作为一枚Android开发者,关于EventBus相信应该都听说过。要是用过就请忽略本文,本文讲得比较基础。
要是没用过,建议你花两分钟看看。
目前EventBus最新版本是3.0,本demo基于3.0编写的。
GitHub : https://github.com/greenrobot/EventBus
官方文档:http://greenrobot.org/eventbus/documentation
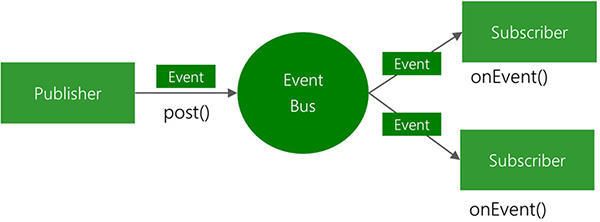
一、EventBus概述
EventBus是一个Android端优化的publish/subscribe消息总线,简化了应用程序内各组件间、组件与后台线程间的通信。
作为一个消息总线主要有三个组成部分:
- 事件(Event)
- 事件订阅者(Subscriber)
-
事件发布者(Publisher)
二、EventBus用法
1、把EventBus依赖到项目
build.gradle添加引用
compile 'org.greenrobot:eventbus:3.0.0'
Maven
org.greenrobot
eventbus
3.0.0
或者直接下载EventBus 架包jar 放到项目中
2、构造发送消息类,也就是发送的对象
public class MainMessage{
private String message;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
3、注册/解除注册
EventBus.getDefault().register(this);//注册
EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);//解除注册
4 、发送消息
EventBus.getDefault().post(new MainMessage("你好,爱开发");
ThreadMode总共四个:
MAIN UI主线程
POSTING 默认调用方式,在调用post方法的线程执行,避免了线程切换,性能开销最少
BACKGROUND 如果调用post方法的线程不是主线程,则直接在该线程执行。
如果是主线程,则切换到后台单例线程,多个方法公用同个后台线程,按顺序执行,避免耗时操作ASYNC 开辟新独立线程,用来执行耗时操作,例如网络访问。
来看一下源码,ThreadMode也就一个枚举,英文自己对照理解吧,不是很复杂
public enum ThreadMode {
/**
* Subscriber will be called in the same thread, which is posting the event. This is the default. Event delivery
* implies the least overhead because it avoids thread switching completely. Thus this is the recommended mode for
* simple tasks that are known to complete is a very short time without requiring the main thread. Event handlers
* using this mode must return quickly to avoid blocking the posting thread, which may be the main thread.
*/
POSTING,
/**
* Subscriber will be called in Android's main thread (sometimes referred to as UI thread). If the posting thread is
* the main thread, event handler methods will be called directly. Event handlers using this mode must return
* quickly to avoid blocking the main thread.
*/
MAIN,
/**
* Subscriber will be called in a background thread. If posting thread is not the main thread, event handler methods
* will be called directly in the posting thread. If the posting thread is the main thread, EventBus uses a single
* background thread, that will deliver all its events sequentially. Event handlers using this mode should try to
* return quickly to avoid blocking the background thread.
*/
BACKGROUND,
/**
* Event handler methods are called in a separate thread. This is always independent from the posting thread and the
* main thread. Posting events never wait for event handler methods using this mode. Event handler methods should
* use this mode if their execution might take some time, e.g. for network access. Avoid triggering a large number
* of long running asynchronous handler methods at the same time to limit the number of concurrent threads. EventBus
* uses a thread pool to efficiently reuse threads from completed asynchronous event handler notifications.
*/
ASYNC
}
5 、事件处理
//ui主线程中执行
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.Main)
public void onMainEventBus(MainMessage msg) {
}
6、priority事件优先级
//priority越大,级别越高
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN,priority = 100)
public void onEvent(MainMessage event) {
}
7、终止事件传递
// 注意中止事件传递,后续事件不在调用
@Subscribe
public void onEvent(MessageEvent event){
EventBus.getDefault().cancelEventDelivery(event) ;
}
下面我们来看一个完整的demo
先看一下效果图:
新建两个activity,分别为MainActivity和 SecondActivity
其中MainActivity来放了五个按钮和一个文本框
SecondActivity只有一个按钮,点击按钮通知MainActivity页面更新。
看一下MainActivity主要代码:
/**
* 主线程中执行
*
* @param msg
*/
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.MAIN)
public void onMainEventBus(MainMessage msg) {
Log.e(TAG, msg.getMessage());
tv_desc.setText(msg.getMessage());
}
/**
* 后台线程
*
* @param msg
*/
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.BACKGROUND)
public void onBackgroundEventBus(BackgroundMessage msg) {
Log.e(TAG, msg.getMessage());
}
/**
* 异步线程
*
* @param msg
*/
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.ASYNC)
public void onAsyncEventBus(AsyncMessage msg) {
Log.e(TAG, msg.getMessage());
}
/**
* 默认情况,和发送事件在同一个线程
*
* @param msg
*/
@Subscribe(threadMode = ThreadMode.POSTING)
public void onPostEventBus(PostingMessage msg) {
Log.e(TAG, msg.getMessage());
}
按钮点击事件
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btnMain:
EventBus.getDefault().post(new MainMessage("MainMessage"));
break;
case R.id.btnBackground:
EventBus.getDefault().post(new BackgroundMessage("BackgroundMessage"));
break;
case R.id.btnAsync:
EventBus.getDefault().post(new AsyncMessage("AsyncMessage"));
break;
case R.id.btnPosting:
EventBus.getDefault().post(new PostingMessage("PostingMessage"));
break;
case R.id.btn1:
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
break;
}
}
分别点击前面四个按钮时控制台按顺序输出:
SecondActivity页面点击发送消息的事件
EventBus.getDefault().post(new MainMessage("传递信息:aikaifa"));
在MianActivity页面我们就能接受到SecondActivity传递过来的信息了。
如果感兴趣想跑一下项目,源码请戳这里
[END]
我是洪生鹏,
热衷旅行、写作,目前过着白天到工地搬砖、晚上写故事的生活。
希望今天的文章对你有帮助。
坚持日更,一般会在晚上10点发文,欢迎交流。
优质文章推荐:
我也很爱面子
为什么有的人工作多年还是老样子
程序员月薪多少才不会焦虑