C++ STL标准库:算法algorithm
文章目录
- 1. 简介
- 2. 非修改序列算法
- 3. 修改序列算法
- 4. 划分、排序算法
- 5. 堆算法
C++ STL标准库系列文章:
[STL] 1.简介
[STL] 2.序列容器 固定数组array(C++ 11)
[STL] 3.序列容器 动态数组vector
[STL] 4.序列容器 双端队列deque
[STL] 5.序列容器 双向链表list
[STL] 6.序列容器 单向链表forward_list(C++ 11)
[STL] 7.适配器简介
[STL] 8.容器适配器 栈stack
[STL] 9.容器适配器 队列queue
[STL] 10.容器适配器 优先队列priority_queue
[STL] 11.关联容器 集合set
[STL] 12.关联容器 映射map
[STL] 13.关联容器 多重集合multiset
[STL] 14.关联容器 多重映射multimap
[STL] 15.关联容器 无序集合unordered_set(C++ 11)
[STL] 16.关联容器 无序集合unordered_map(C++ 11)
[STL] 17.仿函数functor与函数对象
[STL] 18.预定义函数对象、仿函数适配器
[STL] 19.算法algorithm
[STL] 20.迭代器适配器
[STL] 21.空间配置器allocator
algorithm- C++ Reference (cplusplus.com)
1. 简介
STL的设计是将数据和算法独立开来,允许任何算法和任何容器交互。
算法对容器中数据进行操作。
容器用来存放数据。
迭代器则是算法与容器之间的桥梁。
分类:
- 非修改序列算法
指不直接修改所操作的容器内容的算法。
- 修改序列算法
指可以修改所操作的容器内容的算法。
- 划分、排序、合并
包含对序列进行划分排序和合并的算法
- 二分法查找算法
二分法查找
- 堆算法
堆结构
- 最大/最小值算法
求最大最小值
相关头文件:
#include
要使用STL中的算法函数必须包含头文件
#include
定义函数对象(function object)的类模板,算法、比较、逻辑操作
2. 非修改序列算法
| 算法名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
find |
根据值查找某元素 |
find_if |
查找某元素(当函数或仿函数的返回值为true) |
find_first_of |
查找第二个区间中任何一个元素第一次出现的位置 |
for_each |
将每一个元素传到函数或仿函数中去 |
count |
返回某个元素出现的次数 |
count_if |
返回某个元素(当函数或仿函数的返回值为true)出现的次数 |
search |
查找一个序列出现的位置 |
search_n |
在范围中查找第一个连续n个元素都等价于给定值的子范围的位置 |
代码示例:
#include::iterator it=find< vector::iterator, int>(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);
vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3);//类型自动推导
if (it != v.end()) //如果没有找到,返回end()
{
cout << "找到了" << *it << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到!" << endl;
}
}
{
//与find类似,只不需要一元函数(或一元函数对象)对象返回为true时候就是找到了
//find_if 会依次将 元素值放入 Is3中去检查,结果返回true时,认为找到了
//vector::iterator it =find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Is3); //普通函数指针
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Is3_FO() ); //函数对象
if (it != v.end()) //如果没有找到,返回end()
{
cout << "找到了" << *it << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到!" << endl;
}
}
{
//查找到 2,3中的任何一个值就认为查找到了
vector<int> v2 = {
99,88}; //作为查找值
vector<int>::iterator it =find_first_of(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end());
if (it != v.end()) //如果没有找到,返回end()
{
cout << "找到了" << *it << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到!" << endl;
}
}
{
//将每个元素依次作为参数传入到 一元函数Print中执行
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print);//传入函数指针
cout << endl;
}
{
vector<int> v2 = {
1,2,2,2,2,3,4,5 };
//统计一个元素出现的次数
cout << "2出现的次数" << count(v2.begin(), v2.end(), 2) << endl;;
}
{
vector<int> v2 = {
1,2,2,2,2,3,4,5 };
//统计一个元素出现的次数
cout << "3出现的次数" << count_if(v2.begin(), v2.end(), Is3 ) << endl;;
}
{
//在容器序列中,查找一段子序列 12345, 比如 12 、234就是一个子序列
vector<int> v2 = {
2,3,4 };
vector<int>::iterator it=search(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end());
if (it != v.end()) //如果没有找到,返回end()
{
cout << "找到了" << *it << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到!" << endl;
}
}
{
vector<int> v2 = {
1,2,3,4,4,4,5,6 };
//在v2中查找3个连续的元素4
vector<int>::iterator it = search_n(v2.begin(), v2.end(), 3, 4);
if (it != v2.end()) //如果没有找到,返回end()
{
cout << "找到了" << *it << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没找到!" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
3. 修改序列算法
| 算法名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| random_shuffle | 随机打乱指定范围中的元素的位置 |
| replace | 将一个范围中值等价于给定值的元素赋值为新的值 |
| replace_if | 与 replace类似(根据仿函数的比较规则) |
| replace_copy | 与 replace类似,同时拷贝到另外个容器 |
| fill | 将一个范围的元素赋值为给定值 |
| remove | 将一个范围中值等价于给定值的元素删除、并返回新结尾迭代器 |
| reverse | 反转排序指定范围中的元素 |
| unique | 删除指定范围中的所有连续重复元素,仅仅留下每组等值元素中的第一个元素。 |
| transform | 对范围中的每个元素调用某函数,并将新值复制到另一个范围 |
代码示例:
#include4. 划分、排序算法
| 算法名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| partition | 对指定范围内元素重新排序,把传入仿函数结果为true的元素放在结果为 false的元素之前 |
| stable_partition | 与 partition类似,但保留容器中元素的原相对顺序。 |
| sort | 快速排序(根据仿函数的比较规则) |
| stable_sort | 与sort类似,但保留容器中相同元素的原相对顺序。 |
| partial_sort | 只排序所有元素的部分,剩余元素的次序是未指定。比如一个赛跑成绩的集合,我们想知道前三名的成绩但并不关心其他名次的次序 |
| nth_element | 使第n大元素处于第n位置,但不保证其他元素的顺序 |
代码示例:
#include()); //使用STL预定义的函数对象
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyGreater); //使用普通函数指针
//打印
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print);
cout << endl;
}
{
//数据都在容器中
vector<A> v = {
A(1,111) ,A(3,330), A(4,444) , A(3,332) , A(2,222) , A(3,331) };
//降序,保证相同元素值的原有顺序
stable_sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyGreaterA);
//打印
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), PrintA);
cout << endl;
}
{
//数据都在容器中
vector<int> v = {
99, 59, 60 ,23, 89,45,66 };
//想知道所有成绩最高的前三名,不关心后面的成绩顺序
partial_sort(v.begin(), v.begin()+3, v.end() ,greater<int>() );
//打印
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print);
cout << endl;
}
{
//数据都在容器中
vector<int> v = {
99, 59, 60 ,23, 89,45,66 };
//把第n大的元素排到第n个位置,不关心其它元素
nth_element(v.begin(), v.begin() + 4, v.end());
//打印
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print);
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
5. 堆算法
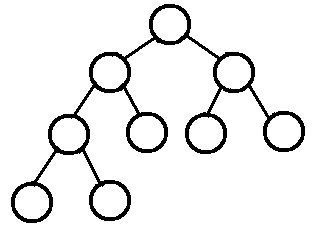
什么是堆?
堆(heap)是一棵完全二叉树(节点都优先集中在最左边),并满足仼意根节点大于(或小于)左右子节点,根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
若设二叉树的深度为k,除第 k 层外,其它各层 (1~k-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第k 层所有的结点都连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。
| 算法名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| make_heap | 用数组中元素构造出一个大根堆(默认) |
| push_heap | 入堆,将数组中最后一个元素放入堆中,使其依然是个堆 |
| pop_heap | 出堆,将堆中的元素删除放到数组最后,排除最后一个,依然是堆 |
| sort_heap | 将堆结构的元素按大小排序到数组,堆结构破坏 |
代码示例:
#include