【离散数学】计算主析取范式(基于真值表)
【问题描述】
请根据给定的命题公式,计算其真值为T的小项,列出主析取范式,并输出结果。
【输入形式】
输入一个字符串(字符串长度<=50)形式的命题公式,以回车表示输入结束。其中的命题公式为仅包含原子命题、联结词和括号的合式公式。联结词仅包含下述5中联结词:
1、否定,表示为“!”
2、合取,表示为“*”
3、析取,表示为“|”
4、条件,表示为“-”
5、双条件,表示为“=”
例如:
(P-Q)-R
注意:输入符号均采用英文输入。
【输出形式】
输出一个以单个空格分隔的字符串,字符串中各项分别对应主析取范式中小项的序号。
如(P-Q)- R对应的小项为
则输出1 3 4 5 7
注意:其中的原子命题按字母表排序。
【样例输入】
(P-Q)-R
【样例输出】
1 3 4 5 7
算法分析
显然将给出的公式中提取出它的n个不同命题变元,显然每个变元的赋值非真即假,而他们的组合情况恰有2^n种情况,故而可用二进制的形式来模拟,对n个变元进行赋值。在二进制赋值中我们采用模拟二进制过程的算法,从0000开始,从最后一位开始加1,直至最后结果为1111;显然这就包含了2 n种情况。
具体实现代码如下
void truth(int times)
{
int i = argument.size() - 1;
while (times)
{
a[i] = (times & 1);
times >>= 1;
--i;
}
int len = argument.size();
for (i = 0; i < len; ++i)
mp[argument[i]] = a[i];
// display
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
cout << a[i] << '\t';
cout << endl;
}
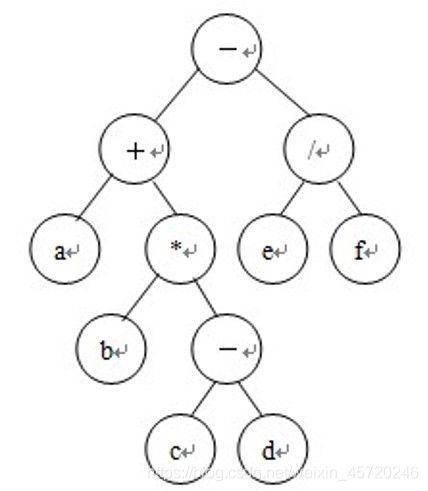
再者,显然该命题公式就是一个中缀表达式的式子,故而在有了对命题变元的赋值后,我们可以采用处理计算中缀表达式的值的算法来做。首先最一般的算法就是写一个模拟过程,采用栈存储,利用运算符的优先级大小关系进行运算。但值得注意的是,中缀表达式可以处理成二叉表达树的形式,如下图
显然,运算符都将会是分支结点,而命题变元将会是叶子结点,因此在构建出二叉表达树后,我们采用后序遍历进行运算直至根节点,便可得出一组赋值的情况,而二叉树的建立也是采用栈的存储,利用优先级关系进行建树。
具体解释将在代码中给出。
/*
* @Author: csc
* @Date: 2020-12-08 14:12:16
* @LastEditTime: 2020-12-11 00:02:42
* @LastEditors: Please set LastEditors
* @Description: In User Settings Edit
* @FilePath: \code\data structure\ls_tree.cpp
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
// 联结词优先 ! * | - = 高到低
unsigned char prior[7][7] = {
//比较大小关系
'>', '<', '<', '<', '<', '<', '>',
'>', '>', '<', '<', '<', '<', '>',
'>', '>', '>', '<', '<', '<', '>',
'>', '>', '>', '>', '<', '<', '>',
'>', '>', '>', '>', '<', '>', '>',
'<', '<', '<', '<', '<', '<', '=',
'>', '>', '>', '>', '>', ' ', '>', };
char opset[7] = {
'=', '-', '/', '*', '!', '(', ')'};
/**
* @description: 假设有两个变量x,y;不妨设x为先出现的变量,则它对应的
* 应为行数,y则对应列数,此时便可列优先级方阵,其中‘<'代表x的优先级小于y
*/
int returnOpOrd(char op, char *TestOp) // 返回运算符对应的下标
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 7; i++)
{
if (op == TestOp[i])
return i;
}
return 0;
}
char precede(char Aop, char Bop)//返回优先级大小关系
{
return prior[returnOpOrd(Aop, opset)][returnOpOrd(Bop, opset)];
}
bool isdigit(char ch) //判断数据
{
if ((ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z'))
return true;
return false;
}
bool isop(char ch) //判断运算符
{
if (ch == '=' || ch == '-' || ch == '|' || ch == '*' || ch == '!')
return true;
return false;
}
stack<char> oper; //运算符栈
map<char, int> mp; //每次赋值
vector<char> argument; //命题变元
vector<int> ans; // 答案向量
int a[55]; //赋值
string formula; //公式
int handle_argument()
/**
* @description: 处理命题公式,提取其中的命题变元,
* 注意这里可能出现两个或两个以上的相同的变元,但存储的
* 时候只需存储一次
*/
{
int len = formula.length();// formula存储命题公式
int ii = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
if (isop(formula[i]) || formula[i] == '(' || formula[i] == ')')
continue;
else
{
if (ii == 0)
{
argument.push_back(formula[i]);
++ii;
}
else
{
bool flag = true;
for (int j = 0; j < ii; ++j)
if (argument[j] == formula[i])
{
flag = false;
break;
}
if (flag)
{
argument.push_back(formula[i]);
++ii;
}
}
}
}
// display
for (auto x : argument)//采用迭代器输出提取好的命题变元
cout << x << '\t';
cout << endl;
return argument.size();
}
void truth(int times)
/**
* @description: 二进制赋值法
* 根据传入参数times的值采用数组进行
* 模拟二进制存储
*/
{
int i = argument.size() - 1;
while (times)
{
a[i] = (times & 1);
times >>= 1;
--i;
}
int len = argument.size();
for (i = 0; i < len; ++i)
mp[argument[i]] = a[i];
// display
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
cout << a[i] << '\t';
cout << endl;
}
typedef struct node
{
char oper;//运算符
char num;//变元
struct node *l;
struct node *r;
} * bitnode;//结点定义
stack<bitnode> tree;//结点栈
bitnode root, lc, rc;
void creat_num(bitnode &root, bitnode L, bitnode R, char ch)
{
bitnode T = new node;
T->num = ch;
T->l = L;
T->r = R;
root = T;
}
void creat_op(bitnode &root, bitnode L, bitnode R, char ch)
{
bitnode T = new node;
T->oper = ch;
T->l = L;
T->r = R;
root = T;
}
void judge_cal()
/**
* @description: 辅助函数
* 判断运算符,并根据运算符不同进行建树
*/
{
char cc;
cc = oper.top();
oper.pop();
if (cc == '!')
/**
* 显然!只管一个命题变元,故而只需将根节点设为!,
* 左孩子连接一个变元,右孩子置空即可
*/
{
lc = tree.top();
tree.pop();
creat_op(root, lc, NULL, cc);
tree.push(root);
}
else
/**
* 对于其他运算符则管得到两个变元,故而左右孩子应各接一个变元
*/
{
rc = tree.top();
tree.pop();
lc = tree.top();
tree.pop();
creat_op(root, lc, rc, cc);
tree.push(root);
}
}
void build()
/**
* @description: 建树过程
*/
{
int len = formula.length();
root = lc = rc = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
if (isdigit(formula[i]))//若为变元,则建议一个树,根节点为变元,左右孩子置空
{
creat_num(root, NULL, NULL, formula[i]);
tree.push(root);
}
else if (isop(formula[i]))//是运算符(联结词)
{
while (1)
{
if (oper.empty() || oper.top() == '(')//联结词栈空或为(直接压栈
{
oper.push(formula[i]);
break;
}
else if (precede(oper.top(), formula[i]) == '<')//后进的优先级较大,则入栈
{
oper.push(formula[i]);
break;
}
else//否则进行运算
judge_cal();
}
}
else//读取的是 ( 或 )
{
if (formula[i] == '(')// 直接压栈
oper.push(formula[i]);
else
{
while (oper.top() != '(')// 对一个()内的内容运算完,建成一棵树
judge_cal();
oper.pop();
}
}
}
while (!oper.empty())//若联结词栈还有元素,则应拿出来建树
judge_cal();
}
int get_value(char c, int L, int R)
/**
* @description: 辅助函数
* 对每一个结点进行运算,判断输入的运算符
* 然后根据不同的联结词对应的值进行运算,看结果为0或1;并将运算结果返回
*/
{
int res = 0;
if (c == '!')
{
L ^= 1;
res = L;
}
else
{
if (c == '*')
res = (L & R);
else if (c == '|')
res = (L | R);
else if (c == '-')
{
if (L == 1 && R == 0)
res = 0;
else
res = 1;
}
else if (c == '=')
{
if ((L && R) || (L == 0 && R == 0))
res = 1;
else
res = 0;
}
}
return res;
}
int calculate(bitnode T)
/**
* @description: 后序遍历二叉表达树进行运算
*/
{
int l = 0, r = 0;
if (T->l == NULL && T->r == NULL)
return mp[T->num];//我对处理好的变元及每一次赋值采用map进行存储,方便找值
else
{
l = calculate(T->l);
if (T->r)
r = calculate(T->r);
return get_value(T->oper, l, r);
}
}
string s[100];//存储主析取范式
void in(int id)//根据最后的结果进行输出对应的主析取范式
{
s[id] = "";
s[id] += '(';
int len = argument.size();
for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i)
{
if (a[i] == 0)
{
s[id] += '!';
s[id] += argument[i];
}
else
{
s[id] += argument[i];
}
if (i != len - 1)
s[id] += '*';
}
s[id] += ')';
}
void init()//若进行若此运算,则应将对应的容器都进行清空,否则容易访问出错
{
while (!tree.empty())
tree.pop();
while (!oper.empty())
oper.pop();
ans.clear();
argument.clear();
}
int main()
{
//cout << "请输入公式:" << endl;
while (cin >> formula)
{
init();
cout << "提取的命题变元及其赋值情况" << endl;
int n = handle_argument();
build();
int times = 0, ma = pow(2, n);//2^n种赋值情况
while (times < ma)
{
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
truth(times);
if (calculate(root))
{
in(ans.size());
ans.push_back(times);
}
times++;
}
cout << "得到的结果:" << endl;
if (ans.empty())
{
cout << "主析取范式不存在" << endl
<< endl;
continue;
}
for (auto v : ans)
cout << v << " ";
cout << endl;
cout << "对应的主析取范式:" << endl;
int cnt = ans.size();
for (int i = 0; i < cnt - 1; cout << "|", ++i)
cout << s[i];
cout << s[cnt - 1] << endl
<< endl;
}
return 0;
}