第四步:controller和service一起使用
controller
user.controller.ts
import {
Controller,
Post,
Body,
HttpCode,
HttpStatus,
} from '@nestjs/common';
import {
UserService } from './user.service';
import {
CreateUserDto } from './dto/create-user.dto';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
constructor(private readonly userService: UserService) {
}
@Post()
@HttpCode(HttpStatus.OK)
async create(@Body() user: CreateUserDto) {
//使用创建dto
return await this.userService.create(user);
}
@Patch(':id')
async update(@Param('id') id: string, @Body() user: UpdateUserDto) {
//使用更新dto
return await this.userService.update(id, user);
}
}
service
user.service.ts
import {
Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import {
Repository } from 'typeorm';
import {
InjectRepository } from '@nestjs/typeorm';
import {
UsersEntity } from './entities/user.entity';
import {
ToolsService } from '../../utils/tools.service';
import {
CreateUserDto } from './dto/create-user.dto';
@Injectable()
export class UserService {
constructor(
@InjectRepository(UsersEntity)
private readonly usersRepository: Repository<UsersEntity>,
) {
}
async create(user: CreateUserDto) {
//使用dto
do some thing....
}
}
学习更多
nest学习导图