mybatis(三)
一、一对一
1、创建实体类
/**
* 成绩 实体类
*
* 一个成绩 一个学生
*
*
*/
public class Score implements Serializable {
private int scoreid;
private String coursename;
private int score;
private int studentid;
private Student student;
public int getScoreid() {
return scoreid;
}
public void setScoreid(int scoreid) {
this.scoreid = scoreid;
}
public String getCoursename() {
return coursename;
}
public void setCoursename(String coursename) {
this.coursename = coursename;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
public int getStudentid() {
return studentid;
}
public void setStudentid(int studentid) {
this.studentid = studentid;
}
public Student getStudent() {
return student;
}
public void setStudent(Student student) {
this.student = student;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Score{" +
"scoreid=" + scoreid +
", coursename='" + coursename + '\'' +
", score=" + score +
", studentid=" + studentid +
", student=" + student +
'}';
}
}
2、写sql
SELECT a.scoreid,a.coursename,a.score,a.studentid,b.id,b.name,b.age,b.sex,b.height FROM score_tb a LEFT JOIN student_tb b ON a.studentid = b.id
3、创建接口
import java.util.List;
public interface ScoreDao {
/**
* 查询 成绩 并包含学生 信息
* @return
*/
List<Score> findAllScoreWithStudent();
}
4、配置xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.qfedu.dao.ScoreDao">
<!--
<association 表示一对多,将查询结果中 一行中的数据 设置到 对应score 对应中属性 student
property="student" Score 类中的属性
javaType="student" 对应类型student
-->
<resultMap id="scoreMap1" type="score">
<id property="scoreid" column="scoreid"></id>
<result property="coursename" column="coursename"></result>
<result property="score" column="score"></result>
<result property="studentid" column="studentid"></result>
<association property="student" javaType="student">
<id property="id" column="studentid"></id>
<result property="name" column="name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="height" column="height"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAllScoreWithStudent" resultMap="scoreMap1">
SELECT a.scoreid,a.coursename,a.score,a.studentid,b.id,b.name,b.age,b.sex,b.height FROM score_tb a LEFT JOIN student_tb b ON a.studentid = b.id
</select>
</mapper>
5、测试
// 测试 一对一
@Test
public void findAllScoreWithStudentTest(){
List<Score> allScoreWithStudent = scoreDao.findAllScoreWithStudent();
for (Score score : allScoreWithStudent) {
System.out.println("score:"+score);
}
}
总结
- association:为多表一对一的的应映射关系
- javaType:为所用属性的java类型
二、一对一懒加载
/**
* 懒加载查选所有学生
* @param
* @return
*/
List<Student> findStudentByLazy();
<!--
一对多懒加载
column="id" 两张表关联的id
select="com.qfedu.dao.ScoreDao.findAllScoreByStudentId" 调用 更具学生id 查询所有成绩方法
fetchType="lazy" 懒加载
fetchType="eager" 立即加载
-->
<resultMap id="studentMap1" type="Student">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="name" column="name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="height" column="height"></result>
<collection property="scoreList" ofType="Score" column="id" select="com.qfedu.dao.ScoreDao.findAllScoreByStudentId"
fetchType="lazy"
>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudentByLazy" resultMap="studentMap1">
select * from student_tb
</select>
测试:
/**
* 一对一懒加载
*/
@Test
public void findAllScoreWithStudentBylazyTest(){
List<Score> scoreList = scoreDao.findAllScoreWithStudentBylazy();
for (Score score : scoreList) {
// System.out.println("score-name"+score.getCoursename()+"--score:"+score.getScore());
// // 所谓懒加载就是 在需要时再去执行 对应sql
// System.out.println("student:"+score.getStudent());
// 在这里不要直接打印score ************* 因为默认情况下 toString,equals,clone,hashCode, 会触发懒加载
System.out.println("score:"+score);
}
}
三、一对多
一对多:一个学生 有多个成绩
1、创建实体类
2、sql测试
SELECT a.id,a.name,a.age,a.sex,a.height,b.scoreid,b.coursename,b.score,b.studentid FROM student_tb a LEFT JOIN score_tb b ON a.id = b.studentid
3、接口
/**
* 一对多:一个学生多个成绩
* @return
*/
List<Student> findAllStudentWithScore();
4、xml
<!--
一对多
<collection property="scoreList" ofType="Score"> 一对多配置
property="scoreList" 对应 student 中属性 scoreList
ofType="Score" 将数据 转换 Score 放置到 集合 scoreList
-->
<resultMap id="studentWithSocreMap" type="student" >
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="name" column="name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="height" column="height"></result>
<collection property="scoreList" ofType="score">
<id property="scoreid" column="scoreid"></id>
<result property="coursename" column="coursename"></result>
<result property="score" column="score"></result>
<result property="studentid" column="id"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAllStudentWithScore" resultMap="studentWithSocreMap" >
SELECT a.id,a.name,a.age,a.sex,a.height,b.scoreid,b.coursename,b.score,b.studentid FROM student_tb a LEFT JOIN score_tb b ON a.id = b.studentid
</select>
5、测试
/**
* 一对多测试
* 一个学生多个 成绩
*/
@Test
public void studentWithScoreMapTest(){
List<Student> allStudentWithScore = studentDao.findAllStudentWithScore();
for (Student student : allStudentWithScore) {
System.out.println("student:"+student);
}
}
四、一对多懒加载
/**
* 懒加载查选所有学生
* @param
* @return
*/
List<Student> findStudentByLazy();
<!--
一对多懒加载
column="id" 两张表关联的id
select="com.qfedu.dao.ScoreDao.findAllScoreByStudentId" 调用 更具学生id 查询所有成绩方法
fetchType="lazy" 懒加载
fetchType="eager" 立即加载
-->
<resultMap id="studentMap1" type="Student">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="name" column="name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="height" column="height"></result>
<collection property="scoreList" ofType="Score" column="id" select="com.qfedu.dao.ScoreDao.findAllScoreByStudentId"
fetchType="lazy"
>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findStudentByLazy" resultMap="studentMap1">
select * from student_tb
</select>
测试:
/**
* 懒加载查选所有学生
* @param
* @return
*/
List<Student> findStudentByLazy();
注意
默认情况mybatis开延迟加载只要调用toString()方法包括Object的object的都会触发懒加载可以通过设置一下解决
<!--解决 懒加载时 打印对象toString 触发 懒加载
lazyLoadTriggerMethods:指定哪个对象的方法触发一次延迟加载。默认值:equals,clone,hashCode,toString
-->
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="false"/>
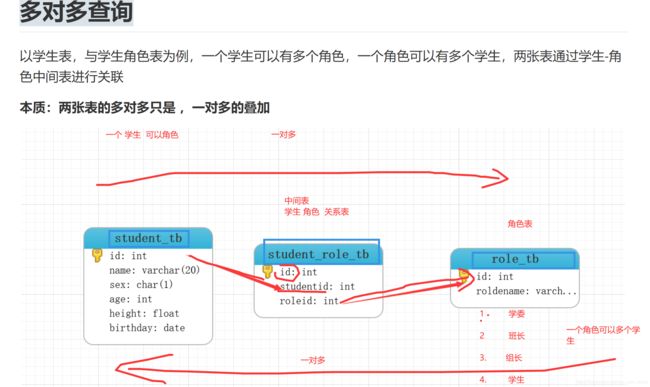
五、多对多
多对多,其实不存在,实际就是两个/多个 一对多
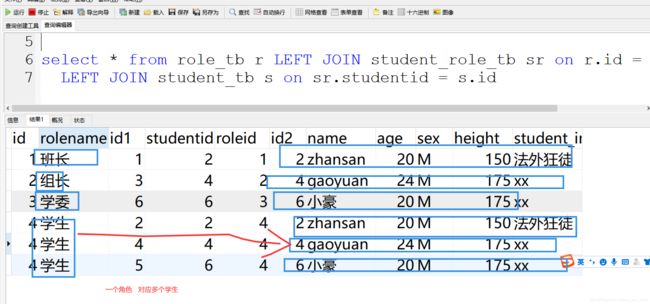
select * from role_tb;
select * from role_tb r LEFT JOIN student_role_tb sr on r.id = sr.roleid;
select * from role_tb r LEFT JOIN student_role_tb sr on r.id = sr.roleid
LEFT JOIN student_tb s on sr.studentid = s.id
public interface RoleDao {
/**
* 查选所有 角色并包含 学生
* @return
*/
List<Role> findAllRoleWithStudent();
int updateRole(Role role);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.qfedu.dao.RoleDao">
<resultMap id="roleMap1" type="role">
<id property="id" column="id"></id>
<result property="rolename" column="rolename"></result>
<collection property="studentList" ofType="Student">
<id property="id" column="studentid"></id>
<result property="name" column="name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="height" column="height"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAllRoleWithStudent" resultMap="roleMap1">
select r.id id,r.rolename rolename,s.name name,s.age age,s.sex sex,s.height height,sr.studentid studentid
from role_tb r LEFT JOIN student_role_tb sr on r.id = sr.roleid
LEFT JOIN student_tb s on sr.studentid = s.id
</select>
<update id="updateRole">
update role_tb set rolename = #{
rolename} where id = #{
id}
</update>
</mapper>
测试:
/**
* 一对多
*/
@Test
public void findAllRoleWithStudentTest(){
List<Role> allRoleWithStudent = roleDao.findAllRoleWithStudent();
for (Role role : allRoleWithStudent) {
System.out.println("role:"+role);
}
}
六、Mybatis 的动态 SQL 语句
if
<!--
<if 如果符合 test="name!=null and name!='' " sql 进行拼接
-->
<select id="findStudentByCondation" resultType="Student">
SELECT * FROM student_tb where 1=1
<if test="name!=null and name!='' ">
and name like #{
name}
</if>
<if test="sex!=null and sex!=''">
and sex = #{
sex}
</if>
</select>
where
<!--
<where> 作用 : 1. 取代 where 1=1 2.自动去除 第一and
-->
<select id="findStudentByCondation" resultType="Student">
SELECT * FROM student_tb
<where>
<if test="name!=null and name!='' ">
and name like #{
name}
</if>
<if test="sex!=null and sex!=''">
and sex = #{
sex}
</if>
</where>
</select>
foreach
SELECT * FROM student_tb WHERE id IN (2,5,7);
<!-- 将公共的sql 抽取出来-->
<sql id="sql1">
select id,name,age,sex,height FROM student_tb
</sql>
<!--
SELECT * FROM student_tb WHERE id IN (2,5,7);
id IN (2,5,7);
<foreach
collection="ids" 获取集合
item="id" 遍历集合中的每一个 并赋值给id
open="id IN (" 设置字符串头
close=")" 设置sql拼接 尾
separator="," 以, 进行分割
-->
<!--
<include <include refid="sql1"></include> 将公共的sql 包含进来
-->
<select id="findStudentByIds" resultType="Student">
<include refid="sql1"></include>
<where>
<if test="ids!=null and ids.size()>0">
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="id IN (" close=")" separator=",">
#{
id}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
sql
声明公共的sql
< include refid=“sql1”> 引用sql
<!-- 将公共的sql 抽取出来 声明-->
<sql id="sql1">
select id,name,age,sex,height FROM student_tb
</sql>
<!--
SELECT * FROM student_tb WHERE id IN (2,5,7);
id IN (2,5,7);
<foreach
collection="ids" 获取集合
item="id" 遍历集合中的每一个 并赋值给id
open="id IN (" 设置字符串头
close=")" 设置sql拼接 尾
separator="," 以, 进行分割
-->
<!--
<include <include refid="sql1"></include> 将公共的sql 包含进来
-->
<select id="findStudentByIds" resultType="Student">
<include refid="sql1"></include>
<where>
<if test="ids!=null and ids.size()>0">
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" open="id IN (" close=")" separator=",">
#{
id}
</foreach>
</if>
</where>
</select>
测试:
@Test
public void findStudentByIdsTest(){
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ids.add(2);
ids.add(5);
ids.add(7);
QuestData questData = new QuestData();
questData.setIds(ids);
// mybatis 无法直接使用集合
List<Student> studentList = studentDao.findStudentByIds(questData);
for (Student student : studentList) {
System.out.println("student:"+student);
}
}
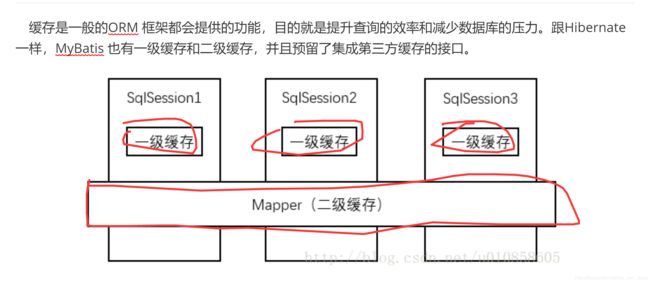
七、mybatis 一级二级缓存
缓存:比如执行select * from student 第一次,sqlsesion 没有缓存,去数据库找,缓存起来,第二次执行select * from student 直接去缓存找
好处:1.查询效率高(快)2.降低mysql服务器请求查询压力
mybatis 一级二级缓存
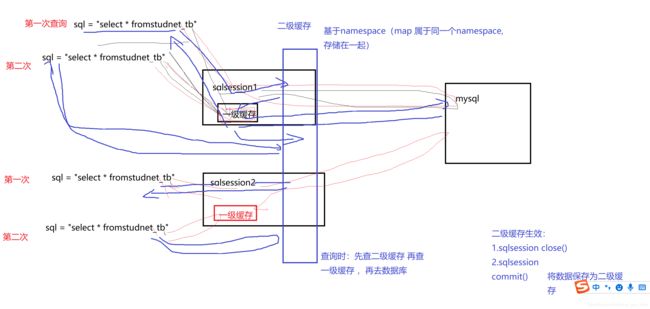
一级缓存就是基于sqlsesion 的缓存
二级缓存基于namespace的缓存,二级缓存是 多个 sqlsesion 共享的
一级缓存
一级缓存是 SqlSession 级别的缓存,只要 SqlSession 没有 flush 或 close,它就存在。一旦发生增删改,缓存立即失效
/**
* 一级缓存测试
*/
@Test
public void firstCacheTest(){
Student student1 = studentDao.findStudentById(2);
System.out.println("student1:"+student1);
// 清空sqlSession 缓存,一级缓存失效
// sqlSession.clearCache();
student1.setName("张三");
//只要发生 增删改 就会清空 缓存
studentDao.updateStudent(student1);
sqlSession.commit();
// 因为 两条查询同一 sql select * from student_tb where id = 2
// studentDao 对应的sqlSession 会进行缓存
Student student2 = studentDao.findStudentById(2);
System.out.println("student2:"+student2);
}
二级缓存
1、开启缓存开关
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
<!-- 开启全局懒加载-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
<!--开启二级缓存-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
2、在对应的Dao.xml中开启缓存
<!--
<cache> 开启二级缓存
eviction="LRU" 缓存是有大小限制,超过大小要 清除一些缓存
- LRU - 最近最少回收,移除最长时间不被使用的对象
- FIFO - 先进先出,按照缓存进入的顺序来移除它们
- SOFT - 软引用,移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象
- WEAK - 弱引用,更积极的移除基于垃圾收集器和弱引用规则的对象
size="1024" 缓存 最多 1024 条数 sql 对应的数据
flushInterval="60000" 60s 缓存 刷新一次
readOnly="true" 是否只读 不能获取缓存中对象 的引用,不能直接修改缓存对象
false 能获取缓存中对象 的引用,能直接修改缓存对象
blocking="true" 在读取缓存时是否阻塞
-->
<cache eviction="LRU" size="1024" flushInterval="60000" readOnly="true" blocking="true" >
</cache>
3、使用缓存
<!--
在查选标签中配置 useCache="true" 使用缓存
默认值就是true 使用缓存
-->
<select id="findStudentById" resultType="Student" useCache="true">
select * from student_tb where id = #{
id}
</select>
4、测试
@Test
public void secondCacheTest(){
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Student student1_a = studentDao1.findStudentById(2);
System.out.println("student1_a:"+student1_a);
// 将查选结果提交到二级缓存
sqlSession1.commit();
Student student1_b = studentDao1.findStudentById(2);
System.out.println("student1_b:"+student1_b);
// 使用另一个sqlSession2 查选
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
// 去二级缓存取
Student student2_a = studentDao2.findStudentById(2);
System.out.println("student2_a:"+student2_a);
}
八、脏数据问题
/**
* 一级缓存 二级缓存同时 存在有可能引入脏数据问题
*/
@Test
public void secondCacheTest2(){
SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
Student student1_a = studentDao1.findStudentById(2);
System.out.println("student1_a:"+student1_a);
// 将查选结果提交到二级缓存
sqlSession1.commit();
// 使用另一个sqlSession2 查选
SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
StudentDao studentDao2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
// 去二级缓存取
Student student2_a = studentDao2.findStudentById(2);
System.out.println("student2_a:"+student2_a);
student2_a.setName("老张");
// 执行增删改 清空对应sqlSession2一级换窜 还有对应namespace的二级缓存
studentDao2.updateStudent(student2_a);
sqlSession2.commit();
// sqlSession1 一级缓存存在,二级缓存 不存在在
// 先去二级缓存获取,没有取一级
Student student1_b = studentDao1.findStudentById(2);
System.out.println("student1_b:"+student1_b);
}
解决方案
第一种:不使用一级缓存
第二种:在spring中使用 mybatis ,每次调用mapper 对应的方法,都会使用新的 sqlSession
九、mybatis基于注解的开发
public interface StudentDao2 {
//增
@Insert("insert into student_tb (name,age,sex,height) values(#{name},#{age},#{sex},#{height})")
int addStudent(Student student);
//删
@Delete("delete from student_tb where id = #{id}")
int deleteStudent(int id);
//更新
@Update("update student_tb set name = #{name},age = #{age},sex=#{sex},height=#{height} where id = #{id}")
int updateStudent(Student student);
//查
@Select("select * from student_tb where id = #{id}")
Student findStudentById(int id);
}