c语言复习之指针本质
程序中的白变量只是一段存储空间的别名,那么是不是必须通过这个别名才能使用这段存储空间。
答案:不一定,可以用指针来进行修改。可以把指针当做一种特殊变量。
#include
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int* pI;
char* pC;
float* pF;
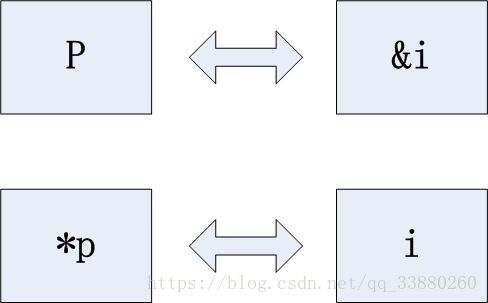
pI = &i;
*pI = 10;
printf("%p, %p, %d\n", pI, &i, i);//pI=&i,i=10
printf("%d, %d, %p\n", sizeof(int*), sizeof(pI), &pI);//
printf("%d, %d, %p\n", sizeof(char*), sizeof(pC), &pC);
printf("%d, %d, %p\n", sizeof(float*), sizeof(pF), &pF);
return 0;
}
delphi@delphi-vm:~$ ./a.out
0xbfc8d26c, 0xbfc8d26c, 10
4, 4, 0xbfc8d268
4, 4, 0xbfc8d264
4, 4, 0xbfc8d260
这段程序里面有两个注意点,就是&pI,指针也是有存储地址的。还有后面sizeof(类型指针)都是一样的,因为指针内存的大小所有系统的多少位决定的,就比如32位的话,我们就是4字节,如果是16位,就是2字节。
关于指针还有一个经典的用法,就是形参和实参的理解上。
特定条件:函数体内,我们要改变一个实参的值,我们要用到指针参数
#include"stdio.h"
int swap(int *a,int *b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
int main()
{
int aa=4;
int bb=5;
swap(&aa,&bb);
printf("aa=%d,bb=%d/n",aa,bb);
}这个所运行的结果就是5和4。这里不能用形参调用,否则还是原值。笔试中会遇到这个问题的
下面讲一下常量与指针
const int *p; //p可变,p指向的内容不可变
int const *p; //p可变,p指向的内容不可变
const int *p; //p不可变,p指向的内容可变
const int *p; //p和p指向的内容都不可变
口诀:左数右指
当const出现在*号左边的时候指针指向的数据为常量
当const出现在*右边时本身为常量
#include
int main()
{
int i = 0;
const int* p1 = &i;
int const* p2 = &i;
int* const p3 = &i;
const int* const p4 = &i;
*p1 = 1;
p1 = NULL;
*p2 = 2;
p2 = NULL;
*p3 = 3;
p3 = NULL;
*p4 = 4;
p4 = NULL;
return 0;
} delphi@delphi-vm:~$ gcc test.c
test.c: In function ‘main’:
test.c:12: error: assignment of read-only location ‘*p1’
test.c:15: error: assignment of read-only location ‘*p2’
test.c:19: error: assignment of read-only variable ‘p3’
test.c:21: error: assignment of read-only location ‘*p4’
test.c:22: error: assignment of read-only variable ‘p4’