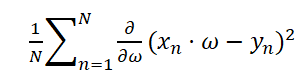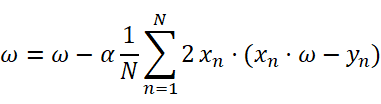pytorch学习(二):梯度下降算法
优化问题:即求loss最小值。
在神经网络中,局部最优点比较小,但是会存在很多的鞍点,即g=0,此时就很难再进行迭代。因此,鞍点是深度学习当中最需要解决的难点。
其中,由于:
∴Update:
平均梯度下降:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_data = [1.0,2.0,3.0]
y_data = [2.0,4.0,6.0]
w = 1.0 #初始权重预测
def forward(x):
return x * w
def cost(xs,ys):
cost = 0
for x,y in zip(xs,ys):
y_pred = forward(x)
cost += (y_pred - y) **2
return cost/len(xs)
def gradient(xs,ys):
grad = 0
for x,y in zip(xs,ys):
grad += 2 * x * (x * w - y)
return grad / len(xs)
print('Predict (before training)',4,forward(4))
epoch_list = []
cost_list = []
for epoch in range(100):
cost_val = cost(x_data,y_data)
grad_val = gradient(x_data,y_data)
w -= 0.01*grad_val #这里的学习率设置成 0.01.
print('Epoch:',epoch,'w=',w,'loss=',cost_val)
epoch_list.append(epoch)
cost_list.append(cost_val)
print('Predict (after training)',4,forward(4))
plt.plot(epoch_list,cost_list)
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.show()
随机梯度下降算法的Update为:![]() 其中,α称为学习率。(采用贪心策略)
其中,α称为学习率。(采用贪心策略)
#随机梯度下降算法
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_data = [1.0,2.0,3.0]
y_data = [2.0,4.0,6.0]
w = 1.0 #初始权重预测
def forward(x):
return x * w
def loss(xs,ys): #这里变换成loss,可去掉原先的cost = 0
y_pred = forward(x)
return (y_pred - ys) **2
def gradient(xs,ys):
return 2 * xs *(xs * w - ys)
print('Predict (before training)',4,forward(4))
epoch_list = []
loss_list = []
for epoch in range(100):
for x,y in zip(x_data,y_data):
grad_val = gradient(x,y)
w -= 0.01*grad_val
print('\tgrad:',x,y,grad_val)
l = loss(x,y)
print('progress:',epoch,'w=',w,'loss=',l)
epoch_list.append(epoch)
loss_list.append(l)
print('Predict (after training)',4,forward(4))
plt.plot(epoch_list,loss_list)
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.show()
之后会采用Batch_size来平衡时间和性能之间的关系。