无人机遥感图像语义分割数据集UAVid使用
一、无人机遥感图像语义分割数据集UAVid
UAVid数据集是用于针对城市场景的语义分割任务的UAV视频数据集。它具有几个特点:
- 语义分割
- 4K分辨率无人机视频
- 8种物体类别
- 街景环境
示例图像:
下载地址(支持百度网盘下载):https://uavid.nl/
二、使用UAVid工具包(python)进行标签转换
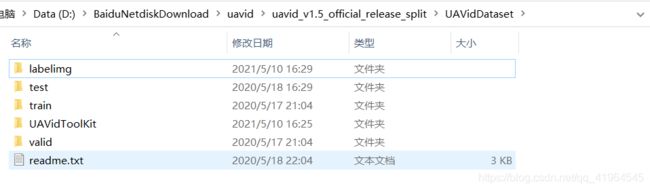
1. 下载数据集后,进入数据集中,将文件名进行修改并组织为以下形式,即将数据集上级目录名修改为UAVidDataset,将目录名uavid_train修改为train,其余也按照以下图片修改目录名
2. 下载工具包
# 首先进入到你的UAVidDataset路径下
# 然后依次使用以下命令开始下载工具包并配置
git clone https://github.com/YeLyuUT/UAVidToolKit.git
cd UAVidToolKit
python setup.py build_ext --inplace
完成好后,你的文件组织形式应该为上图的格式。
3. 标签转化
在UAVidDataset文件下下使用以下命令
python UAVidToolKit/prepareTrainIdFiles.py -s train/ -t labelimg/train/
python UAVidToolKit/prepareTrainIdFiles.py -s valid/ -t labelimg/valid/如果顺利的话,文件夹结构为以下形式
打开labelimg文件夹,里面由train和valid两个文件夹,分别存放的是训练集和验证集的标签图像,可以自行查看一下。
三、编写DataLoader数据加载脚本(使用Pytorch)
训练集和验证集的数据加载脚本,训练集采用了随机缩放、随机翻转、随机位置裁剪三种数据增强方式
import torch
import torch.utils.data
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
train_dirs = ["seq1/", "seq2/", "seq3/", "seq4/", "seq5/",
"seq6/", "seq7/", "seq8/", "seq9/", "seq10/",
"seq11/", "seq12/", "seq13/", "seq14/", "seq15/",
"seq31/", "seq32/", "seq33/", "seq34/", "seq35/"]
val_dirs = ["sep16/", "seq17/", "seq18/","seq19/",
"seq20/", "seq36/", "seq37/"]
class DatasetTrain(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, uavid_data_path, uavid_meta_path):
self.img_dir = uavid_data_path + "/train/"
self.label_dir = uavid_meta_path + "/labelimg/train/"
self.img_h = 2160
self.img_w = 3840
self.new_img_h = 1536
self.new_img_w = 1536
self.examples = []
for train_dir in train_dirs:
train_img_dir_path = self.img_dir + train_dir + "Images/"
label_img__dir_path = self.label_dir + train_dir
file_names = os.listdir(train_img_dir_path)
for file_name in file_names:
img_id = file_name.split(".png")[0]
img_path = train_img_dir_path + file_name
label_img_path = label_img__dir_path + "TrainId/" + img_id + ".png"
example = {}
example["img_path"] = img_path
example["label_img_path"] = label_img_path
example["img_id"] = img_id
self.examples.append(example)
self.num_examples = len(self.examples)
def __getitem__(self, index):
example = self.examples[index]
img_path = example["img_path"]
img = cv2.imread(img_path, -1) # (shape: (2160, 3840, 3))
# resize img without interpolation (want the image to still match
# label_img, which we resize below):
img = cv2.resize(img, (self.new_img_w, self.new_img_h),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST) # (shape: (1536, 1536, 3))
label_img_path = example["label_img_path"]
label_img = cv2.imread(label_img_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) # (shape: (2160, 3840))
# resize label_img without interpolation (want the resulting image to
# still only contain pixel values corresponding to an object class):
label_img = cv2.resize(label_img, (self.new_img_w, self.new_img_h),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST) # (shape: (1536, 1536))
# flip the img and the label with 0.5 probability:
flip = np.random.randint(low=0, high=2)
if flip == 1:
img = cv2.flip(img, 1)
label_img = cv2.flip(label_img, 1)
########################################################################
# randomly scale the img and the label:
########################################################################
scale = np.random.uniform(low=0.7, high=2.0)
new_img_h = int(scale*self.new_img_h)
new_img_w = int(scale*self.new_img_w)
# resize img without interpolation (want the image to still match
# label_img, which we resize below):
img = cv2.resize(img, (new_img_w, new_img_h),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST) # (shape: (new_img_h, new_img_w, 3))
# resize label_img without interpolation (want the resulting image to
# still only contain pixel values corresponding to an object class):
label_img = cv2.resize(label_img, (new_img_w, new_img_h),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST) # (shape: (new_img_h, new_img_w))
########################################################################
# # # # # # # # debug visualization START
# print (scale)
# print (new_img_h)
# print (new_img_w)
#
# cv2.imshow("test", img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
#
# cv2.imshow("test", label_img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# # # # # # # # debug visualization END
########################################################################
# select a 768x768 random crop from the img and label:
########################################################################
start_x = np.random.randint(low=0, high=(new_img_w - 768))
end_x = start_x + 768
start_y = np.random.randint(low=0, high=(new_img_h - 768))
end_y = start_y + 768
img = img[start_y:end_y, start_x:end_x] # (shape: (768, 768, 3))
label_img = label_img[start_y:end_y, start_x:end_x] # (shape: (768, 768))
########################################################################
# # # # # # # # debug visualization START
# print (img.shape)
# print (label_img.shape)
#
# cv2.imshow("test", img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
#
# cv2.imshow("test", label_img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# # # # # # # # debug visualization END
# normalize the img (with the mean and std for the pretrained ResNet):
img = img/255.0
img = img - np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
img = img/np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # (shape: (768, 768, 3))
img = np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1)) # (shape: (3, 768, 768))
img = img.astype(np.float32)
# convert numpy -> torch:
img = torch.from_numpy(img) # (shape: (3, 768, 768))
label_img = torch.from_numpy(label_img) # (shape: (768, 768))
return (img, label_img)
def __len__(self):
return self.num_examples
class DatasetVal(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, uavid_data_path, uavid_meta_path):
self.img_dir = uavid_data_path + "/valid/"
self.label_dir = uavid_meta_path + "/labelimg/valid/"
self.img_h = 2160
self.img_w = 3840
self.new_img_h = 768
self.new_img_w = 768
self.examples = []
for val_dir in val_dirs:
val_img_dir_path = self.img_dir + val_dir + "Images/"
label_img__dir_path = self.label_dir + val_dir
file_names = os.listdir(val_img_dir_path)
for file_name in file_names:
img_id = file_name.split(".png")[0]
img_path = val_img_dir_path + file_name
label_img_path = label_img__dir_path + "TrainId/" + img_id + ".png"
# label_img = cv2.imread(label_img_path, -1) # (shape: (1024, 2048))
example = {}
example["img_path"] = img_path
example["label_img_path"] = label_img_path
example["img_id"] = img_id
self.examples.append(example)
self.num_examples = len(self.examples)
def __getitem__(self, index):
example = self.examples[index]
img_id = example["img_id"]
img_path = example["img_path"]
img = cv2.imread(img_path, -1) # (shape: (2160, 3840, 3))
# resize img without interpolation (want the image to still match
# label_img, which we resize below):
img = cv2.resize(img, (self.new_img_w, self.new_img_h),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST) # (shape: (768, 768, 3))
label_img_path = example["label_img_path"]
label_img = cv2.imread(label_img_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE) # (shape: (2160, 3840))
# resize label_img without interpolation (want the resulting image to
# still only contain pixel values corresponding to an object class):
label_img = cv2.resize(label_img, (self.new_img_w, self.new_img_h),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST) # (shape: (768, 768))
# # # # # # # # debug visualization START
# cv2.imshow("test", img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
#
# cv2.imshow("test", label_img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# # # # # # # # debug visualization END
# normalize the img (with the mean and std for the pretrained ResNet):
img = img/255.0
img = img - np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
img = img/np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # (shape: (768, 768, 3))
img = np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1)) # (shape: (3, 768, 768))
img = img.astype(np.float32)
# convert numpy -> torch:
img = torch.from_numpy(img) # (shape: (3, 768, 768))
label_img = torch.from_numpy(label_img) # (shape: (768, 768))
return (img, label_img, img_id)
def __len__(self):
return self.num_examples