参考:原文地址
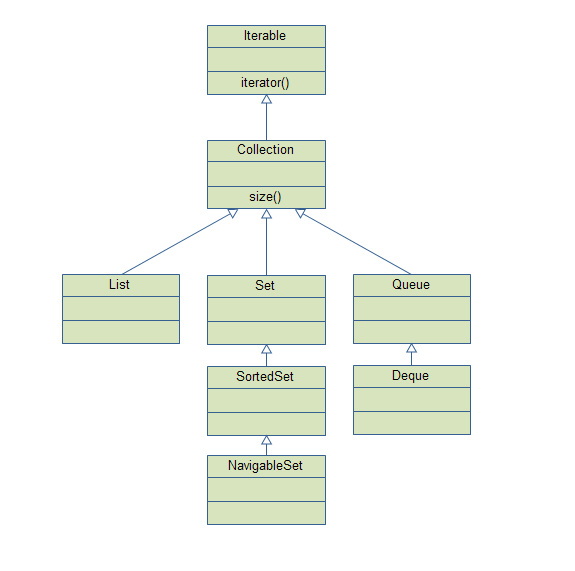
1.java collection overview
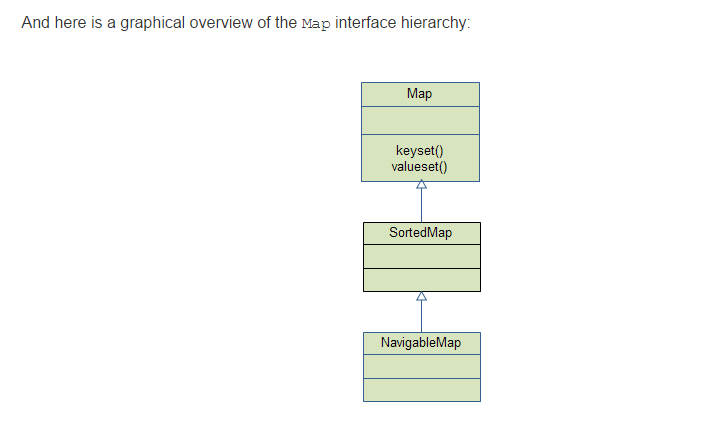
2.Map 接口 概览
3、常用接口方法使用示例
add remove addAll removeAll
package com.interview.base.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
public class MyCollectionUtil {
public static void doSomething(Collection collection) {
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Object object = iterator.next();
//do something to object here...
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String anElement = "an element";
String twoElement = "an element";
Collection setCollection = new HashSet();
Collection listCollection = new ArrayList();
boolean setChange = setCollection.add(anElement);
boolean setChange2 = setCollection.add(anElement);
System.out.println(setChange2);
System.out.println("setCollection: "+ setCollection.size());
System.out.println("contain test: " + setCollection.contains("aobo"));
boolean removeExist = setCollection.remove(anElement);
boolean removeNotExist = setCollection.remove("aobo");
System.out.println("removeExist: " + removeExist);
System.out.println("removeNotExist: " + removeNotExist);
boolean listChange = listCollection.add(anElement);
boolean listChange2 = listCollection.add(anElement);
System.out.println("listCollection: "+ listCollection.size());
// the first output method
for(Object s : listCollection){
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//the secondn output method
Iterator iterator = listCollection.iterator();
System.out.println("----------------------华丽分割线---------------------------------");
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Object object = iterator.next();
//do something to object;
System.out.println(object.toString());
}
}
}