SpringMVC 执行流程(深入源码)
SpringMVC 执行流程
- 1. 简介
- 2. 深入源码
-
- 2.1 Debug
- 2.2 doDispatch
-
- 2.2.1 getHandler(processedRequest)
- 2.2.2 getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler())
- 2.2.3 handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
- 2.2.4 applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv)
- 3. 总结
1. 简介
相信SpringMVC处理请求的流程各位滚瓜烂熟了都,如下图所示。

但是如果没有读过代码,还是有很多问题,如Request如何被接收到,ModelAndView是否可以为空,项目中我们通常返回一串json给前端,是怎么处理的?
2. 深入源码
2.1 Debug
/**
* @author wangzhao
* @date 2020/8/12 23:07
*/
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
return "Hello World";
}
}
首先的话,我们打断点,分析其调用栈。
直接进入到service方法,之前的代码并不需要关心。
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
try {
request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
response = (HttpServletResponse)res;
} catch (ClassCastException var6) {
throw new ServletException(lStrings.getString("http.non_http"));
}
this.service(request, response);
}
该方法位于HttpServlet中,这不就和我们一开始用HttpServlet写的代码一样吗,请求直接进入到了HttpServlet#service方法中。
一直向下进行调用,最后到了org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doDispatch。
至此,请求才算正式进入到MVC 请求的处理流程中,相信你也一定知道请求是如何被DispatcherServlet所接受到。
2.2 doDispatch
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
// 获取异步请求管理器
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 是否是上传文件请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 获取请求的handler
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
// 找不到handler报错
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 获取处理器适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 执行前置拦截器
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 执行handler
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 设置视图名称
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 执行后置拦截器,这里面进行了视图的解析
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
2.2.1 getHandler(processedRequest)
获取请求对应的Handler,可以看到,已经成功获取到目标Handler。
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
2.2.2 getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler())
获取Handler对应的适配器。
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler +
"]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler");
}
2.2.3 handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
执行handle,返回ModelAndView。
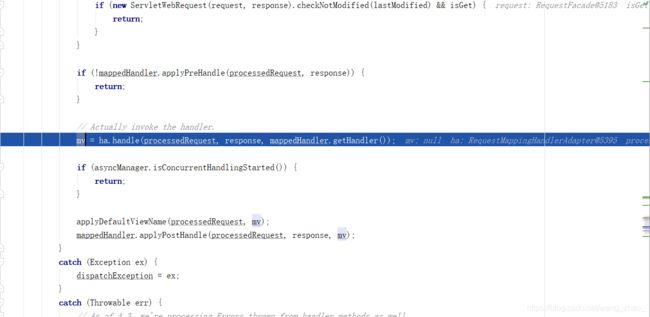
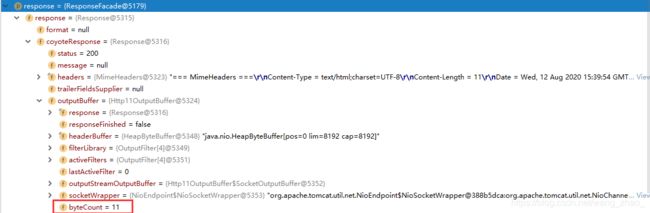
可以看到,返回的ModelAndView是null,这样的逻辑也是符合我们的代码的,我们并没有在sayHello中返回ModelAndView。
那如果我们直接返回json格式的数据,那么该数据哪里去了?答案是已经被封装到了response中,查找了一番没有找到,该对象属性太多,最后只找到了json的长度为11字节,所以可知其也一定被封装到里卖弄。
这一下是不是已经解决了我们开始提问的两个问题?
2.2.4 applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv)
视图解析。
进入该方法后,直接跟踪到如下方法。
// org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter#postHandle
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
@Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
this.requestInterceptor.postHandle(new DispatcherServletWebRequest(request, response),
(modelAndView != null && !modelAndView.wasCleared() ? modelAndView.getModelMap() : null));
}
在这里做的就是将ModelAndView中的数据填充到View中,最后通过Response展示给用户,如下便完成了一个MVC的请求流程。
3. 总结
通过此次代码分析,相信之前很多不懂或模糊的地方可以豁然开朗。
Talk is cheap. Show me the code.