JAVA线程的基本使用
系列文章目录
Java线程学习入门之线程的基本使用
目录
一、XML和excel的写入与读取
1、XML的写入与读取
1、XML的读取
2、XML的写入
2、excel的写入与读取
1、excel的读取
2、excel的写入
二、网络编程
三、反射
1、获取对象的三种方法
2、反射获取类中的属性和方法
3、反射获取类中的构造器
4、反射获取类中方法的包装类Method
5、 Properties类的基本使用
6、利用反射+properties获取配置文件中的内容
7、利用反射+properties在不修改源代码的前提下修改配置文件中的内容对程序进行功能的扩展
四、实现多线程2种方法:
方法一:继承THread类
方法二:实现Runnable接口
区别:实现runnable接口与继承Thread类的区别:
实现runnable接口与继承Thread类所具有的优势:
*方法三:简单写法之通过匿名类的方式开启多线程
五 、线程池
1、单线程化的线程池--singleThreadPool
2、可缓存的线程池--CachedThreadPool
3、定长且支持周期性调度的线程池--newScheduledThreadPool
4、定时器:
六、Callable和Future/FutureTask创建多线程
1、使用Callable+Future获取执行结果
2、使用Callable+Future获取结果和抛出异常
3、使用Callable+FutureTask获取执行结果
七、URL
1.URL基本使用
2.URL应用举例
3.利用URLConnection获取网页的源码
4.URLConnection应用举例实现图片下载
八.commons-io
1、测试利用commons-io.jar构建的操作文件的工具类
一、XML和excel的写入与读取
1、XML的写入与读取
- XML是扩展标记语言,是存储数据的一种方式,特点:遵循围堵
- 使用场景:1)不同语言之间沟通的桥梁 2)配置文件
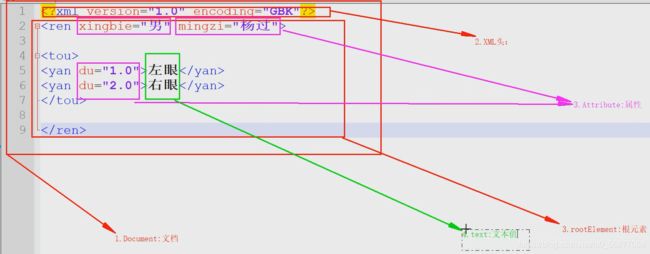
- XML怎样去解析?(XML=元素+属性+文本值)
1、XML的读取
//XML的解析之XML的读取
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws DocumentException {
String path="D:/person.xml";
//1.将该ml文件装入内存中形成一个file对象
File file=new File(path);
//2.解析xml:JDK中自带的类;dom4j.jar这个第三方jar包
//初始化dom4j.jar中的核心解析类
SAXReader reader=new SAXReader();
//3.调用read()方法读取ml文件
Document document=reader.read(file);
System.out.println(document.asXML());
//4.通过Document获取根元素
Element rootElement=document.getRootElement();
//5.通过根元素获取根元素中的属性
List list =rootElement.attributes();
//6.将list中的attribute对象迭代出来
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
Attribute attribute = (Attribute) list.get(i);
System.out.println(attribute.getName()+"\t"+attribute.getValue());
}
}
}
2、XML的写入
public class Test2 {
//XML的写入
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建一个Document
org.dom4j.Document document=DocumentHelper.createDocument();
//2.立足document添加第一个元素,其实就是根元素
Element rootElement=document.addElement("person");
//2.1给根元素添加属性
rootElement.addAttribute("sex", "man");
//3.立足根元素添加其他元素
Element brainElement=rootElement.addElement("brain");
//3.1给brain元素添加属性
brainElement.addAttribute("size", "36");
//3.2给brain元素添加文本值
brainElement.setText("脑袋");
Element leftEyesElement=rootElement.addElement("eyes");
leftEyesElement.addAttribute("du", "1.0");
leftEyesElement.setText("左眼");
Element rightEyesElement=rootElement.addElement("eyes");
rightEyesElement.addAttribute("du", "2.0");
rightEyesElement.setText("右眼");
//4.设定输出格式化
OutputFormat format=OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint();//写入并换行
format.setEncoding("UTF-8");//设定输出的格式为UTF-8
System.out.println(document.asXML());
//5.将内存中的已经创建成功且有内容的xml文件写入硬盘上
//设定文件存放的路径和名字
String path="D:/person02.xml";
//创建文件
FileWriter writer=new FileWriter(path);
//要将内存中的document写入到D:/person02.xml文件中
XMLWriter xmlWriter=new XMLWriter(writer, format);
xmlWriter.write(document);
xmlWriter.close();
writer.close();
}
}2、excel的写入与读取
1、excel的读取
public class Test1 {
//excel的读取
public static void main(String[] args) throws BiffException, IOException {
String path="D:/123.xlsx";
File file=new File(path);
//1.获取工作薄
Workbook workbook=Workbook.getWorkbook(file);
//2.通过工作簿获取sheet
Sheet sheet=workbook.getSheet(0);
//3.通过sheet获取cell对象
Cell cell=sheet.getCell(0, 0);
//4.通过cell获取到cell中的内容
System.out.println(cell.getContents());
workbook.close();
}
}2、excel的写入
public class Test2 {
//excel文件的写入
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, RowsExceededException, WriteException {
String path="D:/789.xls";
File file=new File(path);
//1.创建一个workBook对象
WritableWorkbook workbook=Workbook.createWorkbook(file);
//2.立足workBook创建第一页的sheet
WritableSheet sheet=workbook.createSheet("第一页", 0);
//3.循环写入
for (int i=1;i<9;i++) {
Label label=new Label(i,i,i+"-"+i+"="+(i*i));
sheet.addCell(label);
//4.workBook写入
workbook.write();
//5.关闭workBook对象
workbook.close();
}
}
}二、网络编程
public class Cilent {
//客户端
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException, IOException {
//1.初始化客户端的核心类
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1", 9999);
//2.控制台输入数据
System.out.println("请输入数据:");
Scanner cin=new Scanner(System.in);
String sendInfo=cin.nextLine();
//3.通过socket对象获取一个输出流对象
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
//4.将客户端的输入的数据发送到服务端
PrintStream printStream=new PrintStream(outputStream);
printStream.println(sendInfo);
//5.读取从服务端发送过来的数据
InputStream InputStream = socket.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader=new InputStreamReader(InputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String getStrFormServer = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println("在客户端获取从服务端发送过来的数据为:"+getStrFormServer);
}
}
public class Server {
//网络编程的服务端
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.初始化服务端的核心类
ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(9999);
System.out.println("服务端启动等待客户端连接");
//2.调用accept()方法监控客户端连接
Socket serverSocket = server.accept();
System.out.println("连接成功");
//3.读取客户端发送过来的数据
InputStream intInputStream=serverSocket.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader=new InputStreamReader(intInputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String getInfo = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println("getInfo:"+getInfo);
//4.从服务端向客户端发送数据
System.out.println("服务端在控制台输入:");
Scanner cin=new Scanner(System.in);
String strFromServer=cin.nextLine();
OutputStream outputStream=serverSocket.getOutputStream();
PrintStream printStream=new PrintStream(outputStream);
printStream.println(strFromServer);
}
}三、反射
1、获取对象的三种方法
- 方法一:对象.getClass()方法
- 方法二:类.class属性
- 方法三:Class.forname()
//学生类
public class Student {
public String name;
public int age;
public String address;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Studemt [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", address=" + address + "]";
}
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student类的无参数构造器");
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Student stu=new Student();
//方法一:对象.getClass()方法
Class ca = stu.getClass();
System.out.println(ca);
//方法二:类.class属性
Class ca02 = Student.class;
System.out.println(ca02);
//方法三:Class.forname()
Class ca03 = Class.forName("fss.fs01.Student");
System.out.println(ca03);
}
} 2、反射获取类中的属性和方法
public class Test {
//反射获取类中的属性和方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu=new Student();
//1.获取类对象
Class student01 = stu.getClass();
//2.获取类的简称和全称
System.out.println("类的简称:"+student01.getSimpleName());
System.out.println("类的全称:"+student01.getName());
//3.获取类中的所有的属性
Field[] fields = student01.getFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println("类中属性的类型:"+field.getType()+"\t类中属性的名字:"+field.getName());
}
//4.获取类中的所有方法
Method[] methods = student01.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println("类中方法的名字:"+method.getName()+"\t类中方法的返回值类型"+method.getReturnType());
}
}
}3、反射获取类中的构造器
public class Test {
//反射获取类中的构造器
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
//1.获取到类对象
Class student01 = Class.forName("fss.fs03.Student");
//2.获取student01对象中的构造器
Constructor[] constructors = student01.getConstructors();
//3.取出类中的所有的构造器(前提是public修饰的)
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
//System.out.println(constructor);
//newInstance()构造器的调用,其参数可以是多个,一定要与类中的构造器匹配成功,不然会报错
System.out.println("构造器的调用"+constructor.newInstance(""));
//获取每一个构造器的参数的类型
Class[] parameterTypes = constructor.getParameterTypes();
for (Class parameter : parameterTypes) {
System.out.println(parameter.getName()+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}4、反射获取类中方法的包装类Method
public class Test {
//测试通过反射获取类中方法的包装类Method
public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
//1.获取类对象
Class ownerClass = Student.class;
//2.实例化Student类
Student student = ownerClass.newInstance();
//执行newInstance()方法,效果是Student student-new Student();一样的
//3.
Method method = ownerClass.getMethod("sayHi", String.class);
String result = (String)method.invoke(student, "Jack");
}
} 5、 Properties类的基本使用
public class Test {
//Properties类的基本使用,目的是获取配置文件中的内容
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.初始化Properties
Properties properties=new Properties();
//2.加载配置文件
FileReader fileReader=new FileReader("dbconfig.txt");
//3.载入配置文件
properties.load(fileReader);
//4.获取配置文件中的某一项的值
String username = properties.getProperty("username");
System.out.println("username:"+username);
}
}6、利用反射+properties获取配置文件中的内容
public class Hero {
public void run(String attributes) {
if (attributes.equals("肉盾")) {
System.out.println(attributes+":可以慢跑");
}
else if(attributes.equals("枪手")){
System.out.println(attributes+":可以边打枪边跑");
}
else {
System.out.println("可以正常的跑");
}
}
}
public class Test {
//测试利用反射+properties获取配置文件中的内容
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
//1.初始化
Properties properties=new Properties();
//2.加载配置文件
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("src/config/playerlist.txt");
//3.载入配置文件
properties.load(fileReader);
//4.获取配置文件中的值
String className = properties.getProperty("className");
System.out.println("className:"+className);
String methodName = properties.getProperty("methodName");
System.out.println("methodName:"+methodName);
//5.利用反射获取Hero的类对象
Class cla = Class.forName(className);
//6.获取无参构造器
Constructor constructor = cla.getConstructor();
//7.构造器的初始化
Object hero = constructor.newInstance();
//8.利用反射获取类对象中方法的包装类
Method method = cla.getMethod(methodName, String.class);
//9.函数回调
method.invoke(hero, "肉盾");
}
}7、利用反射+properties在不修改源代码的前提下修改配置文件中的内容对程序进行功能的扩展
public class Devil {
public void run(String attributes) {
if (attributes.equals("boss")) {
System.out.println(attributes+":可以慢跑");
}
else if(attributes.equals("littleboss")){
System.out.println(attributes+":可以边打枪边跑");
}
else {
System.out.println("可以正常的跑");
}
}
}
public class Test {
//测试利用反射+properties在不修改源代码的前提下修改配置文件中的内容对程序进行功能的扩展
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
//1.初始化
Properties properties=new Properties();
//2.加载配置文件
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader("src/config/playerlist.txt");
//3.载入配置文件
properties.load(fileReader);
//4.获取配置文件中的值
String className = properties.getProperty("className");
System.out.println("className:"+className);
String methodName = properties.getProperty("methodName");
System.out.println("methodName:"+methodName);
//5.利用反射获取Hero的类对象
Class cla = Class.forName(className);
//6.获取无参构造器
Constructor constructor = cla.getConstructor();
//7.构造器的初始化
Object hero = constructor.newInstance();
//8.利用反射获取类对象中方法的包装类
Method method = cla.getMethod(methodName, String.class);
//9.函数回调
method.invoke(hero, "boss");
}
}四、实现多线程2种方法:
方法一:继承THread类
//计算器类--通过继承thread实现多线程
public class JiSuanQi extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//System.out.println("JiSuanQi:run()");
//System.out.println("当前线程的名字:" +Thread.currentThread().getName());
//System.out.println("当前线程的名字:"+getName());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("当前线程的名字:"+getName()+"在执行第"+(i+1)+"次");
}
}
public JiSuanQi(String name) {
super(name);
System.out.println("name:"+name);
}
}
public class Test {
//测试通过继承Thread类实现多线程
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("当前线程的名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
//System.out.println("当前线程的名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
JiSuanQi jiSuanQi=new JiSuanQi("线程的名字:计算机的线程");
jiSuanQi.start();//当前调用start()方法的时候,JVM就会自动的调用run()方法
System.out.println("主函数线程打印:002");
System.out.println("主函数线程打印:003");
System.out.println("主函数线程打印:004");
}
}方法二:实现Runnable接口
public class Prims implements Runnable {
//通过实现Punnable接口实现多线程
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程的名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
while (1>0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("当前线程的:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("新线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"因为某种原因被中断了");
}
}
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("主线程打印:001");
Prims prims=new Prims();
Thread thread=new Thread(prims);
thread.start();
System.out.println("主线程打印:002");
}
}
区别:实现runnable接口与继承Thread类的区别:
- 继承THread类耦合度高,
- 实现Runnable接口耦合度低
实现runnable接口与继承Thread类所具有的优势:
- 适合多个相同的程序代码的线程去处理同一个资源
- 可以避免Java中的单继承的限制
- 增加程序的健壮性,代码可以呗多个线程共享,代码和数据独立
- 线程池只能放入实现Runnable或callable类线程,不能直接放入继承Thread的类
*方法三:简单写法之通过匿名类的方式开启多线程
Thread thread=new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("新线程的名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
thread.start();
System.out.println("主函数线程:002");
}五 、线程池
1、单线程化的线程池--singleThreadPool
这个线程只有一个线程在工作,也就是相当于单线程串行执行所有任务,如果这个唯一的线程因为一场结束,那么会有一个新的线程来替代它,此线程池保证所有任务的执行顺序按照任务的提交顺序执行
public class MyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("当前线程的名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
//System.out.println(2/0);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("中断异常");
}
}
}public class Test {
//单线程化的线程池--singleThreadPool
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.通过Executors 获取单线程化的线程池
ExecutorService singleThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//2.创建5个线程
MyThread t1=new MyThread();
MyThread t2=new MyThread();
MyThread t3=new MyThread();
MyThread t4=new MyThread();
MyThread t5=new MyThread();
//3.将创建的多线程装入到线程池中并执行
singleThreadPool.execute(t1);
singleThreadPool.execute(t2);
singleThreadPool.execute(t3);
singleThreadPool.execute(t4);
singleThreadPool.execute(t5);
//4.关闭线程池
singleThreadPool.shutdown();
}
}2、可缓存的线程池--CachedThreadPool
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//1.创建可缓存的线程池
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//2.使用缓存线程池
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
if (! cachedThreadPool.isShutdown()) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
cachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程的名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
});
}
}
//3.关闭线程池
cachedThreadPool.shutdown();
}
}3、定长且支持周期性调度的线程池--newScheduledThreadPool
public class Test {
//定长且支持周期性调度的线程池
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ScheduledExecutorService schedulThreadPool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);
schedulThreadPool.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程的名字:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}, 1, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Thread.sleep(6000);
schedulThreadPool.shutdown();
}
}
4、定时器:
public class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("你好");
}
}public class Test {
//测试Timer&TimerTask
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//1. 定时器的初始化
Timer timer = new Timer();
//2.定时任务的初始化
MyTimerTask timerTask = new MyTimerTask();
//3.定时器执行调度
timer.schedule(timerTask, 0, 2000);
Thread.sleep(4000);//4秒后取消
//4.取消定时器
timer.cancel();
}
}六、Callable和Future/FutureTask创建多线程
1、使用Callable+Future获取执行结果
//Callable接口的实现类
public class Callablelmpl implements Callable {
public int sum=0;//模拟一个累加求和的变量,目的是将来可以演示实现callable接口的多线程,执行完线程任务之后能够获取到返回值
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("当前线程的名字为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("callable接口开启的新的线程开始执行计算");
Thread.sleep(2000);//模拟出计算的这个过程的耗时操作这种感觉
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
System.out.println("callable接口开启的新的线程开始执行计算:结束");
return sum;
}
}
public class Test {
//测试通过callable和Future实现多线程且获取执行之后的结果
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//1.创建单线程化的线程池
ExecutorService singleThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//2.实例化callable接口的实现类
Callablelmpl callableImplTask = new Callablelmpl();
//3.往线程池中加入新的线程
Future future=singleThreadPool.submit(callableImplTask);
//4.关闭线程池
singleThreadPool.shutdown();
//5.主线程的耗时操作
Thread.sleep(2000);
if ((future.get())!=null) {
System.out.println("执行之后的结果为:"+future.get());
}
else {
System.out.println("future.get()执行结果为null");
}
System.out.println("主函数线程执行结束");
}
} 2、使用Callable+Future获取结果和抛出异常
public class MyCallable implements Callable {
public int flag=0;//定义一个变量,用来进行标识的,其目的是为了接下来能够演示出不同线程的情况(可以演示出异常)
@Override
public String call() throws Exception
{
System.out.println("当前线程的名字为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
if (this.flag==0)
{
return "flag==0";
}
if (this.flag==1)
{
try
{
while (1>0)
{
System.out.println("死循环中......");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
}
catch (InterruptedException e)
{
System.out.println("中断异常");
return "false";
}
}
else
{
throw new Exception("您输入的有误");
}
}
public MyCallable(int flag) {
super();
this.flag = flag;
}
}
public class Test {
//测试callable和future获取数据抛出异常
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//1.实例化三个callableTask任务类
MyCallable task0=new MyCallable(0);
MyCallable task1=new MyCallable(1);
MyCallable task2=new MyCallable(2);
//3.创建一个固定数量的线程池
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//4.逐个装入到线程池中
Future future0 = fixedThreadPool.submit(task0);
System.out.println("future0:"+future0.get());
Future future1 = fixedThreadPool.submit(task1);
//System.out.println("future1:"+future1.get());
//为了要演示后边的第三种情况,我们觉得在5s之后停止任务2,因为任务2是死循环的
Thread.sleep(5000);
System.out.println( future1.cancel(true));
try
{
Future future2 = fixedThreadPool.submit(task2);
System.out.println(future2.get());
} catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
3、使用Callable+FutureTask获取执行结果
public class Callablelmpl implements Callable {
public int sum=0;//模拟一个累加求和的变量,目的是将来可以演示实现callable接口的多线程,执行完线程任务之后能够获取到返回值
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("当前线程的名字为:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("callable接口开启的新的线程开始执行计算");
Thread.sleep(2000);//模拟出计算的这个过程的耗时操作这种感觉
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum+=i;
}
System.out.println("callable接口开启的新的线程开始执行计算:结束");
return sum;
}
} public class Test {
// 测试 callable+futureTask实现多线程和获取到结果
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
//1.创建线程池
ExecutorService singleThreadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//2.callable接口的实现类的实例化
Callablelmpl callablelmpl = new Callablelmpl();
//3.将callable接口的实现类的实例化对象传入到TutureTask的构造器实现FutureTask这个类的实例化
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(callablelmpl);
//4.把新的线程装入到线程池中
singleThreadPool.submit(futureTask);
//5.关闭线程池
singleThreadPool.shutdown();
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("模拟出主线程没有结束");
//6.取出子线程计算的结果
System.out.println(futureTask.get());
System.out.println("主线程结束了");
}
} 七、URL
通过URL类可以使Java程序很方便的操作网络资源。
1.URL基本使用
public class Test {
//URL类的基本使用
public static void main(String[] args) throws MalformedURLException {
//1.指定网络资源地址
String urlpath="https://so.youku.com/search_video/q_%E9%92%A2%E9%93%81%E4%BE%A0?searchfrom=1";
//2.初始化URL类
URL realUrl=new URL(urlpath);
//3.通过URL类获取一些网络信息
System.out.println("主机是:"+realUrl.getHost());
System.out.println("协议是:"+realUrl.getProtocol());
System.out.println("默认端口是:"+realUrl.getDefaultPort());
System.out.println("请求参数:"+realUrl.getQuery());
}
}2.URL应用举例
public class Test02 {
//URL实现网页另存为
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.指定网络资源
String urlPath="http://www.baidu.com";
//2.初始化URL类
URL url=new URL(urlPath);
//3.通过url获取一个输入流对象
InputStream inputStream = url.openStream();
//4.IO读写
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(inputStreamReader);
String path="E:/std/baidu.html";
File file=new File(path);
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(file);
String hang="";
while ((hang=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null) {
printWriter.write(hang);
printWriter.flush();
//5.关闭流相关对象
printWriter.close();
bufferedReader.close();
inputStreamReader.close();
inputStream.close();
}
}
}3.利用URLConnection获取网页的源码
public class Test03 {
//利用URLConnection获取网页的源码
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建URL对象
URL url = new URL("https://search.51job.com/list/010000,000000,0000,00,9,99,java,2,1.html?lang=c&stype=&postchannel=0000&workyear=99&cotype=99°reefrom=99&jobterm=99&companysize=99&providesalary=99&lonlat=0%2C0&radius=-1&ord_field=0&confirmdate=9&fromType=&dibiaoid=0&address=&line=&specialarea=00&from=&welfare=");
//2.通过URL对象中的openConnection()方法创建URLConnection对象
URLConnection connection = url.openConnection();
//3.调用URLConnection对象提供的connect方法连接远程服务
connection.connect();
//4.连接服务器后,就可以查询头部信息了
Map> headerMap = connection.getHeaderFields();
Set keySet = headerMap.keySet();
Iterator it = keySet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
{
String key = it.next();
List list = headerMap.get(key);
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i 0)
{
sb.append(",");
}
String str = list.get(i);
sb.append(str);
}
//System.out.println(key+":"+sb);
}
//6.获取输入流,从中读取资源数据
InputStream inputStream = connection.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader reader=new InputStreamReader(inputStream);
BufferedReader bufferedReader=new BufferedReader(reader);
String line="";
while ((line=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null)
{
System.out.println(line);
}
//7.关闭流对象
bufferedReader.close();
reader.close();
inputStream.close();
}
} 4.URLConnection应用举例实现图片下载
public class Test04 {
//利用UrlConnection实现爬取网页上的图片
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建URL对象
URL url = new URL("https://imgsa.baidu.com/forum/w%3D580/sign=a6b7ab9a10dfa9ecfd2e561f52d1f754/48c7a7efce1b9d16a99e53e7f2deb48f8d5464d8.jpg");
//2.通过URL对象中的openConnection()方法创建URLConnection对象
URLConnection connection = url.openConnection();
//3.调用URLConnection对象提供的connect方法连接远程服务
// 设定请求的方法,默认是GET
connection.setRequestProperty("method", "GET");
// 设置字符编码
connection.setRequestProperty("Charset", "UTF-8");
connection.connect();
int fileLength = connection.getContentLength();//获取文件的大小
//4.在客户端(Test04.java)与服务端(网页)建立一个输入流
InputStream inputStream = connection.getInputStream();
//5.将输入流转变成缓冲流
BufferedInputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
//6.设定图片保存的路径
String path = "D:\\zp\\uc\\1.jpg";
File file = new File(path);//根据路径开辟一个内存文件
//如果路径不存在就创建一个路径
if (!file.getParentFile().exists()) {
file.getParentFile().mkdirs();
}
//创建一个输出流
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
int size = 0;
int len = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];//构建一个缓冲区块
while ((size = bin.read(buf)) != -1) //逐行去读
{
len += size;
out.write(buf, 0, size);//写入
// 打印下载百分比
System.out.println("下载了-------> " + len * 100 / fileLength +"%\n");
}
//关闭流对象
bin.close();
out.close();
inputStream.close();
}
}八.commons-io
1、是一款处理IO流的工具包,封装了很多处理IO流和文件的方法,可以大大简化我们处理IO流和操作文件的代码,它主要分为工具类、尾端类、行迭代器、文件过滤器、文件比较器和扩展流。简而言之:是Apache基金会出产的一个能更加方便进行I/O操作的jar。
2、工具类包括:FileUtils、IOUtils、FilenameUtils和FileSystemUtils,前三者的方法并没有多大的区别,只是操作的对象不同。
- FileUtils:主要操作File类;FileUtils:处理文件的打开、移动、读取和判断文件是否存在
- IOUtils:主要操作IO流
- FilenameUtils:则是操作文件名
- FileSystemUtils:包含了一些JDK没有提供的用于访问文件系统的实用方法
1、测试利用commons-io.jar构建的操作文件的工具类
//利用commons-io.jar创建操作文件的工具类
public class FileTools {
/**
* @desc 1.读取文件中的每一行
* @param pathname
* @throws IOException
*/
public void getLinesByRead(String pathname) throws IOException{
File file=new File(pathname);
List list = FileUtils.readLines(file, "GBK");
for (String every : list)
{
System.out.println(every);
}
}
/**
* @desc 2.将字符串写入到文件中
* @param pathname
* @param str
* @throws IOException
*/
public void strWriteToFile(String pathname,String str) throws IOException
{
File file=new File(pathname);
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(file, str, "GBK", true);
System.out.println("字符串写入成功了");
}
/**
* @desc 3.逐行写入文件中,但是效果会是文件的复制
* @param srcPath
* @param purposePath
* @throws IOException
*/
public void strWriteToFile2(String srcPath,String purposePath) throws IOException
{
File file =new File(srcPath);
List line = FileUtils.readLines(file, "GBK");//逐行的读取
File file2=new File(purposePath);
FileUtils.writeLines(file2, line);
System.out.println("逐行写入文件成功了");
}
/**
* @desc 4.文件复制
* @param srcPath
* @param purposePath
* @throws IOException
*/
public void fileCopy(String srcPath,String purposePath) throws IOException
{
File srcFile=new File(srcPath);
File purposeFile=new File(purposePath);
FileUtils.copyFile(srcFile, purposeFile);
System.out.println("文件复制成功了");
}
/**
* @desc 5.根据URL进行赋值,产生的结果就是相当于是另存为
* @param url
* @param pathname
* @throws Exception
*/
public void urlSaveAsFile(String url,String pathname) throws Exception
{
URL urlHtml=new URL(url);
File file=new File(pathname);
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(urlHtml, file);
System.out.println("另存为成功了");
}
/**
* @desc 6.删除路径下的文件和文件夹
* @param pathname
* @throws Exception
*/
public void delete(String pathname) throws Exception
{
File file=new File(pathname);
FileUtils.deleteDirectory(file);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileTools fts=new FileTools();
//fts.getLinesByRead("D:/123.txt");
//fts.strWriteToFile("E:/123.txt", "沙漠之舟");
//fts.strWriteToFile2("D:/123.txt", "E:/123.txt");
// fts.fileCopy("D:/123.txt", "D:/cp/666.txt");
//fts.urlSaveAsFile("https://d-ring.i4.cn/audio/2019/09/02/15/1567407708580_446168.mp3", "D:/cp/mp3/123.mp3");
fts.delete("D:/cp");
}
}