CNN典型模型及pytorch实现 —— VGGNet
VGG 是一种比较稳定的model(实际上是 AlexNet 结构的扩展),连续的 conv 多,计算量巨大,需要更大的存储空间;
2014年竞赛的第二名,但是在一些迁移模型中的表现要优于第一名 GoogleNet;而且在图像中提取 CNN 特征 VGG 是首选模型;
VGG 模型特点:
- 采用更小的卷积核(将卷积核全部替换为3*3,极少还使用1*1的卷积核);
- 还采用较小的池化核,相比于 AlexNet 的3*3池化核,VGG 全部采用2*2的池化核,步长为2;
(以上特点使得 VGG 网络更深、更宽)卷积核拓宽通道数,池化核缩小高和宽,拓宽网络层次;
使用更大的卷积核会使图像中的一部分被多次卷积,这样在特征提取时会造成困难,而3*3的卷积核就足以捕捉到横竖斜不同方向的像素变化,所以 VGG 中使用3*3的卷积核;
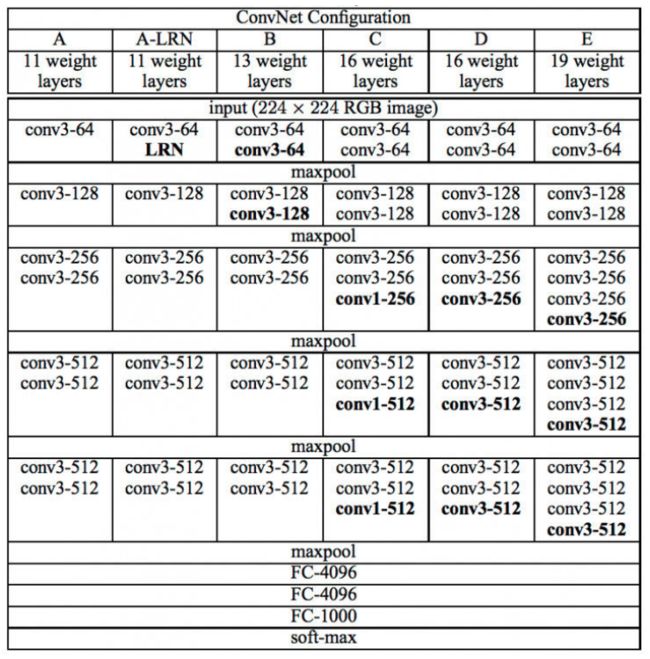
VGG各级别的网络图如下:
下面选取VGG16(即上图D)来分析
(16层网络结构)各层参数如下图:
可以看出,前两个卷积层层占用了较大内存;大部分参数在后面的全连接层;
VGG-16 没有采用LRN(局部相应归一化),因为随着更深的结构的提出,发现LRN没有作用,甚至在11层时起到了负作用;
VGGNet 对 GoogleNet 有一定的启发性作用;
VGG-16模型的pytorch实现:
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
from torch import nn
# VGG-16模型
class VGG_16(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(VGG_16, self).__init__()
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 3, 2, 113),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3, 2, 113),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, 2, 57),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3, 2, 57),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3, 2, 29),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, 2, 29),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, 2, 29),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3, 2, 15),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, 2, 15),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, 2, 15),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, 2, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, 2, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3, 2, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
)
self.layer6 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(7*7*512, 4096),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.Linear(4096, 1000)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.layer5(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.layer6(x)
output = F.softmax(x, dim=1)
return output
if __name__ == '__main__':
vgg_16 = VGG_16()
img = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
vgg_16(img)数据集加载及训练 同【AlexNet】。