Python 支持向量机
学习目标:
Python代码实现向量机
学习内容:
支持向量机,是属于统计学习中的一种常见算法,但这种算法如果使用计算器计算的话也是浪费时间,哪怕是用计算机计算,也会很麻烦,所以使用代码来进行计算,简单快捷。
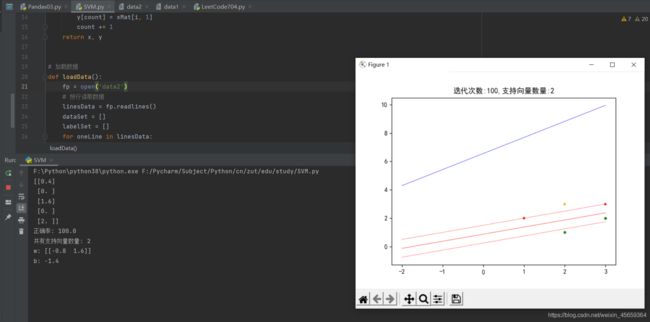
要实现的功能也很简单,我们传入一个文件,文件中写有相关数据,然后代码自动计算w和b在,以及其它的一些参数,如下图,是我们的实现结果
代码实现:
直接上代码吧
from numpy import *
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import svm
def getDataArray(lists, xMat):
x = np.ndarray(len(lists))
y = np.ndarray(len(lists))
count = 0
for i in lists:
x[count] = xMat[i, 0]
y[count] = xMat[i, 1]
count += 1
return x, y
# 加载数据
def loadData():
fp = open('data2')
# 按行读取数据
linesData = fp.readlines()
dataSet = []
labelSet = []
for oneLine in linesData:
oneLine = oneLine.split(',')
dataSet.append([float(oneLine[0].strip()), float(oneLine[1].strip())])
labelSet.append(float(oneLine[2].strip()))
return dataSet, labelSet
class SVM:
def __init__(self, xSet, yArray, C=None, floatingPointError=0.0001):
self.xMat = np.mat(xSet) # (48,2)
self.yMat = np.mat(yArray).T # (48,1)
self.rows = self.xMat.shape[0]
self.cols = self.xMat.shape[1]
self.alpha = np.mat(np.zeros(self.rows)).T # (48,1)
self.w = None # 最后返回,计算过程不需要
self.b = 0
self.C = C # C=None时表示hard margin
self.fpe = floatingPointError
self.trainCount = 0 # 记录训练次数
self.K = np.matmul(self.xMat, self.xMat.transpose())
# Ei 缓存
self.EiCatch = np.zeros(self.rows)
self.updateEi_catch()
def predict(self, xArray):
resultList = []
for i in range(len(xArray)):
v = np.sum(np.multiply(xArray[i], self.w)) + self.b
if v > 0:
resultList.append(1)
else:
resultList.append(-1)
return resultList
def score(self, xArray, yArray):
resultList = self.predict(xArray)
count = 0
for i in range(len(yArray)):
if resultList[i] == yArray[i]:
count += 1
return round(count / len(yArray) * 100, 2)
def train(self, maxCount, debug):
self.trainCount = 0
while self.trainCount < maxCount:
self.update_allPoints(debug)
self.trainCount += 1
# 打印alpha信息
print(self.alpha)
return self.w, self.b
def update_allPoints(self, debug=None):
count = 0
for alpha2_index in range(self.rows):
if self.check_alpha2_needUpdate(alpha2_index):
alpha1_index = self.selectAlpha1_index(alpha2_index)
self.update_alpha_and_b(alpha1_index, alpha2_index)
# 计算w
self.w = np.matmul(np.multiply(self.yMat, self.alpha).T, self.xMat)
if debug:
# 打印alpha信息
print(self.alpha)
# 画图
self.classifyDataAndPlot()
print("调整次数:{}".format(count + 1))
count += 1
# 打印ei信息
print(self.EiCatch)
def check_alpha2_needUpdate(self, alpha2_index):
Ei = self.EiCatch[alpha2_index]
yi = self.yMat[alpha2_index, 0]
alpha2 = self.alpha[alpha2_index, 0]
fx = self.cal_Fx(alpha2_index)
if alpha2 < 0 or alpha2 > self.C:
return True
if yi == 1 and fx >= 1:
return False
elif yi == -1 and fx <= -1:
return False
# 再来看看是否有足够的空间调整
# Ei不为零的,alpha应该是0如果不是就要调整,alpha2调整量就是 -yi*Ei,如果是正的, alpha增加,但如果已经是C的话就不用处理了
alpha2_change_direction = -yi * Ei
if alpha2_change_direction > self.fpe and alpha2 < self.C:
return True
elif alpha2_change_direction < -self.fpe and alpha2 > 0:
return True
else:
return False
def update_alpha_and_b(self, alpha1_index, alpha2_index):
alpha1_old = self.alpha[alpha1_index, 0]
alpha2_old = self.alpha[alpha2_index, 0]
y1 = self.yMat[alpha1_index, 0]
y2 = self.yMat[alpha2_index, 0]
alpha2_new_chiped = self.get_alpha2_new_chiped(alpha1_index, alpha2_index)
alpha1_new = alpha1_old + y1 * y2 * (alpha2_old - alpha2_new_chiped)
b_new = self.get_b_new(alpha1_index, alpha2_index, alpha1_new, alpha2_new_chiped)
# 最后更新数据
alpha2_new_chiped = round(alpha2_new_chiped, 5)
alpha1_new = round(alpha1_new, 5)
b_new = round(b_new, 5)
self.alpha[alpha1_index, 0], self.alpha[alpha2_index, 0] = alpha1_new, alpha2_new_chiped
self.b = b_new
# 更新EiCatch
self.updateEi_catch()
return True
def get_b_new(self, alpha1_index, alpha2_index, alpha1_new, alpha2_new_chiped):
alpha1_old = self.alpha[alpha1_index, 0]
alpha2_old = self.alpha[alpha2_index, 0]
y1 = self.yMat[alpha1_index, 0]
y2 = self.yMat[alpha2_index, 0]
K11 = self.K[alpha1_index, alpha1_index]
K12 = self.K[alpha1_index, alpha2_index]
K22 = self.K[alpha2_index, alpha2_index]
E1 = self.EiCatch[alpha1_index]
E2 = self.EiCatch[alpha2_index]
b1New = self.b - E1 + y1 * K11 * (alpha1_old - alpha1_new) + y2 * K12 * (alpha2_old - alpha2_new_chiped)
b2New = self.b - E2 + y1 * K12 * (alpha1_old - alpha1_new) + y2 * K22 * (alpha2_old - alpha2_new_chiped)
# 只有符合的alpha_new用来调整b
if self.C is None:
alpha1_valid = True if 0 < alpha1_new < self.fpe else False
alpha2_valid = True if 0 < alpha2_new_chiped else False
else:
alpha1_valid = True if 0 < alpha1_new < self.C else False
alpha2_valid = True if 0 < alpha2_new_chiped < self.C else False
if alpha1_valid:
b = b1New
elif alpha2_valid:
b = b2New
else:
b = (b1New + b2New) / 2
return b
def check_kkt_status(self):
# yi和alpha的乘积和为0
if not (-self.fpe < np.sum(np.multiply(self.yMat, self.alpha)) < self.fpe):
return False
# 然后检查每个alpha
for i in range(len(self.alpha)):
if self.check_satisfiy_kkt_onePoint(i) == False:
return False
return True
def cal_Ei(self, index):
v = self.cal_Fx(index) - self.yMat[index, 0]
return round(v, 5)
def cal_Fx(self, index):
# (1,48) * (48,1)=1
v = float(np.multiply(self.alpha, self.yMat).T * self.K[:, index] + self.b)
return round(v, 5)
def updateEi_catch(self):
# alpha变动的时候更新
for i in range(self.rows):
v = self.cal_Ei(i)
self.EiCatch[i] = v
return True
def check_alpha2_vaild(self, alpha1_index, alpha2_index, Ei_list):
# 计算更新量是否足够
if alpha1_index == alpha2_index:
return False
alpha2_new_chiped = self.get_alpha2_new_chiped(alpha1_index, alpha2_index, Ei_list)
alpha2_old = self.alpha[alpha2_index, 0]
if None == alpha2_new_chiped:
return False
else:
if abs(alpha2_new_chiped - alpha2_old) > self.fpe:
return True
else:
return False
def get_alpha2_new_chiped(self, alpha1_index, alpha2_index):
alpha2_old = self.alpha[alpha2_index, 0]
y2 = self.yMat[alpha2_index, 0]
E1 = self.EiCatch[alpha1_index]
E2 = self.EiCatch[alpha2_index]
eta = self.K[alpha1_index, alpha1_index] + self.K[alpha2_index, alpha2_index] - 2.0 * self.K[
alpha1_index, alpha2_index]
if eta == 0:
return None
try:
alpha2_new_unc = alpha2_old + (y2 * (E1 - E2) / eta)
alpha2_new_chiped = self.get_alpha2_chiped(alpha2_new_unc, alpha1_index, alpha2_index)
except:
print()
return alpha2_new_chiped
def get_alpha2_chiped(self, alpha2_new_unc, alpha1_index, alpha2_index):
y1 = self.yMat[alpha1_index, 0]
y2 = self.yMat[alpha2_index, 0]
alpha1 = self.alpha[alpha1_index, 0]
alpha2 = self.alpha[alpha2_index, 0]
if self.C is None:
# hard margin
if y1 == y2:
H = alpha1 + alpha2
L = 0
else:
H = None
L = max(0, alpha2 - alpha1)
else:
# soft margin
if y1 == y2:
H = min(self.C, alpha1 + alpha2)
L = max(0, alpha1 + alpha2 - self.C)
else:
H = min(self.C, self.C - alpha1 + alpha2)
L = max(0, alpha2 - alpha1)
alpha2_new_chiped = None
if alpha2_new_unc < L:
alpha2_new_chiped = L
else:
if H is None:
alpha2_new_chiped = alpha2_new_unc
else:
if alpha2_new_unc > H:
alpha2_new_chiped = H
else:
alpha2_new_chiped = alpha2_new_unc
return alpha2_new_chiped
def classifyDataAndPlot(self):
# 把支持向量取出来
sv_array = []
for i in range(self.rows):
if 0 < self.alpha[i] < self.C:
sv_array.append(i)
print("共有支持向量数量:", len(sv_array))
# 把点区分为四种,正负例并区分是否是支持向量
sv_positive_list = []
sv_negtive_list = []
no_sv_negtive_list = []
no_sv_positive_list = []
for i in range(self.rows):
yi = self.yMat[i, 0]
if i in sv_array:
if yi == 1:
sv_positive_list.append(i)
else:
sv_negtive_list.append(i)
else:
if yi == 1:
no_sv_positive_list.append(i)
else:
no_sv_negtive_list.append(i)
# 画点
sv_p_x, sv_p_y = getDataArray(sv_positive_list, self.xMat)
sv_n_x, sv_n_y = getDataArray(sv_negtive_list, self.xMat)
nosv_p_x, nosv_p_y = getDataArray(no_sv_positive_list, self.xMat)
nosv_n_x, nosv_n_y = getDataArray(no_sv_negtive_list, self.xMat)
plt.scatter(sv_p_x, sv_p_y, s=20, marker="+", c="r")
plt.scatter(sv_n_x, sv_n_y, s=20, marker="*", c="blue")
plt.scatter(nosv_p_x, nosv_p_y, s=20, marker="+", c="orange")
plt.scatter(nosv_n_x, nosv_n_y, s=20, marker="*", c="g")
# 画线
# w0=self.w[0,0].flatten
print("w:", self.w)
print("b:", self.b)
# 画 wx+b=0的实线
X1 = np.linspace(-2, 3, 2).reshape(2, 1)
X2_0 = (0 - self.b - self.w[0, 0] * X1) / self.w[0, 1]
plt.plot(X1, X2_0, color='red', linewidth=0.5, linestyle="-")
# 画wx+b=+1和wx+b=-1的虚线
X2_positive = (1 - self.b - self.w[0, 0] * X1) / self.w[0, 1]
X2_negtive = (-1 - self.b - self.w[0, 0] * X1) / self.w[0, 1]
plt.plot(X1, X2_positive, color='red', linewidth=0.5, linestyle="--")
plt.plot(X1, X2_negtive, color='red', linewidth=0.5, linestyle="--")
# sklearn,数据是跑sklearn出来的 用这个方法 runWithSkleran
sk = [-0.93105886, 0.82281036]
skLearnW = np.array(sk)
skLearnB = -5.39363898
X2_sklearn = (0 - skLearnB - skLearnW[0] * X1) / skLearnW[1]
plt.plot(X1, X2_sklearn, color='blue', linewidth=0.5, linestyle="-")
# # 在我的 notebook 里,要设置下面两行才能显示中文
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['sans-serif']
# 如果是在 PyCharm 里,只要下面一行,上面的一行可以删除
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决保存图像是负号'-'显示为方块的问题
title = "迭代次数:" + str(self.trainCount) + ",支持向量数量:" + str(len(sv_array))
plt.title(title)
plt.show()
def selectJrand(self, i):
j = i
while i == j:
j = int(np.random.uniform(0, self.rows))
return j
def selectAlpha1_index(self, alpha2_index):
# 非零alpha的是sv的几率大
E2 = self.EiCatch[alpha2_index]
nonZeroList = []
for i in range(self.rows):
alpha = self.alpha[i, 0]
if 0 < alpha < self.C:
nonZeroList.append(i)
if len(nonZeroList) == 0:
return self.selectJrand(alpha2_index)
else:
maxDiff = 0
j = -1
for i in range(len(nonZeroList)):
row = nonZeroList[i]
if row == alpha2_index:
continue
else:
E1 = self.EiCatch[row]
if abs(E1 - E2) > maxDiff:
maxDiff = abs(E1 - E2)
j = row
if j == -1:
return self.selectJrand(alpha2_index)
else:
return j
def runWithSkleran(trainX, trainY):
classifier = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')
classifier.fit(trainX, trainY)
value_predict = classifier.predict(trainX)
count = 0
errIndex = []
for i in range(len(value_predict)):
predict = value_predict[i]
if predict == trainY[i]:
count += 1
else:
errIndex.append(i)
print("准确率{:.2%}".format(count / len(trainY)))
print("err:", errIndex)
print('Coefficients:%s, intercept %s' % (classifier.coef_, classifier.intercept_))
print('Score: %.2f' % classifier.score(trainX, trainY))
return classifier.coef_[0], classifier.intercept_[0]
def runMySvm():
xSet, ySet = loadData()
classifier = SVM(xSet, ySet, C=2)
# debug模式每次迭代更新一次图,可以看动画的效果
w, b = classifier.train(100, debug=False)
score = classifier.score(xSet, ySet)
print("正确率:", score)
classifier.classifyDataAndPlot()
def runSklearn():
trainX, trainY = loadData()
w, b = runWithSkleran(trainX, trainY)
print("w", w)
print("b", b)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
runMySvm()
sys.exit()
代码很复杂,我们在开头传入一个data2文件,数据格式如下图
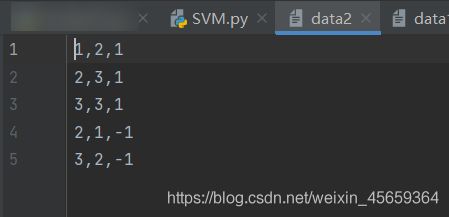
提示,data2文件和代码文件要放在同一级目录下
学习总结:
支持向量机是很麻烦的一种统计方法,计算繁琐,所以可以使用代码来进行计算,相较于朴素贝叶斯、决策树这些算法,个人认为支持向量机很难