前言:
在 Django 模板语言中变量用 { { }},逻辑用 {% %}
在 urls.py 中添加对应关系
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^test/', views.django_test),
]
普通变量:
在 views.py 中编写 django_test 函数
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, HttpResponse
from app01 import models
# Django 模板语言变量
def django_test(request):
name = "John"
age = 28
return render(request, "test.html", {"name1": name, "age1": age}) # 通过字典形式传给 html
接下来写 test.html 页面
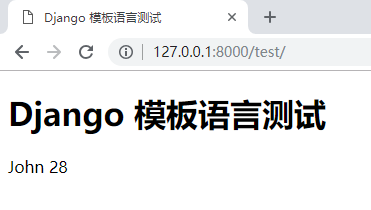
Django 模板语言测试
Django 模板语言测试
{
{ name1 }} {
{ age1 }}
运行效果:
如果是用不存在的变量名,将不会在页面显示
列表:
如果要显示列表成员的话需要使用循环来显示
views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, HttpResponse
from app01 import models
# Django 模板语言变量
def django_test(request):
name = "John"
age = 28
hobby = ["Reading", "Basketball", "Movie", "Music"]
return render(request, "test.html", {"name1": name, "age1": age, "hobby_list": hobby})
test.html:
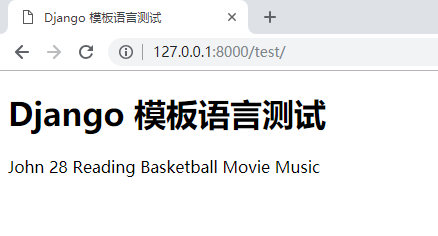
Django 模板语言测试
Django 模板语言测试
{
{ name1 }} {
{ age1 }}
{% for hobby in hobby_list %}
{
{ hobby }}
{% endfor %}
运行效果:
字典:
通过 { { 字典名.key }} 来获取 value
views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, HttpResponse
from app01 import models
# Django 模板语言变量
def django_test(request):
name = "John"
age = 28
hobby = ["Reading", "Basketball", "Movie", "Music"]
info = {"height": 188, "weight": 120}
return render(request, "test.html", {"name1": name, "age1": age, "hobby_list": hobby, "info": info})
test.html:
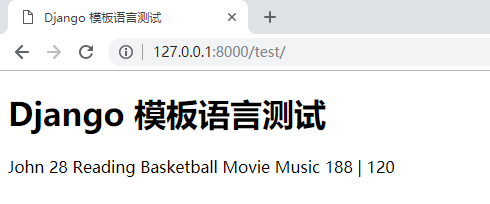
Django 模板语言测试
Django 模板语言测试
{
{ name1 }} {
{ age1 }}
{% for hobby in hobby_list %}
{
{ hobby }}
{% endfor %}
{
{ info.height }} | {
{ info.weight }}
运行效果:
类:
类通过 { { 对象名.属性 }} 来访问属性,通过 { { 对象名.方法 }} 来实现方法
views.py:
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect, HttpResponse
from app01 import models
# 测试类 Animal
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self, specie, name):
self.specie = specie
self.name = name
def sleep(self):
return "%s is sleeping" %self.name
# Django 模板语言变量
def django_test(request):
name = "John"
age = 28
hobby = ["Reading", "Basketball", "Movie", "Music"]
info = {"height": 188, "weight": 120}
a1 = Animal("Cat", "Tom")
a2 = Animal("Dog", "Jim")
return render(
request,
"test.html",
{
"name1": name,
"age1": age,
"hobby_list": hobby,
"info": info,
"a1": a1,
"a2": a2,
})
test.html:
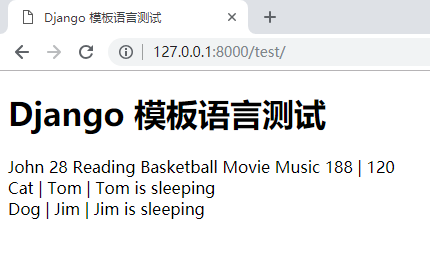
Django 模板语言测试
Django 模板语言测试
{
{ name1 }} {
{ age1 }}
{% for hobby in hobby_list %}
{
{ hobby }}
{% endfor %}
{
{ info.height }} | {
{ info.weight }}
{
{ a1.specie }} | {
{ a1.name }} | {
{ a1.sleep }}
{
{ a2.specie }} | {
{ a2.name }} | {
{ a2.sleep }}
运行效果: