vuex基础--快速上手vuex
vuex基础:
对于初学者,这篇vuex基础版会帮助你快速上手
基本使用:
-
导入vuex依赖包
//1.运行cmd npm install vuex --save //或者运行cmd 执行 vue ui -->直接安装vuex依赖 -
导入vuex包
//vue2.0 --->store/index.js import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) -
创建store对象
//store/index.js const store = new Vuex.Store({ //state中存放的就是全局共享的数据 state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { }, actions: { } }) -
将store对象挂载到vue实例对象中
//main.js new Vue({ el: '#app', render: h=>h(app), router, //将创建的共享实例对象,挂载到实例中 //所有组件就可以直接从store中获取全局的数据了 store }) -
state用法
//1.组件中使用this.$store.state.数据名称 <template> <div class="about"> //插值表达式中省略this <h1>{ { $store.state.count}}</h1> </div> </template> <script> export default { data(){ return{ } } } </script> //2.组件中 从vuex中按需导入mapState函数 <template> <div class="about"> <h1>{ { count}}</h1> </div> </template> //按需导入 mapState import { mapState } form 'vuex' //通过导入的mapState函数,将当前组件需要的全局数据,直接映射到当前组件的 computed 计算属性中: export default { data(){ return{ } }, computed:{ //通过展开运算符,将全局的count映射为此组件的计算属性 ...mapState(['count']) } } -
mutation用法
mutation用于变更Store中的数据。
注意:
-
只能通过
mutation变更Store中的数据,不可以直接操作修改state中的数据 -
此方式虽然操作繁琐,但是便于管理,可以集中监控所有数据的变化
-
在
mutations中不要执行异步操作(页面数据显示变化,但是实际数据不变),如果想执行异步操作,可以放在action中去执行//store/index.js const store = new Vuex.Store({ //state中存放的就是全局共享的数据 state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { add(state,step){ //变更状态 //第一个参数永远是state //剩下的则是传递过来的参数 state.count+=step } }, actions: { } })
组件中调用mutations中的函数
1)直接利用 this.$store.commit调用 mutation中的方法
//触发mutation
methods:{
handlerClick(){
//commit第二个参数就是 就是要传递给mutation中的参数
this.$store.commit('add',5)
}
}
2)从vuex中按需导入mapMutations函数
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
data(){
return{}
},
methods:{
//通过展开运算符,将指定的mutations函数,映射为此组件的methods函数
...mapMutations(['add','xxx'...]),
handlerClick(){
//调用映射过来的方法,并传递参数即可
this.add(5)
}
}
}
- action用法
专门处理异步操作,如果通过异步变更数据,必须通过
action,而不能用mutation。
action不能直接修改state中的数据,需要通过触发mutation的方式变更数据;(通过context.commit()触发某个mutation中的方法)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations:{
add(state,step){
state.count+=step
}
},
actions:{
addAsync(context){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('add',4)
},2000)
}
}
})
- 调用
action中的方法–方式1
//子组件中调用store中的方法
2)调用action中的方法–方式2
//子组件中按需导入mapActions函数
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
data(){
return{}
},
methods:{
//通过展开运算符,将指定的actions函数,映射为此组件的methods函数
...mapActions(['addAsync','xxx'...]),
handlerClick(){
//调用映射过来的方法,并传递参数即可
this.addAsync(5)
}
}
}
-
最终简化版的state,mutations,actions写法
//定义在store组件中 store/index.js import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex) const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations:{ add(state,step){ state.count+= step } }, actions:{ addAsync(context,step){ setTimeout(()=>{ context.commit('add',step) },2000) } } })//子组件调用 <templete> <div> <h3> { { count}} </h3> <button @click="add(5)">调用mutations中的方法</button> <button @click="addAsync(7)">调用actions中的方法</button> </div> </templete> <sctipt> import { mapState, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex' export default { data(){ return{ } }, computed: { ...mapState(['count']) }, methods:{ ...mapMutations(['add']) ...mapActions(['addAsync']) } } </sctipt> -
Getter
Getter用于对Store中的数据进行加工处理形成新的数据,不会修改原数据,只起到包装数据的作用;
-
Getter可以对Store中已有的数据加工处理后形成新数据,类似于vue的计算属性 -
Store中数据发生变化,Getter中的数据也会发生变化
//store/index.js
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
getters:{
showNum(state){
return '当前最新值为:'+state.count
}
}
})
//子组件
//用法1:this.$store.getters.名称
{
{$store.getters.showNum}}
//用法2:按需导入 mapGetters
{
{showNum}}
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
data(){
return{}
},
computed: {
...mapGetters(['showNum'])
}
}
modulesvuex 模块化,大型项目中,vuex状态管理写在一起会显得过于臃肿,不便于维护,所以大多数时候,我们都会倾向于用模块化开发,例:
//组件中
const state = {
count: 0
}
const mutations = {
add:(state,step)=>{
state.count += step
}
}
const actions = {
addAsync: (context,step)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('add',step)
},2000)
},
//解构commit
addSubAsync: ({
commit},step)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
commit('add',step)
},2000)
}
}
const getters = {
showNum: state => {
return '当前最新值为:'+state.count
}
}
//我们通过对象形式暴露出去
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
//store/index.js
//引入我们写的vuex 的modules的js组件
import exModules from './modules/exportModules.js';
Vue.use(Vuex);
export const store = new Vuex.Store({
//注册到modules中即可
modules: {
exModules
}
})
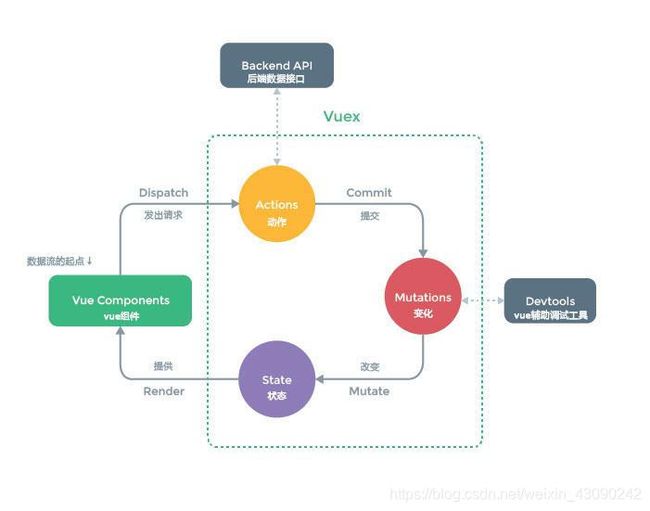
最后:我们再回过头看一下vuex的工作流:
1)当组件进行数据修改的时候我们需要调用dispatch来触发actions里面的方法;
2)actions里面的每个方法中都会有一个commit方法,当方法执行的时候会通过commit来触发mutations里面的方法进行数据的修改;
3)mutations里面的每个函数都会有一个state参数,这样就可以在mutations里面进行state的数据修改;
4)当数据修改完毕后,会传导给页面;
5)页面的数据也会发生改变。
这样,一套完整的vuex状态管理就能应用到我们的项目中了;