二叉树的堂兄弟节点
目录
- 993. 二叉树的堂兄弟节点
- 思路分析
-
- DFS
- BFS
993. 二叉树的堂兄弟节点
在二叉树中,根节点位于深度 0 处,每个深度为 k 的节点的子节点位于深度 k+1 处。
如果二叉树的两个节点深度相同,但 父节点不同 ,则它们是一对堂兄弟节点。
我们给出了具有唯一值的二叉树的根节点 root ,以及树中两个不同节点的值 x 和 y 。
只有与值 x 和 y 对应的节点是堂兄弟节点时,才返回 true 。否则,返回 false。
输入:root = [1,2,3,4], x = 4, y = 3
输出:false
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,4,null,5], x = 5, y = 4
输出:true
示例 3:
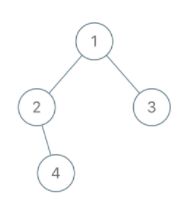
输入:root = [1,2,3,null,4], x = 2, y = 3
输出:false
提示:
二叉树的节点数介于 2 到 100 之间。
每个节点的值都是唯一的、范围为 1 到 100 的整数。
思路分析
我们只需要记录,每个节点的深度、父节点、节点值即可,然后进行检查即可
- 我们定义出两个要比较节点的信息
//x的信息
int x ;
TreeNode xParent;
int xDepth;
boolean xFound = false;
//y的信息
int y;
TreeNode yParent;
int yDepth;
boolean yFound = false;
- 二叉树的遍历有深度优先遍历(DFS)和广度优先遍历(BFS)
DFS
简单说就是将每个节点都遍历一遍,每次遍历节点前都进行检查,有符合条件的两个节点就退出遍历。
public boolean isCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
//第三个参数随便定义,只要是TreeNode类型就行
dfs(root,0,null);
//返回条件
return xDepth == yDepth && xParent != yParent;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root , int depth , TreeNode parent){
if (root == null) return;
if (root.val == x) {
xParent = parent;
xDepth = depth;
xFound = true;
}else if(root.val == y) {
yParent = parent;
yDepth = depth;
yFound = true;
}
if (xFound && yFound) return;
dfs(root.left , depth + 1 , root);
if (xFound && yFound) return;
dfs(root.right , depth + 1 , root);
}
BFS
在广度优先遍历中,我们定义两个栈或者队列,一个用来存节点,一个用来存深度,一一对应;或者也可以使用其他数据结构,只要能达到目的都可以。
其实不管哪种方法都是对二叉树遍历的扩展,本质并没有变化
public boolean isCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> depthQueue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
nodeQueue.offer(root);
depthQueue.offer(0);
while(!nodeQueue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.poll();
int depth = depthQueue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.left);
depthQueue.offer(depth + 1);
check(node.left,depth + 1,node);
}
if (node.right != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.right);
depthQueue.offer(depth + 1);
check(node.right,depth + 1,node);
}
if(xFound && yFound) break;
}
return xDepth == yDepth && xParent != yParent;
}
//检查是否便来到x或y
public void check(TreeNode node , int depth , TreeNode parent) {
if (node.val == x) {
xParent = parent;
xFound = true;
xDepth = depth;
}else if (node.val == y) {
yParent = parent;
yFound = true;
yDepth = depth;
}
}
若有误,请指教!!!

