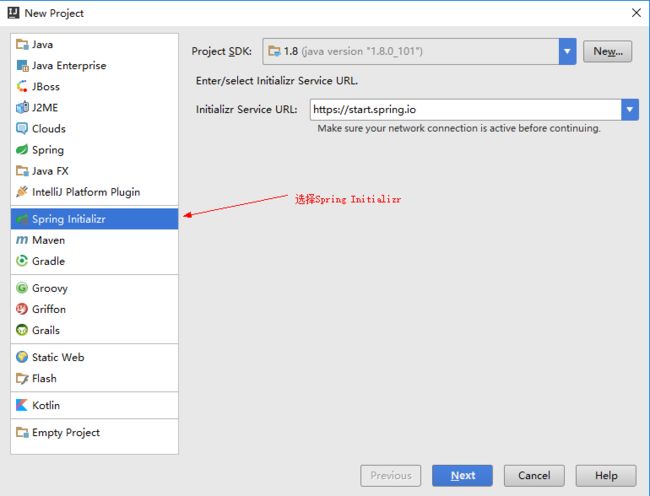
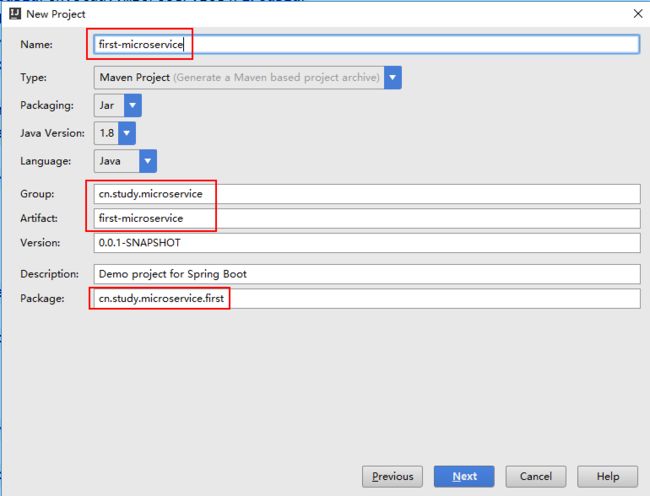
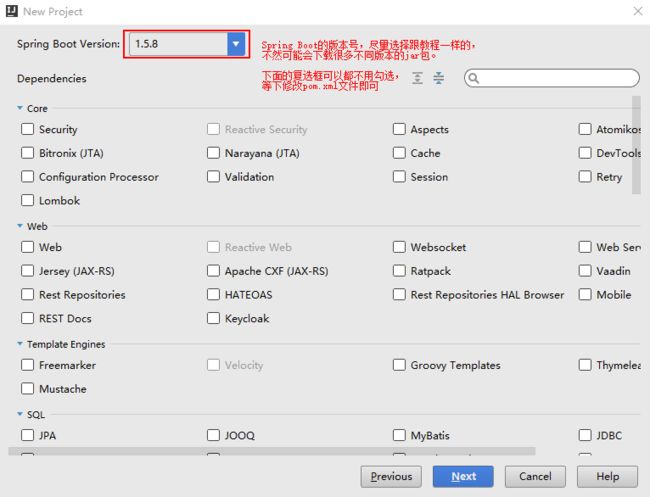
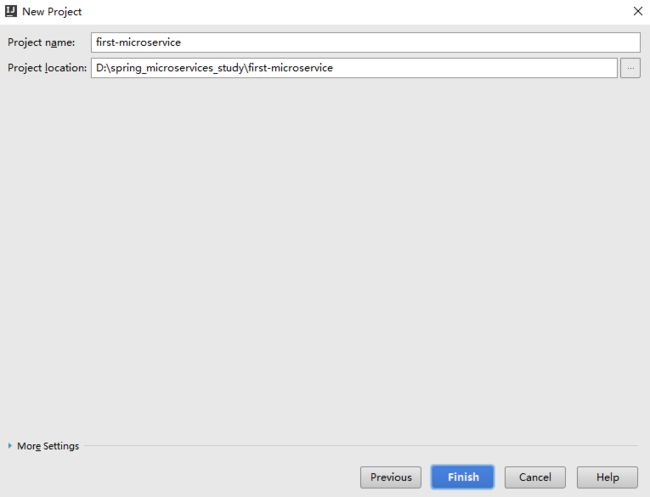
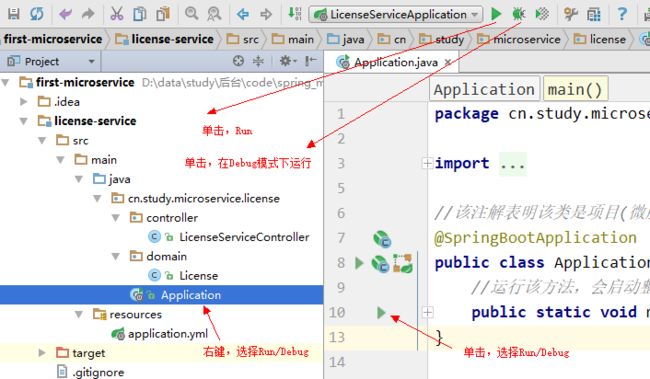
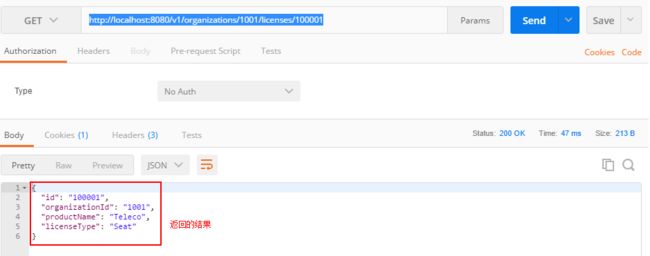
- Eureka vs Zookeeper:谁才是微服务世界的“寻人启事”之王?
码农技术栈
eurekazookeeper微服务架构springcloud
引言:为什么需要“服务发现”?想象一下,你走进一家巨大的购物中心,里面有1000家店铺,但没有任何地图或指示牌。你需要找到一家奶茶店,却只能挨家挨户敲门问路——这就是没有服务发现的微服务世界。服务发现(ServiceDiscovery)就像购物中心的智能导航系统:它能自动告诉你奶茶店的位置、哪家正在营业,甚至哪家人最少。而Eureka和Zookeeper就是两套不同的“导航系统”,但它们的底层逻辑
- Eureka、Zookeeper、Nacos 三国杀:谁才是微服务“全家桶”的终极答案?
码农技术栈
eurekazookeeper微服务springcloudspringboot后端
引言:微服务世界的“三大护法”如果你在微服务领域摸爬滚打过,一定听过这三个名字:Eureka、Zookeeper、Nacos。它们看似都解决了“服务发现”问题,但背后的定位天差地别——Eureka是Netflix的“退休老干部”(已停更),主打高可用;Zookeeper是Apache的“强迫症管家”,专注强一致性;Nacos是阿里的“全能新秀”,号称“服务发现+配置管理”二合一。到底怎么选?我们通
- Apache Lucene 详解及示例
微笑听雨。
java进阶教程apachelucenejava全文检索
ApacheLucene详解及示例1.简介ApacheLucene是一个开源的高性能全文搜索引擎库,广泛应用于构建各种搜索系统和信息检索应用。Lucene提供了丰富的API来进行索引和搜索,支持高效的文本处理和查询。本文将深入解析Lucene的核心概念和主要功能,并通过示例代码演示其使用方法。2.核心概念2.1倒排索引倒排索引(InvertedIndex)是Lucene的核心数据结构。它将文档中的
- Spring 核心技术解析【纯干货版】- XII:Spring 数据访问模块 Spring-R2dbc 模块精讲
m0_74825003
面试学习路线阿里巴巴springjava后端
在现代应用架构中,高并发、低延迟的需求推动了响应式编程的发展,而传统的JDBC由于其同步阻塞机制,在高吞吐场景下可能成为瓶颈。R2DBC(ReactiveRelationalDatabaseConnectivity)作为响应式关系型数据库访问标准,正是为了解决这一问题而诞生的。SpringR2DBC作为Spring生态对R2DBC的封装,提供了非阻塞、异步的数据库访问能力,并与SpringWebF
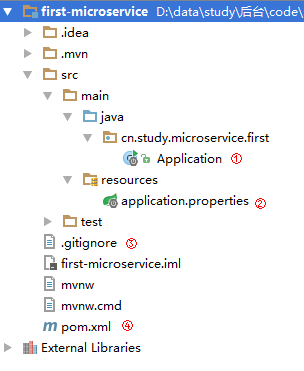
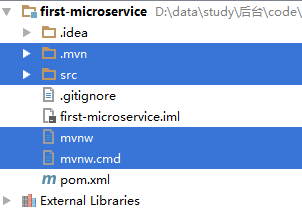
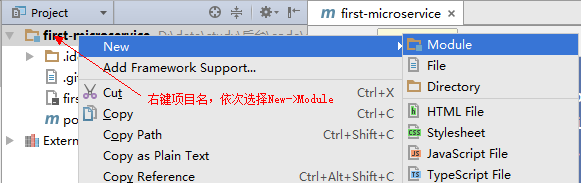
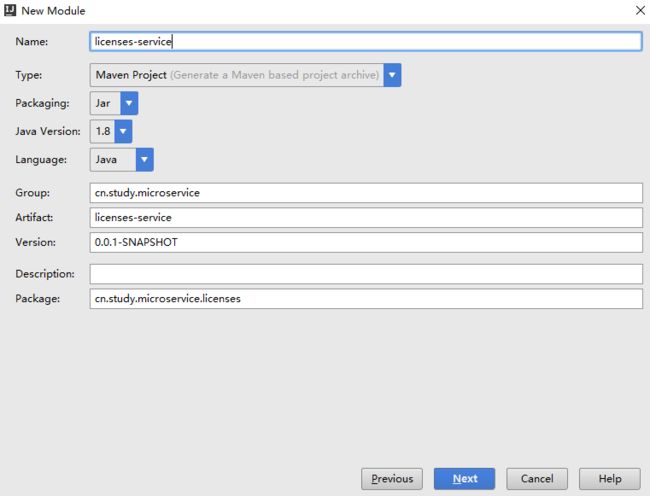
- Spring Boot的项目结构
m0_74823983
面试学习路线阿里巴巴springboot后端java
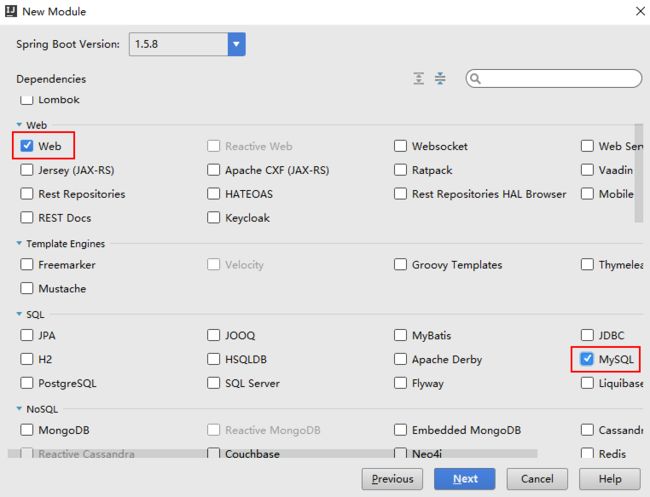
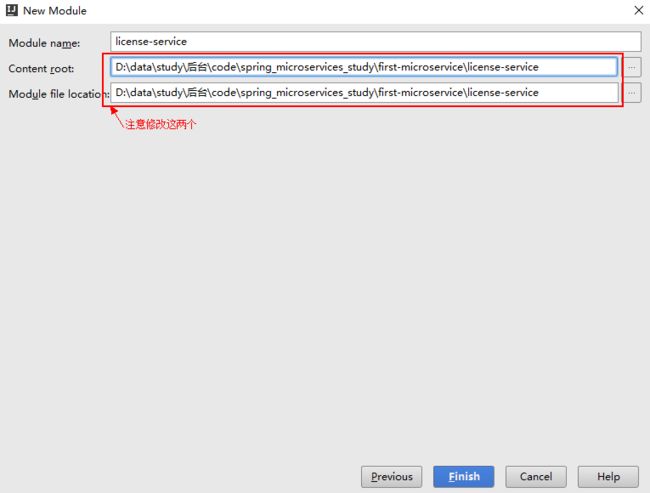
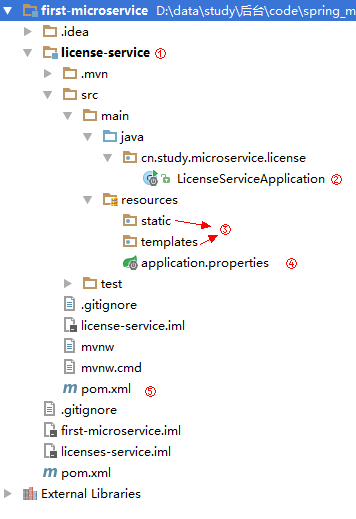
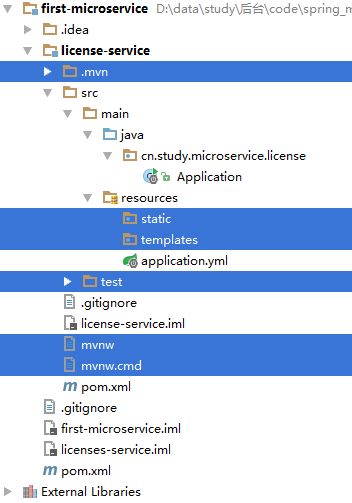
SpringBoot的项目结构技术背景SpringBoot项目结构遵循Maven或Gradle的标准目录结构,同时融入了SpringBoot的特定约定。良好的项目结构不仅有助于代码组织,还能提高开发效率和项目可维护性。了解SpringBoot的项目结构对于开发高质量的应用至关重要。1.基础项目结构1.1标准目录结构基本的SpringBoot项目结构如下:myproject/├──src/│├──m
- 深入剖析 Java 反序列化:FASTjson 漏洞与 Shiro 漏洞
阿贾克斯的黎明
网络安全phpweb安全开发语言
目录深入剖析Java反序列化:FASTjson漏洞与Shiro漏洞引言Java反序列化原理示例代码FASTjson漏洞分析漏洞成因示例代码防护措施Shiro漏洞分析漏洞成因示例代码(模拟攻击场景)防护措施总结引言在Java应用开发中,反序列化是一项重要的技术,但同时也隐藏着巨大的安全风险。FASTjson和Shiro作为Java开发中常用的工具和框架,其反序列化漏洞曾引发了广泛关注。本文将深入探讨
- 2024年BCSP-X小学低年级组初赛测试题(模拟题解析)
天秀信奥编程培训
#BCXP-X模拟题北京BCSP-X试题讲解专栏BCXP-X信息学奥赛c++
一、单项选择(共15题,每题2分,共计30分,每题有且仅有一个正确选项)以下是题目和解析的完整格式:不可以作为c++中的变量名的是()。A.I以下loveChinaB.I_loveChinaC.I_love_ChinaD.i_loveChina正确答案:A.I以下loveChina解析:在C++中,变量名命名需要遵循一定的规则。变量名可以由字母、数字和下划线组成,但是第一个字符不能是数字。此外,变
- 【C++设计模式】工厂方法设计模式:深入解析从基础到进阶
老猿讲编程
C++编程c++设计模式开发语言
1.引言在软件开发的世界里,设计模式如同巧妙的建筑蓝图,为解决常见问题提供了行之有效的方案。工厂方法模式作为一种广受欢迎的创建型设计模式,以其独特的优势在众多项目中得到广泛应用。它不仅能够为对象的创建提供通用且灵活的方式,还能有效隐藏实现细节,提升代码的可维护性和可扩展性。本文将全方位深入探讨工厂方法模式,从基础定义、实现过程,到进阶优化和功能扩展,带领读者全面掌握这一重要的设计模式。2.工厂方法
- Java微服务的注册中心Nacos
铁锤学代码
微服务java微服务开发语言
文章目录Nacos的主要作用Nacos实现动态配置更新的技术Nacos实现CAPNacos实现CAP原理Nacos使用Distro和Raft分别干什么用?ZAB与Raft的区别Nacos的主要作用配置中心:可以将微服务中的一些配置信息放到Nacos进行统一管理,也可以通过Nacos实现动态配置管理。也可以将不同环境的配置放在不同的Namespace下的group下,实现动态选择配置发布部署。服务注
- ArrayList 源码分析
2401_85327573
java开发语言
ArrayList简介ArrayList的底层是数组队列,相当于动态数组。与Java中的数组相比,它的容量能动态增长。在添加大量元素前,应用程序可以使用ensureCapacity操作来增加ArrayList实例的容量。这可以减少递增式再分配的数量。ArrayList继承于AbstractList,实现了List,RandomAccess,Cloneable,java.io.Serializabl
- javaweb文件上传:@MultipartConfig注解与Apache Commons FileUpload对比
yuren_xia
后端技术apachejavatomcat
在JavaWeb应用中处理文件上传时,可以选择使用@MultipartConfig注解或第三方库如ApacheCommonsFileUpload(通常简称为fileupload)。以下是两者的比较和建议:使用@MultipartConfig注解简介:@MultipartConfig是JavaServlet规范中用于处理multipart/form-data请求(通常是文件上传)的注解。它简化了在S
- Exception:data did not match any variant of untagged enum PyPreTokenizerTypeWrapper at line 69 解决方案
爱编程的喵喵
Python基础课程pythontokenizerPyPreTokenizer解决方案
大家好,我是爱编程的喵喵。双985硕士毕业,现担任全栈工程师一职,热衷于将数据思维应用到工作与生活中。从事机器学习以及相关的前后端开发工作。曾在阿里云、科大讯飞、CCF等比赛获得多次Top名次。现为CSDN博客专家、人工智能领域优质创作者。喜欢通过博客创作的方式对所学的知识进行总结与归纳,不仅形成深入且独到的理解,而且能够帮助新手快速入门。 本文主要介绍了Exception:datadidn
- Linux驱动开发: USB驱动开发
DS小龙哥
Linux系统编程与驱动开发linuxUSB驱动嵌入式
一、USB简介1.1什么是USB?USB是连接计算机系统与外部设备的一种串口总线标准,也是一种输入输出接口的技术规范,被广泛地应用于个人电脑和移动设备等信息通讯产品,USB就是简写,中文叫通用串行总线。最早出现在1995年,伴随着奔腾机发展而来。自微软在Windows98中加入对USB接口的支持后,USB接口才推广开来,USB设备也日渐增多,如数码相机、摄像头、扫描仪、游戏杆、打印机、键盘、鼠标等
- 如何使用Python编程实现捕获笔记本电脑麦克风的音频并通过蓝牙耳机实时传输
winfredzhang
python音视频实时传输蓝牙耳机
在现代的工作和生活环境中,音频传输的需求日益增加。无论是远程会议、在线教育,还是家庭娱乐,音频的实时传输都扮演着至关重要的角色。今天,我将向大家介绍一个简单而实用的应用程序,它能够捕获笔记本电脑麦克风的音频,并通过蓝牙耳机实时传输。这款应用程序特别适用于需要在会议室等场景中远程听取声音的情况。接下来,我将详细讲解这个应用程序的实现过程,并提供完整的代码和使用指南。引言想象一下这样的场景:你需要离开
- 多线程之三:MFC多线程及实例(转)
Stef若木
MFC线程
MFC中有两类线程,分别称之为工作者线程和用户界面线程。二者的主要区别在于工作者线程没有消息循环,而用户界面线程有自己的消息队列和消息循环。工作者线程没有消息机制,通常用来执行后台计算和维护任务,如冗长的计算过程,打印机的后台打印等。用户界面线程一般用于处理独立于其他线程执行之外的用户输入,响应用户及系统所产生的事件和消息等。但对于Win32的API编程而言,这两种线程是没有区别的,它们都只需线程
- emmc kernel driver流程
zjuestcer
linuxkernel存储emmcdriver
首先执行的第一个函数:mmc_blk_register(__init触发)1.完成了mmcblock设备的注册,可以在proc/devices下看到这个Block设备2.将mmc_driver和mmc_bus_type进行绑定,这样将mmc_bus_probe和mmc_blk_probe联系起来了第二个函数:sprd_sdhc_probe(__init触发)
- Linux Device Driver 3rd 上
xiaozi63
linux内核驱动程序
第一章设备驱动程序的简介处于上层应用与底层硬件设备的软件层区分机制和策略是Linux最好的思想之一,机制指的是需要提供什么功能,策略指的是如何使用这个功能!通常不同的环境需要不同的方式来使用硬件,则驱动应当尽可能地不实现策略.驱动程序设计需要考虑一下几个方面的因素:提供给用户尽量多的选项编写驱动程序所占用的时间,驱动程序的操作耗时需要尽量缩减.尽量保持程序简单内核概览:进程管理:负责创建和销毁进程
- 坚持学习100天:MFC多线程开发
smile- sunshine
编程语言C++笔记mfc学习c++
前言Hello,我是修齊。学习C++的第一百零二十六天,5.18的今天,520快到了,要去花店买两朵玫瑰,用心学习。在这里记录一些学习的东西和学习的心情,内容主要是一些自己学习整理的小笔记。一、类CWinThread1.MFC,用类CWinThread的对象来表示一个线程,每个MFC程序的主线程都有一个继承自CWinApp的应用程序类,而CWinApp继承自CWinThread。2.类CWinTh
- 探索React的深度应用:React Survey——构建问卷神器
傅尉艺Maggie
探索React的深度应用:ReactSurvey——构建问卷神器去发现同类优质开源项目:https://gitcode.com/在浩瀚的前端开发世界里,React与Redux已成为构建复杂Web应用的得力助手,但它们的强大往往隐藏在基础教程之后。今天,让我们一同探索【ReactSurvey】,一个将React与Redux之力发挥至极致的开源项目,教你如何轻松打造专业的在线问卷系统。项目介绍Reac
- 开目MOM数字化制造运营管理系统介绍
开目软件
制造
开目MOM系统是制造业数据化架构中的重要组成部分,为企业提供制造数据管理、制造运营管理、质量管理、仓储管理、工具工装管理、设备管理等模块,打造一个可靠、全面的制造协同管理平台。开目MOM系统-即制造运营管理系统,是面向CPS的新一代数字化管理解决方案。随着企业对制造运营管控的认知和升级,MOM逐渐被广泛应用于市场中,MOM概念首次于2000年被提出,MOM系统覆盖了制造运营管理的全部活动范围,其主
- 开目CAPP三维装配工艺设计在企业的应用价值
开目软件
开目CAPP三维装配工艺设计三维装配工艺设计应用价值
目前,国内三维装配CAPP技术的应用还处于起步阶段,其主要应用于高产值、高附加值以及信息化程度较高的航空航天、汽车、军用电子等行业。通过应用,主要实现了以下价值:提升产品上市速度在产品设计到产品交付的过程中,通过采用数字化预装配进行装配工艺规划,可以帮助企业通过装配过程的模拟分析尽早发现和解决问题,优化装配方案,为设计与工艺、制造的并行提供条件,从而提高装配设计、现场装配工作的工作效率,缩减产品交
- 【3D格式转换SDK】HOOPS Exchange技术概览(一):3D 数据处理高效能与定制化
工业3D_大熊
3DCAD开发工具3d3D建模3D模型轻量化3D模型Web可视化3D数据格式转换3D格式转换CAD格式转换
HOOPSExchange是一款专为3D工程应用开发而设计的SDK,旨在助力开发者便捷地访问和重用由CAD与BIM设计应用所生成的3D数据,为3D产品运营提供了强大的数据基础。借助单一且集成化的界面,HOOPSExchange能够高效地导入、转换以及导出超过30种原生及标准格式的3D数据,具体涵盖以下格式:机械计算机辅助设计(MCAD)领域:CATIA、NX、Creo、SOLIDWORKS、Inv
- RabbitMQ系列(零)概要
yyueshen
RabbitMQrabbitmq分布式消息队列
一、消息队列总览1.什么是消息队列?消息队列(MessageQueue)是一种异步通信机制,允许分布式系统中的服务通过生产-消费模型传递数据。其核心价值在于:解耦性:生产者与消费者无需同时在线或直接交互削峰填谷:应对流量突发场景,避免系统过载(如秒杀系统请求缓冲)可靠性:通过持久化、重试机制保障消息不丢失2.典型应用场景场景实现原理案例服务异步化耗时操作异步执行(如日志记录)用户注册后异步发送通知
- 第十阶段 -- Flask框架05:【Flask高级06:Restful接口】
亚呦u椰
python学习Flask框架
文章目录1.RESTful接口规范2.RESTful的基本使用3.参数验证4.返回标准化参数5.返回标准化参数强化6.结合蓝图使用和渲染模板7.示例1.RESTful接口规范Restful接口规范介绍REST:RepresentationalStateTransfer,REST指的是一组架构约束条件和原则。满足这些约束条件和原则的应用程序或设计就是RESTful。是一种软件架构风格、设计风格,而不
- 基于STM32的无人机自主导航与避障系统
STM32发烧友
stm32无人机嵌入式硬件
目录引言环境准备2.1硬件准备2.2软件准备无人机自主导航与避障系统基础3.1控制系统架构3.2功能描述代码实现:实现无人机自主导航与避障系统4.1数据采集模块4.2数据处理与控制算法4.3通信与远程监控实现4.4用户界面与数据可视化应用场景:无人机智能化与任务执行问题解决方案与优化收尾与总结1.引言无人机自主导航与避障技术是无人机系统实现智能化和高效任务执行的核心功能。基于STM32微控制器,该
- 实现设备认证功能鸿蒙示例代码
介绍本示例使用鸿蒙ohos.distributedDeviceManager模块,实现设备间相互认证的能力。实现设备认证功能源码链接效果预览使用说明进入应用会出现是否允许应用发现和连接附近设备的弹窗,点击允许,会获取当前设备的信息并显示在应用首页。点击“搜索周边设备”按钮,会搜索周边未绑定设备,并显示结果。点击“查看已绑定设备”按钮,会以列表形式显示所有可信设备。实现思路发现和连接附近设备弹窗向用
- 【spug】使用
勤不了一点
CI/CDpythondjangoci/cd运维devops
目录简介下载与安装初始化配置启动与日志版本更新登录与使用工作台主机管理批量执行配置中心应用发布系统管理监控与告警使用问题简介手动部署|Spugwalle的升级版本轻量级无Agent主机管理主机批量执行主机在线终端文件在线上传下载应用发布部署在线任务计划配置中心监控报警如果有测试错误请指出。下载与安装测试环境:Python3.7.8CentOSLinuxrelease7.4.1708(Core)sp
- 风险管理必备工具:从SWOT分析到蒙特卡洛模拟软件
程序员
在商业世界中,风险管理是企业取得成功的关键因素之一。有效的风险管理可以帮助企业识别潜在的风险,制定相应的策略来降低风险的影响,并抓住潜在的机会。在风险管理中,有许多工具可以帮助企业进行分析和决策。本文将介绍两种常用的风险管理工具:SWOT分析和蒙特卡洛模拟软件。SWOT分析:全面评估企业的优势、劣势、机会和威胁SWOT分析是一种广泛应用的战略规划工具,它可以帮助企业全面地评估自身的内部优势(Str
- React Native 0.76:重大更新引领移动开发新潮流
前端react-native
博主小程序体验|博主公众号分享2024年10月23日,ReactNative发布了具有里程碑意义的0.76版本,这一版本带来了众多令人瞩目的更新,将对移动应用开发产生深远影响。一、主要更新内容概览(一)新架构默认启用从0.76版本起,新架构在项目中默认开启,这标志着它已经具备了用于生产环境的条件。新架构是自2018年以来对ReactNative的全面重写,与旧架构相比有诸多优势。(二)ReactN
- Spring Boot 集成 Kafka
m0_74823471
面试学习路线阿里巴巴springbootkafkalinq
在现代软件开发中,分布式系统和微服务架构越来越受到关注。为了实现系统之间的异步通信和解耦,消息队列成为了一种重要的技术手段。Kafka作为一种高性能、分布式的消息队列系统,被广泛应用于各种场景。而SpringBoot作为一种流行的Java开发框架,提供了便捷的方式来构建应用程序。本文将介绍如何在SpringBoot项目中集成Kafka,包括Kafka的基本概念、SpringBoot集成Kafka的
- ASM系列五 利用TreeApi 解析生成Class
lijingyao8206
ASM字节码动态生成ClassNodeTreeAPI
前面CoreApi的介绍部分基本涵盖了ASMCore包下面的主要API及功能,其中还有一部分关于MetaData的解析和生成就不再赘述。这篇开始介绍ASM另一部分主要的Api。TreeApi。这一部分源码是关联的asm-tree-5.0.4的版本。
在介绍前,先要知道一点, Tree工程的接口基本可以完
- 链表树——复合数据结构应用实例
bardo
数据结构树型结构表结构设计链表菜单排序
我们清楚:数据库设计中,表结构设计的好坏,直接影响程序的复杂度。所以,本文就无限级分类(目录)树与链表的复合在表设计中的应用进行探讨。当然,什么是树,什么是链表,这里不作介绍。有兴趣可以去看相关的教材。
需求简介:
经常遇到这样的需求,我们希望能将保存在数据库中的树结构能够按确定的顺序读出来。比如,多级菜单、组织结构、商品分类。更具体的,我们希望某个二级菜单在这一级别中就是第一个。虽然它是最后
- 为啥要用位运算代替取模呢
chenchao051
位运算哈希汇编
在hash中查找key的时候,经常会发现用&取代%,先看两段代码吧,
JDK6中的HashMap中的indexFor方法:
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
- 最近的情况
麦田的设计者
生活感悟计划软考想
今天是2015年4月27号
整理一下最近的思绪以及要完成的任务
1、最近在驾校科目二练车,每周四天,练三周。其实做什么都要用心,追求合理的途径解决。为
- PHP去掉字符串中最后一个字符的方法
IT独行者
PHP字符串
今天在PHP项目开发中遇到一个需求,去掉字符串中的最后一个字符 原字符串1,2,3,4,5,6, 去掉最后一个字符",",最终结果为1,2,3,4,5,6 代码如下:
$str = "1,2,3,4,5,6,";
$newstr = substr($str,0,strlen($str)-1);
echo $newstr;
- hadoop在linux上单机安装过程
_wy_
linuxhadoop
1、安装JDK
jdk版本最好是1.6以上,可以使用执行命令java -version查看当前JAVA版本号,如果报命令不存在或版本比较低,则需要安装一个高版本的JDK,并在/etc/profile的文件末尾,根据本机JDK实际的安装位置加上以下几行:
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.7.0_25
- JAVA进阶----分布式事务的一种简单处理方法
无量
多系统交互分布式事务
每个方法都是原子操作:
提供第三方服务的系统,要同时提供执行方法和对应的回滚方法
A系统调用B,C,D系统完成分布式事务
=========执行开始========
A.aa();
try {
B.bb();
} catch(Exception e) {
A.rollbackAa();
}
try {
C.cc();
} catch(Excep
- 安墨移动广 告:移动DSP厚积薄发 引领未来广 告业发展命脉
矮蛋蛋
hadoop互联网
“谁掌握了强大的DSP技术,谁将引领未来的广 告行业发展命脉。”2014年,移动广 告行业的热点非移动DSP莫属。各个圈子都在纷纷谈论,认为移动DSP是行业突破点,一时间许多移动广 告联盟风起云涌,竞相推出专属移动DSP产品。
到底什么是移动DSP呢?
DSP(Demand-SidePlatform),就是需求方平台,为解决广 告主投放的各种需求,真正实现人群定位的精准广
- myelipse设置
alafqq
IP
在一个项目的完整的生命周期中,其维护费用,往往是其开发费用的数倍。因此项目的可维护性、可复用性是衡量一个项目好坏的关键。而注释则是可维护性中必不可少的一环。
注释模板导入步骤
安装方法:
打开eclipse/myeclipse
选择 window-->Preferences-->JAVA-->Code-->Code
- java数组
百合不是茶
java数组
java数组的 声明 创建 初始化; java支持C语言
数组中的每个数都有唯一的一个下标
一维数组的定义 声明: int[] a = new int[3];声明数组中有三个数int[3]
int[] a 中有三个数,下标从0开始,可以同过for来遍历数组中的数
- javascript读取表单数据
bijian1013
JavaScript
利用javascript读取表单数据,可以利用以下三种方法获取:
1、通过表单ID属性:var a = document.getElementByIdx_x_x("id");
2、通过表单名称属性:var b = document.getElementsByName("name");
3、直接通过表单名字获取:var c = form.content.
- 探索JUnit4扩展:使用Theory
bijian1013
javaJUnitTheory
理论机制(Theory)
一.为什么要引用理论机制(Theory)
当今软件开发中,测试驱动开发(TDD — Test-driven development)越发流行。为什么 TDD 会如此流行呢?因为它确实拥有很多优点,它允许开发人员通过简单的例子来指定和表明他们代码的行为意图。
TDD 的优点:
&nb
- [Spring Data Mongo一]Spring Mongo Template操作MongoDB
bit1129
template
什么是Spring Data Mongo
Spring Data MongoDB项目对访问MongoDB的Java客户端API进行了封装,这种封装类似于Spring封装Hibernate和JDBC而提供的HibernateTemplate和JDBCTemplate,主要能力包括
1. 封装客户端跟MongoDB的链接管理
2. 文档-对象映射,通过注解:@Document(collectio
- 【Kafka八】Zookeeper上关于Kafka的配置信息
bit1129
zookeeper
问题:
1. Kafka的哪些信息记录在Zookeeper中 2. Consumer Group消费的每个Partition的Offset信息存放在什么位置
3. Topic的每个Partition存放在哪个Broker上的信息存放在哪里
4. Producer跟Zookeeper究竟有没有关系?没有关系!!!
//consumers、config、brokers、cont
- java OOM内存异常的四种类型及异常与解决方案
ronin47
java OOM 内存异常
OOM异常的四种类型:
一: StackOverflowError :通常因为递归函数引起(死递归,递归太深)。-Xss 128k 一般够用。
二: out Of memory: PermGen Space:通常是动态类大多,比如web 服务器自动更新部署时引起。-Xmx
- java-实现链表反转-递归和非递归实现
bylijinnan
java
20120422更新:
对链表中部分节点进行反转操作,这些节点相隔k个:
0->1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9
k=2
8->1->6->3->4->5->2->7->0->9
注意1 3 5 7 9 位置是不变的。
解法:
将链表拆成两部分:
a.0-&
- Netty源码学习-DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder
bylijinnan
javanetty
看DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder的API,有举例:
接收到的ChannelBuffer如下:
+--------------+
| ABC\nDEF\r\n |
+--------------+
经过DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(Delimiters.lineDelimiter())之后,得到:
+-----+----
- linux的一些命令 -查看cc攻击-网口ip统计等
hotsunshine
linux
Linux判断CC攻击命令详解
2011年12月23日 ⁄ 安全 ⁄ 暂无评论
查看所有80端口的连接数
netstat -nat|grep -i '80'|wc -l
对连接的IP按连接数量进行排序
netstat -ntu | awk '{print $5}' | cut -d: -f1 | sort | uniq -c | sort -n
查看TCP连接状态
n
- Spring获取SessionFactory
ctrain
sessionFactory
String sql = "select sysdate from dual";
WebApplicationContext wac = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
String[] names = wac.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for(int i=0; i&
- Hive几种导出数据方式
daizj
hive数据导出
Hive几种导出数据方式
1.拷贝文件
如果数据文件恰好是用户需要的格式,那么只需要拷贝文件或文件夹就可以。
hadoop fs –cp source_path target_path
2.导出到本地文件系统
--不能使用insert into local directory来导出数据,会报错
--只能使用
- 编程之美
dcj3sjt126com
编程PHP重构
我个人的 PHP 编程经验中,递归调用常常与静态变量使用。静态变量的含义可以参考 PHP 手册。希望下面的代码,会更有利于对递归以及静态变量的理解
header("Content-type: text/plain");
function static_function () {
static $i = 0;
if ($i++ < 1
- Android保存用户名和密码
dcj3sjt126com
android
转自:http://www.2cto.com/kf/201401/272336.html
我们不管在开发一个项目或者使用别人的项目,都有用户登录功能,为了让用户的体验效果更好,我们通常会做一个功能,叫做保存用户,这样做的目地就是为了让用户下一次再使用该程序不会重新输入用户名和密码,这里我使用3种方式来存储用户名和密码
1、通过普通 的txt文本存储
2、通过properties属性文件进行存
- Oracle 复习笔记之同义词
eksliang
Oracle 同义词Oracle synonym
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2098861
1.什么是同义词
同义词是现有模式对象的一个别名。
概念性的东西,什么是模式呢?创建一个用户,就相应的创建了 一个模式。模式是指数据库对象,是对用户所创建的数据对象的总称。模式对象包括表、视图、索引、同义词、序列、过
- Ajax案例
gongmeitao
Ajaxjsp
数据库采用Sql Server2005
项目名称为:Ajax_Demo
1.com.demo.conn包
package com.demo.conn;
import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.SQLException;
//获取数据库连接的类public class DBConnec
- ASP.NET中Request.RawUrl、Request.Url的区别
hvt
.netWebC#asp.nethovertree
如果访问的地址是:http://h.keleyi.com/guestbook/addmessage.aspx?key=hovertree%3C&n=myslider#zonemenu那么Request.Url.ToString() 的值是:http://h.keleyi.com/guestbook/addmessage.aspx?key=hovertree<&
- SVG 教程 (七)SVG 实例,SVG 参考手册
天梯梦
svg
SVG 实例 在线实例
下面的例子是把SVG代码直接嵌入到HTML代码中。
谷歌Chrome,火狐,Internet Explorer9,和Safari都支持。
注意:下面的例子将不会在Opera运行,即使Opera支持SVG - 它也不支持SVG在HTML代码中直接使用。 SVG 实例
SVG基本形状
一个圆
矩形
不透明矩形
一个矩形不透明2
一个带圆角矩
- 事务管理
luyulong
javaspring编程事务
事物管理
spring事物的好处
为不同的事物API提供了一致的编程模型
支持声明式事务管理
提供比大多数事务API更简单更易于使用的编程式事务管理API
整合spring的各种数据访问抽象
TransactionDefinition
定义了事务策略
int getIsolationLevel()得到当前事务的隔离级别
READ_COMMITTED
- 基础数据结构和算法十一:Red-black binary search tree
sunwinner
AlgorithmRed-black
The insertion algorithm for 2-3 trees just described is not difficult to understand; now, we will see that it is also not difficult to implement. We will consider a simple representation known
- centos同步时间
stunizhengjia
linux集群同步时间
做了集群,时间的同步就显得非常必要了。 以下是查到的如何做时间同步。 在CentOS 5不再区分客户端和服务器,只要配置了NTP,它就会提供NTP服务。 1)确认已经ntp程序包: # yum install ntp 2)配置时间源(默认就行,不需要修改) # vi /etc/ntp.conf server pool.ntp.o
- ITeye 9月技术图书有奖试读获奖名单公布
ITeye管理员
ITeye
ITeye携手博文视点举办的9月技术图书有奖试读活动已圆满结束,非常感谢广大用户对本次活动的关注与参与。 9月试读活动回顾:http://webmaster.iteye.com/blog/2118112本次技术图书试读活动的优秀奖获奖名单及相应作品如下(优秀文章有很多,但名额有限,没获奖并不代表不优秀):
《NFC:Arduino、Andro