前言
最近公司让我维护Spring+Servlet+Hibernate+Spring Security+Jsp的老项目,正好可以锻炼我的业务逻辑和掌控项目的能力。虽然项目很老,但是其中还是有很多值我学习的地方。
电商项目优化
1.我们大致优化的点是秒杀接口:redis预减库存,减少数据库访问;内存标记较少redis的访问;rabbitmq队列缓冲,异步下单,增强用户体验。那么具体步骤如下。
1.处理秒杀业务的Controller在Spring容器周期内加载就绪。也就是实现InitializingBean,在afterPropertiesSet()方法中把商品库存加载到redis中,并且设置在内存中设置商品是否秒杀结束的flag。
/**
* 内存标记初始化
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
List goodsVoList = goodsService.listGoodsVo();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(goodsVoList)) {
return;
}
goodsVoList.forEach(goodsVo -> {
redisService.set(GoodsKey.getMiaoshaGoodsStock, "" + goodsVo.getId(), goodsVo.getStockCount());
localOverMap.put(goodsVo.getId(), false);
});
}
2.后台收到秒杀请求,首先查看内存flag标记,然后减少redis中的商品库存。如果商品秒杀结束,在内存中设置秒杀结束的flag。如果商品秒杀还在进行中,那么进入下一步。
3.把秒杀商品的消息进行入队缓冲,直接返回。这里并不是返回成功,而是返回到排队中。此时,前台不能直接提示秒杀成功,而是启动定时器,过一段时间再去查看是否成功。
4.消息出队,修改db中的库存,创建秒杀订单。
2.分布式Session的解决方案是生成唯一token,token标识用户,把token写到Cookie中,然后把token+用户信息写进Redis,token在redis的失效时间要和Cookie失效时间保持一致。每当用户登录一次,要延迟Session的有效期和Cookie有效期。
3.从缓存的角度来说,我们可以进行页面缓存+URL缓存+对象缓存来达到优化的目的。我们可以手动渲染Thymeleaf模板,把商品详情页和商品列表页缓存到redis中,这里用商品列表页举例。
@RequestMapping(value = "/to_list", produces = "text/html;charset=UTF-8")
@ResponseBody
public String list(MiaoshaUser miaoshaUser) throws IOException {
modelMap.addAttribute("user", miaoshaUser);
//取缓存
String htmlCached = redisService.get(GoodsKey.getGoodsList, "", String.class);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(htmlCached)) {
return htmlCached;
}
List goodsVoList = goodsService.listGoodsVo();
modelMap.addAttribute("goodsList", goodsVoList);
SpringWebContext springWebContext = new SpringWebContext(request, response, request.getServletContext(),
request.getLocale(), modelMap, applicationContext);
String html = thymeleafViewResolver.getTemplateEngine().process("goods_list", springWebContext);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(html)) {
redisService.set(GoodsKey.getGoodsList, "", html);
}
return html;
}
4.从静态资源角度考虑,我们进行页面静态化、前后端分离、静态资源优化、CDN节点优化。这里用静态资源优化举例。
1.JS/CSS压缩、减少流量。
2.多个JS/CSS组合,减少连接数
3.CDN就近访问,减少请求时间。
4.将一些界面缓存到用户的浏览器中。
5.安全优化。密码两次加盐,第一次加盐是固定的,写在Java代码的。第二次加盐是随机的,存储在数据库中。在商品秒杀页,添加数学公式验证码,分散用户的请求。对接口加入限流防刷机制。这里以接口限流防刷机制举例。
1.定义AccessLimit注解,作用于方法。
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface AccessLimit {
int seconds();
int maxCount();
boolean needLogin() default true;
}
2.定义AccessInterceptor拦截器,获得方法中AccessLimit注解中的参数。请求的reqeusturi作为redis中的key,seconds作为key的失效时间。每次请求加1,如果在指定时间内访问该url的次数超过设置的maxCount,那么返回“访问太频繁”。
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
MiaoshaUser user = getUser(request, response);
UserContext.setUser(user);
HandlerMethod hm = (HandlerMethod) handler;
AccessLimit accessLimit = hm.getMethodAnnotation(AccessLimit.class);
if (Objects.isNull(accessLimit)) {
return true;
}
int seconds = accessLimit.seconds();
int maxCount = accessLimit.maxCount();
boolean needLogin = accessLimit.needLogin();
String key = request.getRequestURI();
if (needLogin) {
if (Objects.isNull(user)) {
render(response, CodeMsg.SESSION_ERROR);
return false;
}
}
AccessKey ak = AccessKey.withExpire(seconds);
Integer count = redisService.get(ak, key, Integer.class);
if (Objects.isNull(count)) {
redisService.set(ak, key, 1);
} else if (count < maxCount) {
redisService.incr(ak, key);
} else {
render(response, CodeMsg.ACCESS_LIMIT_REACHED);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
6.部署优化。LVS+Keepalived双机热备模式+Nginx+Tomcat。
Intelli J IDEA使用技巧
1.全局搜索 Ctrl + Shift + F
2.全局替换 Ctrl +Shift + R
Vim编辑器使用技巧
1.在vim编辑器中进行查找。
1.命令模式输入“/字符串”,例如"/xiaoma"
2.如果继续查找下一个,按n即可。
Redis设置密码
1.因为在application-dev.properties中配置了spring.redis.password=,如果没有在redis.conf没有设置requirepass ${password},控制台会抛出连接拒绝异常。
HTTP
Cache Control的用法
no cache : 强制每次请求直接发送给源服务器,而不用经过本地缓存版本的校验。
max-age > 0 : 直接从浏览器缓存中提取。
RabbitMQ
1.AMQP(Advance Message Queuing Protocol)是一个提供统一消息服务的应用层标准高级消息队列协议,是应用层协议。
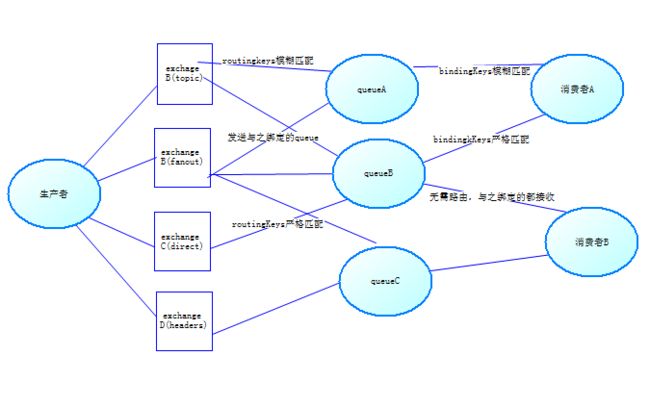
2.Exchange在RabbitMQ中充当交换机的角色,也相当于路由。当然也可以形象的理解成RabbitMQ的过滤器。RabbitMQ有4种模式。
1.Direct:按照Routing Key分到指定的Queue中。
2.Topic:和Direct差不多,但是可以多关键字匹配。
3.Fanout:无Routing Key概念,相当于广播模式,将消息分发给所有绑定FanoutExchange中的Queue。
4.Header:和上面3个不一样,通过添加属性key-value进行匹配。
3.编写RabbitMQ代码
配置RabbitMQ的4种模式
/**
* @author cmazxiaoma
* @version V1.0
* @Description: TODO
* @date 2018/6/4 11:36
*/
@Configuration
public class MQConfig {
public static final String MIAOSHA_QUEUE = "miaosha.queue";
public static final String QUEUE = "queue";
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE1 = "topic.queue1";
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE2 = "topic.queue2";
public static final String HEADER_QUEUE = "header.queue";
public static final String TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "topicExchange";
public static final String FANOUT_EXCHANGE = "fanoutExchange";
public static final String HEADERS_EXCHANGE = "headersExchange";
/**
* Direct模式
* @return
*/
@Bean
public Queue queue() {
return new Queue(QUEUE, true);
}
@Bean
public Queue miaoshaoQue() {
return new Queue(MQConfig.MIAOSHA_QUEUE, true);
}
/**
* Topic模式
* @return
*/
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(TOPIC_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue1() {
return new Queue(TOPIC_QUEUE1, true);
}
@Bean
public Queue topicQueue2() {
return new Queue(TOPIC_QUEUE2, true);
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding1() {
return BindingBuilder
.bind(topicQueue1())
.to(topicExchange())
.with("topic.key1");
}
@Bean
public Binding topicBinding2() {
return BindingBuilder
.bind(topicQueue2())
.to(topicExchange())
.with("topic.#");
}
/**
* Fanout模式
* @return
*/
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
return new FanoutExchange(FANOUT_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue1())
.to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding2() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2())
.to(fanoutExchange());
}
/**
* Header模式
* @return
*/
@Bean
public HeadersExchange headersExchange() {
return new HeadersExchange(HEADERS_EXCHANGE);
}
@Bean
public Queue headerQueue1() {
return new Queue(HEADER_QUEUE, true);
}
@Bean
public Binding headerBinding() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("header1", "value1");
map.put("header2", "value2");
return BindingBuilder.bind(headerQueue1()).to(headersExchange())
.whereAll(map).match();
}
}
配置消息生产者
/**
* @author cmazxiaoma
* @version V1.0
* @Description: TODO
* @date 2018/6/4 13:05
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQSender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
public void sendMiaoshaMessageDirect(MiaoshaMessage miaoshaMessage) {
String msg = RedisService.beanToString(miaoshaMessage);
log.info("send direct message = {}", msg);
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.MIAOSHA_QUEUE, msg);
}
public void sendDirect(Object message) {
String msg = RedisService.beanToString(message);
log.info("send direct message = {}", msg);
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.QUEUE, msg);
}
public void sendTopic(Object message) {
String msg = RedisService.beanToString(message);
log.info("send topic message = {}", msg);
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "topic.key1", msg + "-1");
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, "topic.key2", msg + "-2");
}
public void sendFanout(Object message) {
String msg = RedisService.beanToString(message);
log.info("send fanout message = {}", msg);
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "", msg);
}
public void sendHeader(Object message) {
String msg = RedisService.beanToString(message);
log.info("send header message = {}", msg);
MessageProperties messageProperties = new MessageProperties();
messageProperties.setHeader("header1", "value1");
messageProperties.setHeader("header2", "value2");
Message newMessage = new Message(msg.getBytes(), messageProperties);
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(MQConfig.HEADERS_EXCHANGE, "", newMessage);
}
}
配置消息消费者
/**
* @author cmazxiaoma
* @version V1.0
* @Description: TODO
* @date 2018/6/4 13:47
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class MQReceiver {
@Autowired
private RedisService redisService;
@Autowired
private GoodsService goodsService;
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@Autowired
private MiaoshaService miaoshaService;
@RabbitListener(queues = MQConfig.MIAOSHA_QUEUE)
public void receiveMiaoshaMessageDirect(String message) {
log.info("receive direct miaosha message = {}", message);
MiaoshaMessage miaoshaMessage = RedisService.stringToBean(message, MiaoshaMessage.class);
MiaoshaUser miaoshaUser = miaoshaMessage.getMiaoshaUser();
Long goodsId = miaoshaMessage.getGoodsId();
GoodsVo goodsVo = goodsService.getGoodsVoByGoodsId(goodsId);
int stock = goodsVo.getStockCount();
if (stock <= 0) {
return;
}
//判断是否已经秒杀过
MiaoshaOrder order = orderService.getMiaoshaOrderByUserIdGoodsId(miaoshaUser.getId(), goodsId);
if (!Objects.isNull(order)) {
return;
}
//减库存 下订单 写入秒杀订单
miaoshaService.miaosha(miaoshaUser, goodsVo);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = MQConfig.QUEUE)
public void receiveDirect(String message) {
log.info("receive direct message = {}", message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = MQConfig.TOPIC_QUEUE1)
public void receiveTopic1(String message) {
log.info("receive topic queue1 message = {}", message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = MQConfig.TOPIC_QUEUE2)
public void receiveTopic2(String message) {
log.info("receive topic queue2 message = {}", message);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = MQConfig.HEADER_QUEUE)
public void receiveHeader(byte[] message) {
log.info("receive header message = {}", new String(message));
}
}
测试RabbitMQ的Controller
/**
* @author cmazxiaoma
* @version V1.0
* @Description: TODO
* @date 2018/5/29 16:36
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/rabbitmq")
public class RabbitmqController extends BaseController {
@Autowired
private MQSender mqSender;
@GetMapping("/header")
@ResponseBody
public Result header() {
mqSender.sendHeader("hello, header");
return Result.success("hello, header");
}
@GetMapping("/fanout")
@ResponseBody
public Result fanout() {
mqSender.sendFanout("hello, fanout");
return Result.success("hello, fanout");
}
@GetMapping("/topic")
@ResponseBody
public Result topic() {
mqSender.sendTopic("hello, topic");
return Result.success("hello, topic");
}
@GetMapping("/direct")
@ResponseBody
public Result direct() {
mqSender.sendDirect("hello, direct");
return Result.success("hello, direct");
}
}
Nginx
Nginx的命令过一阵子不写,老是忘记。还是记在上面吧。
启动:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -C /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
关闭:/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
我们在nginx.conf配置max_fail和fail_timeout参数,当失败次数超过max_fail,nginx会把接下来的请求交给其他Real Server去处理。fail_timeout是失败等待时间,当请求被认定失败后,等待fail_timeout时间再去请求,判断是否成功。
Git容易混淆的知识点
工作区:包括实际更改的文件,当前修改还未add进入暂存区的文件变化信息。
暂存区:临时存储文件的变化信息
git reset filename:清空add命令向暂存区提交的关于filename文件的修改。
git checkout --filename:撤销对工作区的修改。
JS基础知识
众所周知,Java有三大特性:封装,继承,多态。我们可以用JS的protoType往java对象中注入这三大特性。
Spring MVC冷门注解
1.produces="text/html"表示方法将产生“text/html”格式的数据,并且响应条的ContentType。我们在写入消息返回响应前,调用addDefaultHeaders()设置响应条中ContentType和ContentLength属性。
protected void addDefaultHeaders(HttpHeaders headers, T t, MediaType contentType) throws IOException{
if (headers.getContentType() == null) {
MediaType contentTypeToUse = contentType;
if (contentType == null || contentType.isWildcardType() || contentType.isWildcardSubtype()) {
contentTypeToUse = getDefaultContentType(t);
}
else if (MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM.equals(contentType)) {
MediaType mediaType = getDefaultContentType(t);
contentTypeToUse = (mediaType != null ? mediaType : contentTypeToUse);
}
if (contentTypeToUse != null) {
if (contentTypeToUse.getCharset() == null) {
Charset defaultCharset = getDefaultCharset();
if (defaultCharset != null) {
contentTypeToUse = new MediaType(contentTypeToUse, defaultCharset);
}
}
headers.setContentType(contentTypeToUse);
}
}
if (headers.getContentLength() < 0 && !headers.containsKey(HttpHeaders.TRANSFER_ENCODING)) {
Long contentLength = getContentLength(t, headers.getContentType());
if (contentLength != null) {
headers.setContentLength(contentLength);
}
}
}
2.@ResponseBody该注解用于将Controller中方法的返回对象,根据HttpRequest中请求头中Accept的内容,再通过合适的HttpMessageConverter转换指定格式后,写入到response对象(HttpOutputMessage)的body数据区中。若指定方法中consume为“application/json”,那么方法仅处理请求头中ContentType属性值为"application/json"的请求。
3.判断某个方法是否有指定的注解、某个方法所在的类上是否有指定的注解、某个方法的参数上是否有指定的注解。
parameter.hasParameterAnnotation(RequestBody.class)
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(returnType.getContainingClass(), ResponseBody.class)
returnType.hasMethodAnnotation(ResponseBody.class)
4.@ModelAttribute的妙用
1.运用在方法的参数上,会将客户端传递过来的参数按名称注入到指定对象中,并且会将这个对象自动加入到modelMap中,便于view层调用
2.运用在方法中,会在每一个@RequestMapping标注的方法前执行,如果有返回值,则自动将该返回值加入modelMap中。我一般用于封装BaseController
public abstract class BaseController {
protected HttpServletRequest request;
protected HttpServletResponse response;
protected HttpSession session;
protected ModelMap modelMap;
@ModelAttribute
protected void initSpringMvc(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
HttpSession session, ModelMap modelMap) {
this.request = request;
this.response = response;
this.session = session;
this.modelMap = modelMap;
}
}
5.定时任务,我们在WebApplication类注解@EnableScheduling,开启定时任务。cron表达式的参数从左到右分别是秒 、分、 时、 天、 月、 星期、 年。详细的cron表达式用法请看这个网站http://cron.qqe2.com/
@Component
public class TestTask {
@Scheduled(cron = "4-40 * * * * ?")
public void reportCurrentTime() {
System.out.println("现在时间:" + DateFormatUtils.format(new Date(),
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
}
}
6.开启异步任务,我们在WebApplication类注解@EnableAsync。
我们可以写一个AsyncTask任务类
@Component
public class AsyncTask {
@Async
public Future doTask1() throws Exception {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(1000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务1耗时:" + (end - start));
return new AsyncResult<>((true));
}
@Async
public Future doTask2() throws Exception {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(2000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务2耗时:" + (end - start));
return new AsyncResult<>((true));
}
@Async
public Future doTask3() throws Exception {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Thread.sleep(3000);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务3耗时:" + (end - start));
return new AsyncResult<>((true));
}
}
然后在写TaskController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/tasks")
public class TaskController extends BaseController {
@Autowired
private AsyncTask asyncTask;
@RequestMapping("test")
public Result test() throws Exception {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Future a = asyncTask.doTask1();
Future b = asyncTask.doTask2();
Future c = asyncTask.doTask3();
while (!a.isDone() || !b.isDone() || !c.isDone()) {
if (a.isDone() && b.isDone() && c.isDone()) {
break;
}
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
String times = "任务全部完成,总耗时:" + (end - start) + "毫秒";
return Result.success(times);
}
}
我们可以看到这3个任务总耗时是3000ms,证明任务是异步执行的。如果去掉@Async,这3个任务执行是同步的,总耗时应该是6000多ms。
{"code":0,"data":"任务全部完成,总耗时:3005毫秒","msg":""}
7.SpringBoot部署到外部Tomcat,配置pom文件。使tomcat作用域设置为provided,provided表明只在编译器和测试时候使用,因为我们部署到外部Tomcat,运行期间有外部Tomcat的支持。
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
provided
记得把打包的方式从jar改成war
com.cmazxiaoma
seckillSystem
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
war
重写SpringApplication这个启动类,我这里重新创建了一个类,名为WebApplication
@SpringBootApplication
//开启定时任务
@EnableScheduling
//开启异步调用方法
@EnableAsync
public class WebApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(WebApplication.class);
}
}
然后Build Artifacts即可。
OSI
OSI是开放式系统互联,英文是Open System Interconnection
应用层
表示层
会话层
传输层
网络层
数据链路层
物理层
TCP/IP模型
应用层 =》 HTTP(超文本传输协议)、TFTP(简单文件传输协议)、SMTP(简单邮件传输协议)、DNS(域名系统)、SNMP(简单网络管理协议)、NFS(网络文件系统)、Telnet(终端登录)
传输层 =》 TCP、IP
网络层 =》 IP、ICMP(国际控制报文协议)、ARP(地址解析协议)、RARP(反地址解析协议)
数据链路层 =》 PPP(点对点协议)
HttpMessageConverter所引发的异常
当我去请求/login/to_login会返回login视图,login界面会去加载背景图片。此时我们没有去配置资源映射,导致背景图片会请求后端的Controller。如果没有找到合适的Controller去处理这个请求,会进入全局异常捕获器进入异常处理。在RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor中的writeWithMessageConverters()方法中,我们会调用getProducibleMediaTypes()方法获取该请求的所有返回消息格式类型。
HttpServletRequest request = inputMessage.getServletRequest();
List requestedMediaTypes = getAcceptableMediaTypes(request);
List producibleMediaTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, valueType, declaredType);
if (outputValue != null && producibleMediaTypes.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No converter found for return value of type: " + valueType);
}
由于我们没有在全局异常捕获器HandlerMapping中显式设置produces属性,我们只能通过遍历所有的HttpMessageConverter,通过canWrite()方法找到支持解析Java对象的HttpMessageConverter,并且把其所支持的mediaType加入mediaTypes集合里面。
protected List getProducibleMediaTypes(HttpServletRequest request, Class valueClass, Type declaredType) {
Set mediaTypes = (Set) request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(mediaTypes)) {
return new ArrayList(mediaTypes);
}
else if (!this.allSupportedMediaTypes.isEmpty()) {
List result = new ArrayList();
for (HttpMessageConverter converter : this.messageConverters) {
if (converter instanceof GenericHttpMessageConverter && declaredType != null) {
if (((GenericHttpMessageConverter) converter).canWrite(declaredType, valueClass, null)) {
result.addAll(converter.getSupportedMediaTypes());
}
}
else if (converter.canWrite(valueClass, null)) {
result.addAll(converter.getSupportedMediaTypes());
}
}
return result;
}
else {
return Collections.singletonList(MediaType.ALL);
}
}
我们得出producibleMediaTypes都是关于"application/json"的格式,我们for循环2次,将requestedMediaTypes和producibleMediaTypes一一比较,得出兼容的compatibleMediaTypes。如果请求消息格式和返回消息格式没有一个匹配的话,则抛出HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException异常。
Set compatibleMediaTypes = new LinkedHashSet();
for (MediaType requestedType : requestedMediaTypes) {
for (MediaType producibleType : producibleMediaTypes) {
if (requestedType.isCompatibleWith(producibleType)) {
compatibleMediaTypes.add(getMostSpecificMediaType(requestedType, producibleType));
}
}
}
if (compatibleMediaTypes.isEmpty()) {
if (outputValue != null) {
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(producibleMediaTypes);
}
return;
}
解决办法
在application-dev.properties文件中配置静态资源自动映射
spring.resources.add-mappings=true
或者是手动配置资源映射
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/static/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/static/");
super.addResourceHandlers(registry);
}
Java基础知识
PreparedStatement对象有addBatch()、executeBatch()方法,用于批量插入。
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConn();
String sql = "insert into miaosha_user(login_count, nickname, register_date, salt, password, id)values(?,?,?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
for (int i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) {
MiaoshaUser user = users.get(i);
pstmt.setInt(1, user.getLoginCount());
pstmt.setString(2, user.getNickname());
pstmt.setTimestamp(3, new Timestamp(user.getRegisterDate().getTime()));
pstmt.setString(4, user.getSalt());
pstmt.setString(5, user.getPassword());
pstmt.setLong(6, user.getId());
pstmt.addBatch();
}
pstmt.executeBatch();
pstmt.close();
conn.close();
isAssignableFrom()的用法,判断Class1和Class2是否相同,判断Class1是否是Class2的接口或者是其父类。
Class1.isAssignableFrom(Class2)
instance of 容易和isAssignableFrom()混淆,这用cmazxiaoma instance of Object举例子,判断一个对象实例是否是一个类、接口的实例,或者是其父类、子接口的实例
JSR303用法
JSR303是一个数据验证的规范,这里用手机号验证举例子
定义@IsMobile注解,这个注解要被IsMobileValidator类去实现验证。
@Target({METHOD, FIELD, ANNOTATION_TYPE, CONSTRUCTOR, PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = {IsMobileValidator.class})
public @interface IsMobile {
boolean required() default true;
String message() default "手机号码格式错误";
Class[] groups() default {};
Class[] payload() default {};
}
定义手机号验证类,验证没通过会抛出BindException
public class IsMobileValidator implements ConstraintValidator {
private boolean required = false;
@Override
public void initialize(IsMobile isMobile) {
required = isMobile.required();
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext constraintValidatorContext) {
if (required) {
return ValidatorUtil.isMobile(value);
} else {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(value)) {
return true;
} else {
return ValidatorUtil.isMobile(value);
}
}
}
}
验证没通过会抛出BindException,我们在全局异常捕获器中捕获这个异常。
@ControllerAdvice
@ResponseBody
@Slf4j
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public Result exceptionHandler(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage());
if (e instanceof GlobalException) {
GlobalException ex = (GlobalException) e;
return Result.error(ex.getCm());
} else if (e instanceof BindException) {
BindException ex = (BindException) e;
List errors = ex.getAllErrors();
ObjectError error = errors.get(0);
String msg = error.getDefaultMessage();
return Result.error(CodeMsg.BIND_ERROR.fillArgs(msg));
} else {
return Result.error(CodeMsg.SERVER_ERROR.fillArgs(e.getMessage()));
}
}
}
尾言
每次逛博客的时候,看到不懂的地方,一定要拿小本本记住。然后整理到上面,日积月累,量变引发质变。