安卓navigation系列——入门
-
作者
大家好,我叫小琪;
本人16年毕业于中南林业科技大学软件工程专业,毕业后在教育行业做安卓开发,后来于19年10月加入37手游安卓团队;
目前主要负责国内发行安卓相关开发,同时兼顾内部几款App开发。
目录
-
navigation——入门篇(本章讲解)
-
navigation——进阶篇
-
navigation——实战篇 (敬请期待…)
前言
在日常开发中,越来越多的会使用到一个activity嵌套多个fragment的场景,典型的例子就是app的首页,一般都会由一个activity+多个子tab组成,那对于Fragment的显示、隐藏等我们通常都是通过FragmentManager进行管理,但这种方式很容易造成代码臃肿,难以维护。
而通过Jetpack的导航组件——Navigation,就可以很方便的管理各fragment之间的切换,让开发变得更简单。
组成三要素
Navigation graph
一个包含所有导航相关信息的 XML 资源
NavHostFragment
一种特殊的Fragment,用于承载导航内容的容器
NavController
管理应用导航的对象,实现Fragment之间的跳转等操作
基本使用
引入依赖
implementation 'androidx.navigation:navigation-fragment-ktx:2.3.1' implementation 'androidx.navigation:navigation-ui-ktx:2.3.1'创建导航视图
首先确保AndroidStudio为3.3以上
1.右键res,点击New -> Android Resource Directory
2.在出现的面板第二行Resource type 下拉列表中选择 Navigation,然后点击 OK
3.res目录下会多出一个navigation的资源目录,右键该目录,点击New -> Navigation Resource File,输入需要新建的资源文件名,这里命名nav_graph,点击ok,一个nav_graph.xml就创建好了。
配置graph
新建好的nav_graph.xml切换到design模式下,点击2处的加号,选择Create new destination,即可快速创建新的Fragment,这里分别新建了FragmentA、FragmentB、FragmentC三个fragment
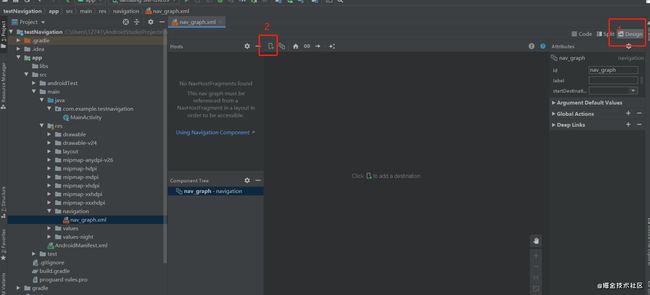
建好后,可通过手动配置页面之间的跳转关系,点击某个页面,右边会出现一个小圆点,拖曳小圆点指向跳转的页面,这里设置跳转的关系为FragmentA -> FragmentB -> FragmentC。
切换到Code栏,可以看到生成了如下代码
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/nav_graph" app:startDestination="@id/fragmentA"> <fragment android:id="@+id/fragmentA" android:name="com.example.testnavigation.FragmentA" android:label="fragment_a" tools:layout="@layout/fragment_a" > <action android:id="@+id/action_fragmentA_to_fragmentB2" app:destination="@id/fragmentB" /> fragment> <fragment android:id="@+id/fragmentB" android:name="com.example.testnavigation.FragmentB" android:label="fragment_b" tools:layout="@layout/fragment_b" > <action android:id="@+id/action_fragmentB_to_fragmentC2" app:destination="@id/fragmentC" /> fragment> <fragment android:id="@+id/fragmentC" android:name="com.example.testnavigation.FragmentC" android:label="fragment_c" tools:layout="@layout/fragment_c" /> navigation>- navigation是根标签,通过startDestination配置默认启动的第一个页面,这里配置的是FragmentA
- fragment标签代表一个fragment,其实这里不仅可以配置fragment,也可以配置activity,甚至还可以自定义(暂不讨论,后续会讲到)
- action标签定义了页面跳转的行为,相当于上图中的每条线,destination定义跳转的目标页,还可以定义跳转时的动画等等
添加NavHostFragment
在MainActivity的布局文件中配置NavHostFragment
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <fragment android:id="@+id/fragment" android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" app:defaultNavHost="true" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" app:navGraph="@navigation/nav_graph" /> androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>- android:name指定NavHostFragment
- app:navGraph指定导航视图,即建好的nav_graph.xml
- app:defaultNavHost=true 意思是可以拦截系统的返回键,可以理解为默认给fragment实现了返回键的功能,这样在fragment的跳转过程中,当我们按返回键时,就可以使得fragment跟activity一样可以回到上一个页面了
现在我们运行程序,就可以正常跑起来了,并且看到了FragmentA展示的页面,这是因为MainActivity的布局文件中配置了NavHostFragment,并且给NavHostFragment指定了导航视图,而导航视图中通过startDestination指定了默认展示FragmentA。
通过NavController 管理fragment之间的跳转
上面说到三个fragment之间的跳转关系是FragmentA -> FragmentB -> FragmentC,并且已经可以展示了FragmentA,那怎么跳转到FragmentB呢,这就需要用到NavController 了
打开FragmentA类,给布局中的TextView定义一个点击事件
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState) tv.setOnClickListener { val navController = Navigation.findNavController(it) navController.navigate(R.id.action_fragmentA_to_fragmentB2) } }如果发现不能自动导入布局文件,大概率是要给app.build添加插件‘kotlin-android-extensions’
apply plugin: 'com.android.application' apply plugin: 'kotlin-android' apply plugin: 'kotlin-android-extensions'AndroidStudio4.1以后改成了
plugins { id 'com.android.application' id 'kotlin-android' id 'kotlin-android-extensions' }可以看到,通过navController管理fragment的跳转非常简单,首先得到navController对象,然后调用它的navigate方法,传入前面nav_graph中定义的action的id即可。
按同样的方法给FragmentB中的TextView也设置一个点击事件,使得点击时跳转到FragmentC
运行程序,FragmentA -> FragmentB -> FragmentC,此时按返回键,也是一个一个页面返回,如果把前面的app:defaultNavHost设置为false,按返回键后会发现直接返回到桌面了,现在能体会到app:defaultNavHost这个属性的含义了吧。
更多用法
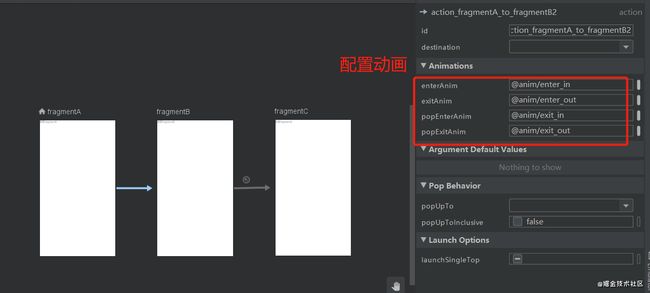
在编辑nav_graph的时候,action属性除了设置目标页外,还可以设置动画、页面间参数传递、fragment回退栈管理等
动画
-
enterAnim: 跳转时的目标页面动画
-
exitAnim: 跳转时的原页面动画
-
popEnterAnim: 回退时的目标页面动画
-
popExitAnim:回退时的原页面动画
配置动画后会发现action多了四个动画相关的属性
<fragment android:id="@+id/fragmentA" android:name="com.example.testnavigation.FragmentA" android:label="fragment_a" tools:layout="@layout/fragment_a" > <action android:id="@+id/action_fragmentA_to_fragmentB2" app:destination="@id/fragmentB" app:enterAnim="@anim/enter_in" app:exitAnim="@anim/enter_out" app:popEnterAnim="@anim/exit_in" app:popExitAnim="@anim/exit_out" /> fragment>参数
上面的例子中介绍fragment之间的跳转,当然也可以支持参数传递。
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState) tv.setOnClickListener { val navController = Navigation.findNavController(it) val bundle = Bundle() bundle.putString("key", "test") navController.navigate(R.id.action_fragmentA_to_fragmentB2, bundle) } }参数传递推荐使用谷歌官方的safeArgs,safe args与传统传参方式相比,好处在于安全的参数类型,并且通过谷歌官方的支持,能很方便的进行参数传值。
在项目的根build.gradle下添加插件
classpath "androidx.navigation:navigation-safe-args-gradle-plugin:2.3.1"buildscript { ext.kotlin_version = "1.3.72" repositories { google() jcenter() } dependencies { classpath "com.android.tools.build:gradle:4.1.1" classpath "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin:$kotlin_version" classpath "androidx.navigation:navigation-safe-args-gradle-plugin:2.3.1" } } allprojects { repositories { google() jcenter() } }然后在app的build.gradle中引用 ‘androidx.navigation.safeargs.kotlin’
apply plugin: 'com.android.application' apply plugin: 'kotlin-android' apply plugin: 'kotlin-android-extensions' apply plugin: 'androidx.navigation.safeargs.kotlin'AS4.1以后:
plugins { id 'com.android.application' id 'kotlin-android' id 'kotlin-android-extensions' id 'androidx.navigation.safeargs.kotlin' }添加完插件后,回到nav_graph,切到design模式,给目标页面添加需要接收的参数,这里需要在FragmentA跳转到FragmentB时传参数,所以给FragmentB设置参数,点击FragmentB,点击右侧面板的Arguments右侧的+,输入参数的key值,指定参数类型和默认值,即可快速添加参数
添加完后,rebuild一下工程,safeArgs会自动生成一些代码,在/build/generated/source/navigation-args目录下可以看到
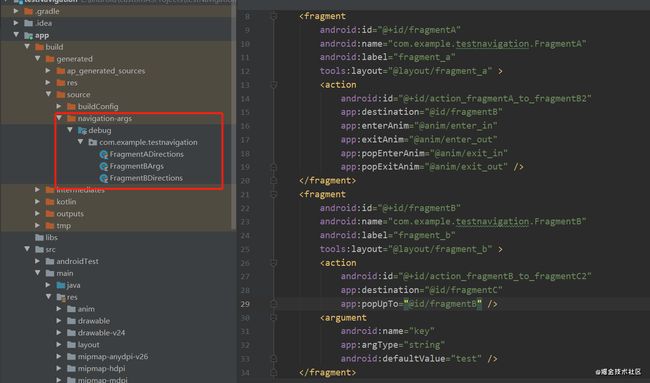
safeArgs会根据nav_graph中的fragment标签生成对应的类,action标签会以“类名+Directions”命名,argument标签会以“类名+Args”命名。
使用safeArgs后,传递参数是这样的
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState) tv.setOnClickListener { val navController = Navigation.findNavController(it) //通过safeArgs传递参数 val navDestination = FragmentADirections.actionFragmentAToFragmentB2("test") navController.navigate(navDestination) // 普通方式传递参数 // val bundle = Bundle() // bundle.putString("key", "test") // navController.navigate(R.id.action_fragmentA_to_fragmentB2, bundle) } }接收参数是这样的
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onViewCreated(view, savedInstanceState) arguments?.let { val value = FragmentBArgs.fromBundle(it).key ....... } ....... }栈管理
点击destination,右侧面板中还可以看到popUpTo、popUpToInclusive、launchSingleTop
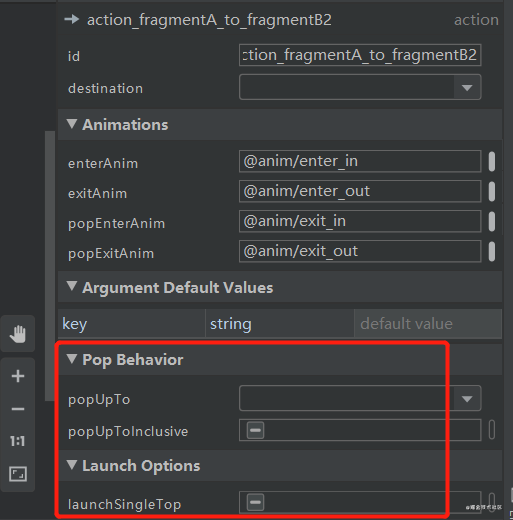
- launchSingleTop:如果栈中已经包含了指定要跳转的界面,那么只会保留一个,不指定则栈中会出现两个界面相同的Fragment数据,可以理解为类似activity的singleTop,即栈顶复用模式,但又有点不一样,比如FragmentA@1 -> FragmentA@2,FragmentA@1会被销毁,但如果是FragmentA@01>FragmentB@02>FragmentA@03,FragmentA@1不会被销毁。
- popUpTo(tag):表示跳转到某个tag,并将tag之上的元素出栈。
- popUpToInclusive:为true表示会弹出tag,false则不会
例子:FragmentA -> FragmentB -> FragmentC -> FragmentA
设置FragmentC -> FragmentA 的action为popUpTo=FragmentA ,popUpToInclusive=false,那么栈内元素变化为
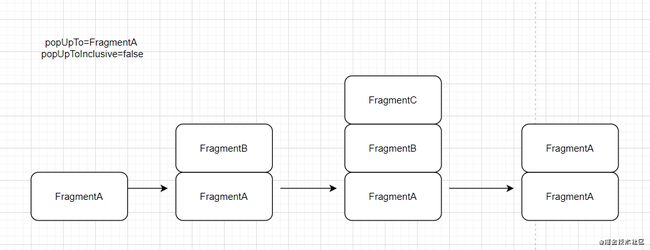
最后会发现需要按两次返回键才会回退到桌面
设置popUpToInclusive=true时,栈内元素变化为

此时只需要按一次返回键就回退到桌面了,从中可以体会到popUpTo和popUpToInclusive的含义了吧。
deeplink
深度链接,就是可以直接跳转到某个页面。navigation创建深度链接可以通过显示和隐式两种方式
按之前的方式新建一个需要通过深度链接打开的目标页面FragmentDeepLink,
接下来为它创建一个deeplink
nav_graph.xml相应的在生成了如下代码
<fragment android:id="@+id/fragmentDeepLink" android:name="com.example.testnavigation.FragmentDeepLink" android:label="fragment_deep_link" tools:layout="@layout/fragment_deep_link"> <argument android:name="key" android:defaultValue="测试" app:argType="string" /> <deepLink android:id="@+id/deepLink" app:uri="www.deeplink.com/{id}" /> fragment>-
显示深度链接
显示深层链接使用PendingIntent来导航到特定页面,比如点击通知栏,快速打开目标页面。
tv_deeplink.setOnClickListener { //显示深度链接 val notificationManager = NotificationManagerCompat.from(requireContext()) if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.O) { val importance = NotificationManager.IMPORTANCE_DEFAULT val channel = NotificationChannel(channelId, channelName, importance) channel.description = "deeplink" notificationManager.createNotificationChannel(channel) } val navController = Navigation.findNavController(it) val deepLinkBuilder = navController.createDeepLink() val bundle = Bundle() bundle.putString("key", "deeplink") val pendingIntent = deepLinkBuilder //传入graph资源文件 .setGraph(R.navigation.nav_graph) //传入参数 .setArguments(bundle) //传入需要通过深度链接打开的目标页面 .setDestination(R.id.fragmentDeepLink) .createPendingIntent() val builder = NotificationCompat.Builder(requireContext(), channelId) .setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher_foreground) .setContentTitle("测试deepLink") .setContentText("哈哈哈") .setContentIntent(pendingIntent) .setAutoCancel(true) .setPriority(NotificationCompat.PRIORITY_DEFAULT) notificationManager.notify(1, builder.build()) } -
隐式深度链接
隐式链接是当用户点击某个链接的时候,通过URI跳转到某个页面,刚刚已经为nav_graph.xml中的FragmentDeepLink添加了
<deepLink app:uri="www.deeplink.com/{id}" />该uri没有声明是http还是https,那么这两个都能匹配。大括号内的是传递的参数。
AndroidManifest.xml中给FragmentDeepLink所属的activity添加一个
<activity android:name=".MainActivity"> ...... <nav-graph android:value="@navigation/nav_graph"/> activity>在build后,通过目录app - > build - > outputs - > apk - > debug - > app-debug.apk查看AndroidManifest.xml中的MainActivity节点下会多出如下代码
<intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" /> <data android:scheme="http" /> <data android:scheme="https" /> <data android:host="www.deeplink.com" /> <data android:pathPrefix="/" /> intent-filter>Navigation 组件会将
我们可以通过adb来测试隐式深层链接的效果,打开命令行输入
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d "http://www.deeplink.com/1"在系统弹出的窗口中,选择自己的应用打开,就能跳转到目标页面了。
总结
本篇是navigation的入门篇,主要介绍了navigation的基本使用,下篇将从源码角度,剖析navigation是如何做到页面之间跳转的。
-