【PCL自学篇】一、SolidWorks三维建模STL,OBJ采样生成PCD点云数据(附源码)
目录&索引
- 1 前言
- 2 准备工作(相关软件及库)
- 3 实现步骤
-
- 3.1 三维建模保存stl网格文件
- 3.2 stl网格文件转obj网格文件
-
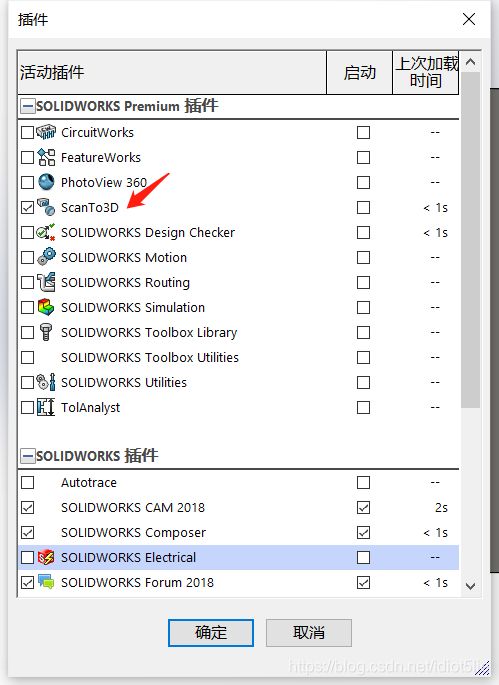
- a) 在工具里勾选SW插件ScanTo3D,后续格式保存要用
- b) 以ScanTo3D网格文件打开保存的stl
- c) 另存为ScanTo3D(*.obj)文件
- 3.3 利用PCL采样可执行程序,实现obj网格文件转pcd点云
-
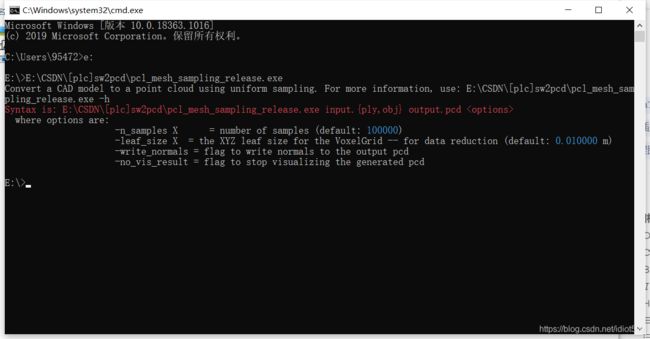
- a) 接下来就是最重要的两步了,在安装PCL的路径下bin文件夹打开,找到pcl_mesh_sampling_debug.exe或pcl_mesh_sampling_release.exe
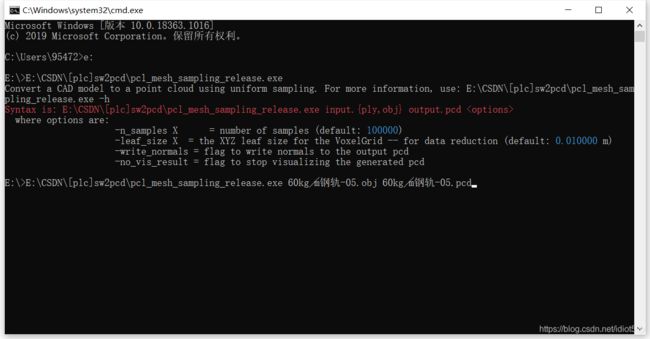
- b) cmd运行可执行采样文件(obj文件相同目录)
- 4 结果
- 5 mesh_sampling 源码(应读者需求,已更新)
这阵子做线结构光视觉检测(钢轨磨耗检测)项目的过程中,发现之前的许多知识点在逐渐遗忘,常言好记性不如烂笔头,故决定把项目中所用到的,把笔者认为有价值且对博友能够产生帮助的内容,记录分享于此。能力有限,如有纰漏,希望博友留下意见与建议。
1 前言
磨耗检测项目中,配准阶段将结构光采集的数据集映射到标准廓形的数据集上,以识别其特征,进而计算分析。
其中,建立标准轨头廓形数据模型有两种方法,a)分段函数描述;b)三维模型转PCD(所选方案);
选定方案之后,查阅三维模型提取点云数据的相关资料时,发现在SolidWorks三维模型中提取生成点云数据的资料较少,且需要下载相关软件或配置需求过高。于是在笔者仔细查阅相关资料后,总结了一种较为方便且利于没有这方面基础的小白阅读完成。
2 准备工作(相关软件及库)
- SolidWorks等三维建模软件
- PCL点云库
3 实现步骤
3.1 三维建模保存stl网格文件
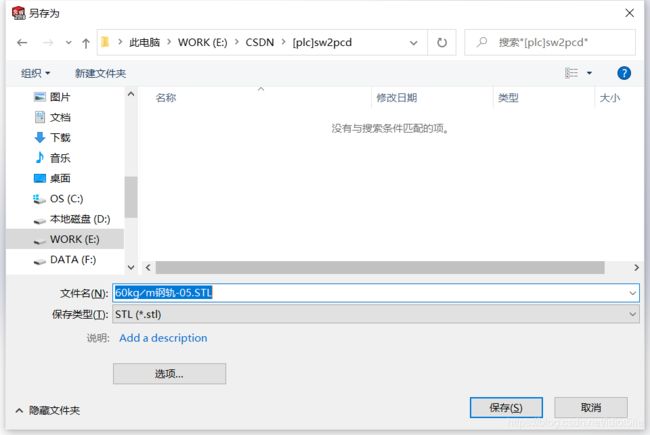
3.2 stl网格文件转obj网格文件
a) 在工具里勾选SW插件ScanTo3D,后续格式保存要用
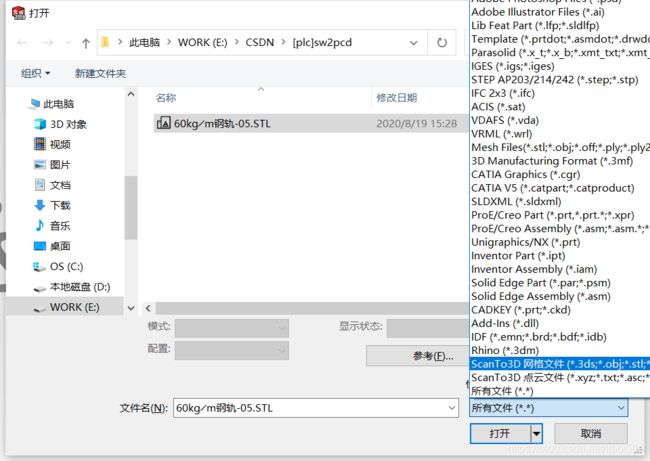
b) 以ScanTo3D网格文件打开保存的stl
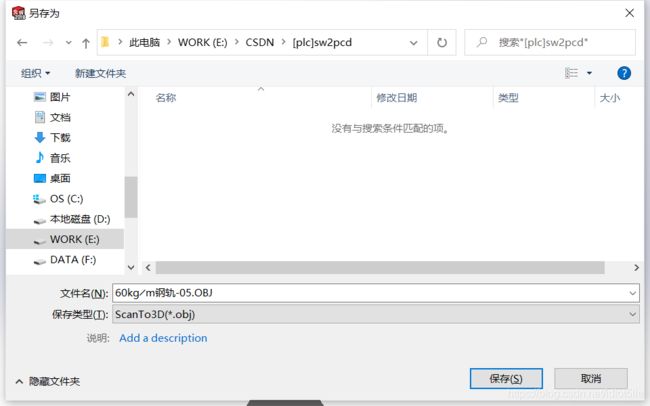
c) 另存为ScanTo3D(*.obj)文件
3.3 利用PCL采样可执行程序,实现obj网格文件转pcd点云
a) 接下来就是最重要的两步了,在安装PCL的路径下bin文件夹打开,找到pcl_mesh_sampling_debug.exe或pcl_mesh_sampling_release.exe

b) cmd运行可执行采样文件(obj文件相同目录)
4 结果
结果显示,点云文件获取完毕

当前目录下生成60kg╱m钢轨-05.pcd的文件。下采样控制体素点距或投影模型等相关后续必要操作,标准点云模型满足需求。
如有不明白的地方,欢迎交流。
5 mesh_sampling 源码(应读者需求,已更新)
/*
* Software License Agreement (BSD License)
*
* Point Cloud Library (PCL) - www.pointclouds.org
* Copyright (c) 2010-2011, Willow Garage, Inc.
*
* All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
*
* * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above
* copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
* disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided
* with the distribution.
* * Neither the name of the copyright holder(s) nor the names of its
* contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
* from this software without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
*/
#include \n" , argv[0]);
print_info (" where options are:\n");
print_info (" -n_samples X = number of samples (default: ");
print_value ("%d", default_number_samples);
print_info (")\n");
print_info (
" -leaf_size X = the XYZ leaf size for the VoxelGrid -- for data reduction (default: ");
print_value ("%f", default_leaf_size);
print_info (" m)\n");
}
/* ---[ */
int
main (int argc, char **argv)
{
print_info ("Convert a CAD model to a point cloud using uniform sampling. For more information, use: %s -h\n",
argv[0]);
if (argc < 3)
{
printHelp (argc, argv);
return (-1);
}
// Parse command line arguments
int SAMPLE_POINTS_ = default_number_samples;
parse_argument (argc, argv, "-n_samples", SAMPLE_POINTS_);
float leaf_size = default_leaf_size;
parse_argument (argc, argv, "-leaf_size", leaf_size);
// Parse the command line arguments for .ply and PCD files
std::vector<int> pcd_file_indices = parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".pcd");
if (pcd_file_indices.size () != 1)
{
print_error ("Need a single output PCD file to continue.\n");
return (-1);
}
std::vector<int> ply_file_indices = parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".ply");
std::vector<int> obj_file_indices = parse_file_extension_argument (argc, argv, ".obj");
if (ply_file_indices.size () != 1 && obj_file_indices.size () != 1)
{
print_error ("Need a single input PLY/OBJ file to continue.\n");
return (-1);
}
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polydata1;
if (ply_file_indices.size () == 1)
{
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPLYReader> readerQuery = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPLYReader>::New ();
readerQuery->SetFileName (argv[ply_file_indices[0]]);
}
else if (obj_file_indices.size () == 1)
{
vtkSmartPointer<vtkOBJReader> readerQuery = vtkSmartPointer<vtkOBJReader>::New ();
readerQuery->SetFileName (argv[obj_file_indices[0]]);
polydata1 = readerQuery->GetOutput ();
polydata1->Update ();
}
//make sure that the polygons are triangles!
vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangleFilter> triangleFilter = vtkSmartPointer<vtkTriangleFilter>::New ();
triangleFilter->SetInput (polydata1);
triangleFilter->Update ();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> triangleMapper = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New ();
triangleMapper->SetInputConnection (triangleFilter->GetOutputPort ());
triangleMapper->Update();
polydata1 = triangleMapper->GetInput();
polydata1->Update ();
bool INTER_VIS = false;
bool VIS = true;
if (INTER_VIS)
{
visualization::PCLVisualizer vis;
vis.addModelFromPolyData (polydata1, "mesh1", 0);
vis.setRepresentationToSurfaceForAllActors ();
vis.spin();
}
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_1 (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
uniform_sampling (polydata1, SAMPLE_POINTS_, *cloud_1);
if (INTER_VIS)
{
visualization::PCLVisualizer vis_sampled;
vis_sampled.addPointCloud (cloud_1);
vis_sampled.spin ();
}
// Voxelgrid
VoxelGrid<PointXYZ> grid_;
grid_.setInputCloud (cloud_1);
grid_.setLeafSize (leaf_size, leaf_size, leaf_size);
grid_.filter (*cloud_1);
if (VIS)
{
visualization::PCLVisualizer vis3 ("VOXELIZED SAMPLES CLOUD");
vis3.addPointCloud (cloud_1);
vis3.spin ();
}
savePCDFileASCII (argv[pcd_file_indices[0]], *cloud_1);
}