昨天写完了Android触摸事件(下)——事件的分发,写完后以为这一部分终将告一段落了。今早无意间突然想起,好像关于点击事件、长按事件这一部分并没有分析啊!!垂死病中惊坐起,粗略的看了下源码,好像没啥东西啊。仔细看看吧,发现有些地方真的是叫人头疼。没办法,仔细看吧看吧。正是:
码中自有颜如玉,码中自有黄金屋。
onTouchEvent会迟到,有时也会缺席
Android触摸事件(下)——事件的分发中写过:
- 如果设置了OnTouchListener,那么在执行过程中会先执行OnTouchListener的onTouch方法,接着根据返回值来确定是否需要执行onTouchEvent方法。
- onTouchEvent是否需要调用是和result的值有关:如果result为true,则不调用;反之,则调用。
所以说:onTouchEvent会迟到,有时也会缺席。不过缺席的时候并不是我们关心的,我们需要看下正常流程中onTouchEvent到底做了什么:
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
final float x = event.getX();
final float y = event.getY();
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
final int action = event.getAction();
// 判断是否可以点击
final boolean clickable = ((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE
|| (viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE)
|| (viewFlags & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) == CONTEXT_CLICKABLE;
// View是否不可用:如果不可用,返回值是是否可点击
// 注释:不可用的但是可点击的View仍然可以接收触摸事件,仅仅是不响应他们
if ((viewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == DISABLED) {
if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0) {
setPressed(false);
}
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN;
// A disabled view that is clickable still consumes the touch
// events, it just doesn't respond to them.
return clickable;
}
if (mTouchDelegate != null) {
if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
// 可点击或者有标志位TOOLTIP
if (clickable || (viewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
switch (action) {
// 抬起时进行的操作,这里面有点击事件的调用
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN;
if ((viewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
handleTooltipUp();
}
// 如果不可点击,则需要把callBack移除
if (!clickable) {
removeTapCallback();
removeLongPressCallback();
mInContextButtonPress = false;
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
}
// 这里Prepressed也用于识别快速按下
boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;
// 如果按下或者快速按下
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {
// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in
// touch mode.
// 如果我们没有获得焦点,那么我们要根据触摸模式来判断是否可以获得焦点
// 这里问题比较多,后面会说
boolean focusTaken = false;
if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
focusTaken = requestFocus();
}
if (prepressed) {
// The button is being released before we actually
// showed it as pressed. Make it show the pressed
// state now (before scheduling the click) to ensure
// the user sees it.
// 按下按钮之前,我们已经释放按钮。 现在显示按下的状态(调度点击之前),以确保用户看到它。
setPressed(true, x, y);
}
// 如果没有执行长按事件并且不忽略下次抬起事件
if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent) {
// This is a tap, so remove the longpress check
// 这是点击事件,所以需要移除掉长按事件的检查
removeLongPressCallback();
// Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state
// 如果当前View已经获得焦点或者触摸模式为false
if (!focusTaken) {
// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
// performClick directly. This lets other visual state
// of the view update before click actions start.
// 通过performClick执行click事件
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClick();
}
}
}
if (mUnsetPressedState == null) {
mUnsetPressedState = new UnsetPressedState();
}
if (prepressed) {
postDelayed(mUnsetPressedState,
ViewConfiguration.getPressedStateDuration());
} else if (!post(mUnsetPressedState)) {
// If the post failed, unpress right now
mUnsetPressedState.run();
}
removeTapCallback();
}
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if (event.getSource() == InputDevice.SOURCE_TOUCHSCREEN) {
mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN;
}
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
// 如果不可点击,那么检查长按事件
if (!clickable) {
checkForLongClick(0, x, y);
break;
}
if (performButtonActionOnTouchDown(event)) {
break;
}
// Walk up the hierarchy to determine if we're inside a scrolling container.
boolean isInScrollingContainer = isInScrollingContainer();
// 如果View在正在滚动的容器中,那么延迟发送这条消息
// For views inside a scrolling container, delay the pressed feedback for
// a short period in case this is a scroll.
if (isInScrollingContainer) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PREPRESSED;
if (mPendingCheckForTap == null) {
mPendingCheckForTap = new CheckForTap();
}
mPendingCheckForTap.x = event.getX();
mPendingCheckForTap.y = event.getY();
postDelayed(mPendingCheckForTap, ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout());
} else {
// Not inside a scrolling container, so show the feedback right away
// 不在正在滚动的容器中,直接设置按下,并检查长按事件
setPressed(true, x, y);
checkForLongClick(0, x, y);
}
break;
// 取消,移除callBack
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
if (clickable) {
setPressed(false);
}
removeTapCallback();
removeLongPressCallback();
mInContextButtonPress = false;
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN;
break;
// 移动
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
if (clickable) {
drawableHotspotChanged(x, y);
}
// Be lenient about moving outside of buttons
if (!pointInView(x, y, mTouchSlop)) {
// Outside button
// Remove any future long press/tap checks
removeTapCallback();
removeLongPressCallback();
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0) {
setPressed(false);
}
mPrivateFlags3 &= ~PFLAG3_FINGER_DOWN;
}
break;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
上面的代码去除注释,去除移动和取消动作,真正的代码并不多:
- 判断View是否不可用:如果不可用,那么onTouchEvent返回值是否可点击(clickable )
- 如果View可以点击或者有TOOLTIP标志位的话,则进行对事件的不同动作的处理。
ACTION_DOWN:主要包括了setPressed和checkForLongClick两个操作:
-
setPressed用于设置按下状态,此时PFLAG_PRESSED标志位被设置。 -
checkForLongClick用于检查LongClick是否可以触发,以及发送延迟消息来响应长按事件。
private void checkForLongClick(int delayOffset, float x, float y) {
// 如果可以长按
if ((mViewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE) {
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
if (mPendingCheckForLongPress == null) {
mPendingCheckForLongPress = new CheckForLongPress();
}
mPendingCheckForLongPress.setAnchor(x, y);
mPendingCheckForLongPress.rememberWindowAttachCount();
// 延迟执行CheckForLongPress操作,时间默认值 DEFAULT_LONG_PRESS_TIMEOUT = 500ms
postDelayed(mPendingCheckForLongPress,
ViewConfiguration.getLongPressTimeout() - delayOffset);
}
}
private final class CheckForLongPress implements Runnable {
private int mOriginalWindowAttachCount;
private float mX;
private float mY;
@Override
public void run() {
if (isPressed() && (mParent != null)
&& mOriginalWindowAttachCount == mWindowAttachCount) {
// 如果长按事件返回值true,那么设置mHasPerformedLongPress为true
// 表示已经执行了长按事件,并且返回值为true
if (performLongClick(mX, mY)) {
mHasPerformedLongPress = true;
}
}
}
public void setAnchor(float x, float y) {
mX = x;
mY = y;
}
public void rememberWindowAttachCount() {
mOriginalWindowAttachCount = mWindowAttachCount;
}
}
// 执行长按事件
public boolean performLongClick(float x, float y) {
mLongClickX = x;
mLongClickY = y;
// 调用performLongClick()方法
final boolean handled = performLongClick();
mLongClickX = Float.NaN;
mLongClickY = Float.NaN;
return handled;
}
public boolean performLongClick() {
// 继续调用
return performLongClickInternal(mLongClickX, mLongClickY);
}
// 真正执行长按方法
private boolean performLongClickInternal(float x, float y) {
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_LONG_CLICKED);
boolean handled = false;
// ListenerInfo中mOnLongClickListener属性是否不为空,不为空则执行onLongClick操作,并将返回值赋给handled
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnLongClickListener != null) {
handled = li.mOnLongClickListener.onLongClick(View.this);
}
if (!handled) {
final boolean isAnchored = !Float.isNaN(x) && !Float.isNaN(y);
handled = isAnchored ? showContextMenu(x, y) : showContextMenu();
}
if (handled) {
performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.LONG_PRESS);
}
return handled;
}
执行长按过程如下:
- 判断是否可以长按,可以的话进行下面操作。这里如果先设置不可长按又设置
OnLongClickListener的话,此时长按事件仍有效。但是,如果顺序颠倒下的话,就长按事件就无效了。 - 如果可以长按,那么通过
Handler将CheckForLongPress延迟发送,时间是时间默认值DEFAULT_LONG_PRESS_TIMEOUT = 500ms。 -
CheckForLongPress在其run方法中会根据performLongClick方法的返回值来设置mHasPerformedLongPress变量的值,这个变量的值在后面会用到,这里先不说。 - 接着会一路调用最终从
ListenerInfo中获得OnLongClickListener,如果不为null,则执行其onLongClick方法。
ACTION_UP:
- 不可点击,则需要把callBack移除
- 可以点击的话,通过是否可以点击(
clickable)、长按事件的返回值(mHasPerformedLongPress)、是否忽略下次抬起(mIgnoreNextUpEvent)以及焦点是否拿到(focusTaken)这四个值来判断可否执行click事件。一般来说,大部分博客都会直接分析performClick过程,很少会提到为什么这个条件会成立。我这边深究一下,看下到底为什么能够执行performClick操作:
2.1.prepressed的值(mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0,这个可以在ACTION_DOWN中可以看到赋值,但赋值的情况是在正在滚动的容器中。
2.2(mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED)此处PFLAG_PRESSED赋值同样也是在ACTION_DOWN中赋值,与prepressed相反,此时View不在正在滚动的容器中。
2.3focusTaken的值,这个值涉及的东西有点多。首先判断条件isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused():isFocusable()一般为true;isFocusableInTouchMode()如果不设置setFocusableInTouchMode(true)的话,默认为false;isFocused()这个值需要注意下,此值意思是是否拥有焦点,但是我们可以看到判断条件为!isFocused(),所以如果前面条件都为true的情况下,若此时isFocused()返回true,那么将不会再次请求焦点,因为此时已经拥有焦点,否则,则会调用requestFocus获取焦点,并将返回值赋给focusTaken。
还是来看下这边的代码吧,挺重要的:
private boolean requestFocusNoSearch(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
// need to be focusable
if ((mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE) != FOCUSABLE
|| (mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != VISIBLE) {
return false;
}
// need to be focusable in touch mode if in touch mode
if (isInTouchMode() &&
(FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE != (mViewFlags & FOCUSABLE_IN_TOUCH_MODE))) {
return false;
}
// need to not have any parents blocking us
if (hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus()) {
return false;
}
handleFocusGainInternal(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
return true;
}
private boolean hasAncestorThatBlocksDescendantFocus() {
final boolean focusableInTouchMode = isFocusableInTouchMode();
ViewParent ancestor = mParent;
// 查找View的父View,看其是否有FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS标志位
// 这里出现一个常用的变量FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS,这里是关于焦点设置,后面有代码分析
while (ancestor instanceof ViewGroup) {
final ViewGroup vgAncestor = (ViewGroup) ancestor;
if (vgAncestor.getDescendantFocusability() == ViewGroup.FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS
|| (!focusableInTouchMode && vgAncestor.shouldBlockFocusForTouchscreen())) {
return true;
} else {
ancestor = vgAncestor.getParent();
}
}
return false;
}
void handleFocusGainInternal(@FocusRealDirection int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
// 如果没有获取到焦点,则设置获取焦点
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FOCUSED) == 0) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FOCUSED;
View oldFocus = (mAttachInfo != null) ? getRootView().findFocus() : null;
if (mParent != null) {
mParent.requestChildFocus(this, this);
updateFocusedInCluster(oldFocus, direction);
}
if (mAttachInfo != null) {
mAttachInfo.mTreeObserver.dispatchOnGlobalFocusChange(oldFocus, this);
}
onFocusChanged(true, direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
refreshDrawableState();
}
}
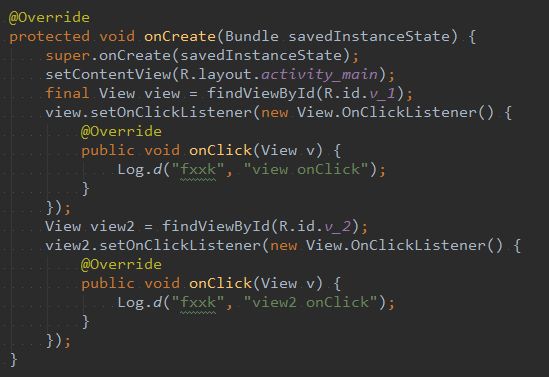
上面的代码很容易理解,为什么需要单独看一下呢?首先来说,如果去请求获取焦点的话,真正获取成功后此时返回值为true,那么根据后面的判断条件是不会执行performClick操作的。这里可以假设有如下代码:
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
......
View view2 = findViewById(R.id.v_2);
view2.setFocusable(true);
view2.setFocusableInTouchMode(true);
view2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Log.d("fxxk", "view2 onClick");
}
});
......
}
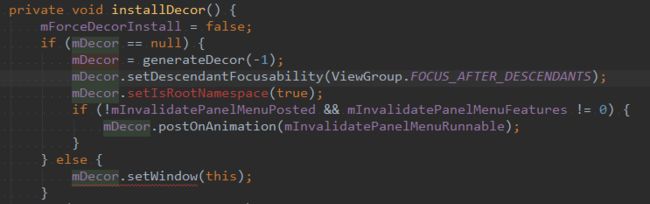
那么按照上面的分析此时第一次点击的时候应该会去请求焦点的,此时点击事件不会生效。但,真的会这样吗?不会的,最初我以为也是这样,但是经过测试发现:View在设置成可见(VISIBLE)是,会调用mParent.focusableViewAvailable(this);方法。在之前从源码分析Activity启动时的生命周期有源码decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE),之后会调用Activity.makeVisible()将mDecor.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);,这时候我们看下setVisibility方法:
@RemotableViewMethod
public void setVisibility(@Visibility int visibility) {
setFlags(visibility, VISIBILITY_MASK);
}
void setFlags(int flags, int mask) {
final boolean accessibilityEnabled =
AccessibilityManager.getInstance(mContext).isEnabled();
final boolean oldIncludeForAccessibility = accessibilityEnabled && includeForAccessibility();
int old = mViewFlags;
mViewFlags = (mViewFlags & ~mask) | (flags & mask);
int changed = mViewFlags ^ old;
if (changed == 0) {
return;
}
......
final int newVisibility = flags & VISIBILITY_MASK;
// 如果新的状态是VISIBLE
if (newVisibility == VISIBLE) {
// 如果有改变
if ((changed & VISIBILITY_MASK) != 0) {
/*
* If this view is becoming visible, invalidate it in case it changed while
* it was not visible. Marking it drawn ensures that the invalidation will
* go through.
*/
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN;
invalidate(true);
needGlobalAttributesUpdate(true);
// a view becoming visible is worth notifying the parent
// about in case nothing has focus. even if this specific view
// isn't focusable, it may contain something that is, so let
// the root view try to give this focus if nothing else does.
// 这里的DecorView的Parent是ViewRootImpl
if ((mParent != null)) {
// ViewRootImpl的方法
mParent.focusableViewAvailable(this);
}
}
}
......
}
这里偷懒了,把无关代码省去了,我们可以看到如果设置的状态和以前不一致的话需要重新根据状态执行不同过程。我们这里设置的是可见,所以会执行mParent.focusableViewAvailable(this);方法:
ViewRootImpl.java:
@Override
public void focusableViewAvailable(View v) {
checkThread();
if (mView != null) {
// mView是我们的DecorView,我们并没有设置其获取焦点
if (!mView.hasFocus()) {
if (sAlwaysAssignFocus) {
// 调用DecorView的requestFocus方法
v.requestFocus();
}
} else {
// the one case where will transfer focus away from the current one
// is if the current view is a view group that prefers to give focus
// to its children first AND the view is a descendant of it.
View focused = mView.findFocus();
if (focused instanceof ViewGroup) {
ViewGroup group = (ViewGroup) focused;
if (group.getDescendantFocusability() == ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS
&& isViewDescendantOf(v, focused)) {
v.requestFocus();
}
}
}
}
}
requestFocus会调用requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect)方法,在ViewGroup中重写,这里着重看下。
ViewGroup.java:
@Override
public boolean requestFocus(int direction, Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
int descendantFocusability = getDescendantFocusability();
switch (descendantFocusability) {
case FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS:
// 直接去调用View的requestFocus,不管子View
return super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
case FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS: {
// 先于子View请求获取焦点,如果自身获取焦点成功,子View不会请求获取焦点
final boolean took = super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
return took ? took : onRequestFocusInDescendants(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
}
case FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS: {
// 先让子View请求获取焦点,如果子View获取焦点成功,那么父View不会请求获取焦点
final boolean took = onRequestFocusInDescendants(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
return took ? took : super.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect);
}
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("descendant focusability must be "
+ "one of FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS, FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS, FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS "
+ "but is " + descendantFocusability);
}
}
ViewGroup.java:
protected boolean onRequestFocusInDescendants(int direction,
Rect previouslyFocusedRect) {
int index;
int increment;
int end;
int count = mChildrenCount;
if ((direction & FOCUS_FORWARD) != 0) {
index = 0;
increment = 1;
end = count;
} else {
index = count - 1;
increment = -1;
end = -1;
}
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = index; i != end; i += increment) {
View child = children[i];
// 只对可见的View请求获取焦点,并且一旦有View获取焦点则不会让其他View请求获取焦点
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE) {
if (child.requestFocus(direction, previouslyFocusedRect)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
ViewGroup获取焦点时需要根据descendantFocusability的值来判断,这里descendantFocusability可能出现三个值:
- FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS:父View直接请求获取焦点。
- FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS:父View会优先其子View,请求获取焦点,如果没有获取到焦点,则会让其子View请求获取焦点。
- FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS:与FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS相反,子View会先请求获取焦点,如果获取到焦点,那么父View不会请求获取焦点。
默认情况ViewGroup在初始化的时候设置为FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS,但是DecorView设置为FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS
好了,到这里我们知道为什么刚才的代码可以执行点击事件了。不过,如果改成下面的代码执行结果需要自己试试了:
此时,点击事件执行会出现:View1获取焦点后,点击正常,点击View2,无反应,再次点击事件正常。
我们接着分析继续来:
这次我们知道条件成立后会通过
Handler发送
PerformClick对象,如果发送成功,则执行
PerformClick.run方法,否则执行
performClick()方法(
PerformClick.run也调用了
performClick方法),最终执行
OnClickListener的
onClick方法。
总结
写了这么多,还是来个总结吧:
- 在按下的时候,如果长按事件执行了,并且返回值为false,那么此时点击事件不会执行;反之则会执行点击事件。
- 关于ViewGroup和子View获取焦点的先后顺序,根据
descendantFocusability的值来判断:
FOCUS_BLOCK_DESCENDANTS:父View直接请求获取焦点。
FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS:父View会优先其子View,请求获取焦点,如果没有获取到焦点,则会让其子View请求获取焦点。
FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS:与FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS相反,子View会先请求获取焦点,如果获取到焦点,那么父View不会请求获取焦点。 - 如果同一个页面中,有多个View都可以获得焦点,那么只有当前获取焦点的点击事件可以正常执行,其他View需要先点击一次获取焦点,之后可以正常执行点击事件。
OK,这篇分析到此结束了。如果有问题,请指出(估计也就是自己来发现问题吧)。
这里多说几句:之前,我觉得许多博客分析的真的是头头是道,当轮到我去分析某些东西的时候再去看他们的博客却发现:好多东西都说的不明确,太模糊。所以,自己分析的时候尽量把所有过程全部分析完成,争取步骤完整,方便以后自己回顾。
That's all!