Python每日一练(23)-基于百度 AI 识别抓取的表情包
目录
- 一、百度 AI 开放平台的 Key 申请方法
- 二、抓取贴吧表情包
- 三、使用 Baidu-aip
本文先抓取网络上的表情图像,然后利用百度 AI 识别表情包上的说明文字,并利用表情文字重命名文件,这样当发表情包时,不需要逐个打开查找,直接根据文件名选择表情并发送。
一、百度 AI 开放平台的 Key 申请方法
本例使用了百度 AI 的 API 接口实现文字识别。因此需要先申请对应的 API 使用权限,具体步骤如下:
- 在网页浏览器(比如 Chrome 或者火狐) 的地址栏中输入 ai.baidu.com,进入到百度云 AI 的官网,在该页面中单击右上角的
控制台按钮。

- 进入到百度云 AI 官网的登录页面,输入百度账号和密码,如果没有,可以单击
立即注册超链接进行注册申请。 - 登录成功后,进入到百度云 AI 官网的控制台页面,单击左侧导航的
产品服务,展开列表,在列表的最右侧下方看到有人工智能的分类,然后选择图像识别,或者直接选择文字识别,如下图所示。

- 进入
图像识别一概览页面,要使用百度云 AI 的 API,首先需要申请权限,申请权限之前需要先创建自己的应用,因此单击创建应用按钮,如下图所示。

- 进入到
创建应用页面,该页面中需要输入应用的名称,选择应用类型,并选择接口,注意:这里的接口可以多选择一些,把后期可能用到的接口全部选择上,这样,在开发其他实例时,就可以直接使用了;选择完接口后,选择文字识别包名,这里选择不需要,输入应用描述,单击立即创建按钮,如下图所示。



- 创建完成后,单击
返回应用列表按钮,页面跳转到应用列表页面,在该页面中即可查看创建的应用,以及百度云自动为您分配的 AppID,API Key,Secret Key,这些值根据应用的不同而不同,因此一定要保存好,以便开发时使用。

二、抓取贴吧表情包
本例在百度贴吧中找到了一些自制的表情包:https://tieba.baidu.com/p/5522091060
现在想把图片都爬下来,具体操作步骤如下:
-
Network 抓包看下返回的数据是否和 Element 一致,即是否包含想要的数据,而不是通过 JS 黑魔法进行加载的。复制下第一个图的图片链接,到 Network 选项卡里的 Response 里查找一下。

-
在 Network 抓包中没有发现 Ajax 动态加载数据的踪迹。
-
三个参数猜测 pn 为 page_number,即页数,postman 或者自己写代码模拟请求,记得塞入 Host 和 X-Requested-With,验证 pn=1 是否为第一页数据,验证通过,即所有页面数据都可以通过这个接口拿到。
-
先加载拿到末页是第几页,然后走一波循环遍历即可解析数据获得图片 url,写入文件,使用多个线程进行下载,详细代码如下。
# 抓取百度贴吧某个帖子里的所有图片 import requests import time import threading import queue from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import chardet import os tiezi_url = "https://tieba.baidu.com/p/5522091060" headers = { 'Host': 'tieba.baidu.com', 'User-Agent': 'User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KH' 'TML, like Gecko) Chrome/90.0.4430.212 Safari/537.36', } pic_save_dir = 'tiezi_pic/' if not os.path.exists(pic_save_dir): # 判断文件夹是否存在,不存在就创建 os.makedirs(pic_save_dir) pic_urls_file = 'tiezi_pic_urls.txt' download_q = queue.Queue() # 下载队列 # 获得页数 def get_page_count(): try: resp = requests.get(tiezi_url, headers=headers, timeout=5) if resp is not None: resp.encoding = chardet.detect(resp.content)['encoding'] html = resp.text soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') a_s = soup.find("ul", attrs={ 'class': 'l_posts_num'}).findAll("a") for a in a_s: if a.get_text() == '尾页': return a['href'].split('=')[1] except Exception as e: print(str(e)) # 下载线程 class PicSpider(threading.Thread): def __init__(self, t_name, func): self.func = func threading.Thread.__init__(self, name=t_name) def run(self): self.func() # 获得每页里的所有图片URL def get_pics(count): params = { 'pn': count, 'ajax': '1', 't': int(time.time()) } try: resp = requests.get(tiezi_url, headers=headers, timeout=5, params=params) if resp is not None: resp.encoding = chardet.detect(resp.content)['encoding'] html = resp.text soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') imgs = soup.findAll('img', attrs={ 'class': 'BDE_Image'}) for img in imgs: print(img['src']) with open(pic_urls_file, 'a') as fout: fout.write(img['src']) fout.write('\n') return None except Exception: pass # 下载线程调用的方法 def down_pics(): global download_q while not download_q.empty(): data = download_q.get() download_pic(data) download_q.task_done() # 下载调用的方法 def download_pic(img_url): try: resp = requests.get(img_url, headers=headers, timeout=10) if resp.status_code == 200: print("下载图片:" + img_url) pic_name = img_url.split("/")[-1][0:-1] with open(pic_save_dir + pic_name, "wb+") as f: f.write(resp.content) except Exception as e: print(e) if __name__ == '__main__': print("检索判断链接文件是否存在:") if not os.path.exists(pic_urls_file): print("不存在,开始解析帖子...") page_count = get_page_count() if page_count is not None: headers['X-Requested-With'] = 'XMLHttpRequest' for page in range(1, int(page_count) + 1): get_pics(page) print("链接已解析完毕!") headers.pop('X-Requested-With') else: print("存在") print("开始下载图片~~~~") headers['Host'] = 'imgsa.baidu.com' fo = open(pic_urls_file, "r") pic_list = fo.readlines() threads = [] for pic in pic_list: download_q.put(pic) for i in range(0, len(pic_list)): t = PicSpider(t_name='线程' + str(i), func=down_pics) t.daemon = True t.start() threads.append(t) download_q.join() for t in threads: t.join() print("图片下载完毕")运行结果:

下面通过 OCR 文字识别技术,直接把表情里的文字提出来,然后来命名图片,这样就可以直接文件搜索表情关键字,可以快速找到需要的表情图片。使用谷歌的 OCR 文字识别引擎:Tesseract,对于此类大图片小文字,不太适合,识别率太低,甚至无法识别,这时使用百度云 OCR 比较合适,它能够自动定位到图片中具体位置,并找出图片中所有的文字。
三、使用 Baidu-aip
申请百度 AI 的应用 key 之后,就可以在本地系统中安装 Baidu-aip,代码如下:
pip install baidu-aip
先识别一张图片,看看效果如何:
from aip import AipOcr
# 新建一个AipOcr对象
config = {
'appId': '填写自己的appId',
'apiKey': '填写自己的apiKey',
'secretKey': '填写自己的secretKey'
}
client = AipOcr(**config)
# 识别图片里的文字
def img_to_str(image_path):
# 读取图片
with open(image_path, 'rb') as fp:
image = fp.read()
# 调用通用文字识别, 图片参数为本地图片
result = client.basicGeneral(image)
# 返回拼接结果
if 'words_result' in result:
return '\n'.join([w['words'] for w in result['words_result']])
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(img_to_str('tiezi_pic/5c0ddb1e4134970aebd593e29ecad1c8a5865dbd.jpg'))
运行程序,结果如下图所示:
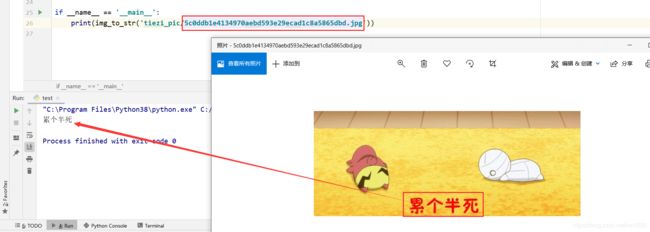
百度 AI 返回的是一个 JSON 格式数据,如下所示。返回一个字典对象,包含 log_id、words_result_num、words_result 三个键,其中 words_result_num 表示识别的文本行数,words_result 是一个列表,每个列表项目记录一条识别的文本,每个项目返回一个字典对象,包含 words 键,words 表示识别的文本。
{'words_result': [{'words': 'o。o'}, {'words': '6226-16:59'}, {'words': '绝望jpg'}], 'log_id': 1393611954748129280, 'words_result_num': 3}
o。o
6226-16:59
绝望jpg
由于每个图片中可能包含很多文字信息,如水印的日期文字,以及个别特殊的文字符号被误解析,我们需要提出的是汉字或字母信息,同时可能会包含多条汉字信息,本例选择汉字或字母最长的一条来命名文件。完整的示例代码如下:
# 识别图片文字,批量命名图片文字
import os
from aip import AipOcr
import re
import datetime
# 新建一个AipOcr对象
config = {
'appId': '填写自己的appId',
'apiKey': '填写自己的apiKey',
'secretKey': '填写自己的secretKey'
}
client = AipOcr(**config)
pic_dir = r"tiezi_pic/"
# 读取图片
def get_file_content(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'rb') as fp:
return fp.read()
# 识别图片里的文字
def img_to_str(image_path):
image = get_file_content(image_path)
# 调用通用文字识别, 图片参数为本地图片
result = client.basicGeneral(image)
# 结果拼接返回
words_list = []
if 'words_result' in result:
if len(result['words_result']) > 0:
for w in result['words_result']:
words_list.append(w['words'])
file_name = get_longest_str(words_list)
print(file_name)
file_dir_name = pic_dir + str(file_name).replace("/", "") + '.jpg'
if os.path.exists(file_dir_name): # 处理文件重名问题
sec = datetime.datetime.now().microsecond # 获取当前毫秒时值
file_dir_name = pic_dir + str(file_name).replace("/", "") + str(sec) + '.jpg'
try:
os.rename(image_path, file_dir_name)
except Exception:
print(" 重命名失败:", image_path, " => ", file_name)
# 获取字符串列表中最长的字符串
def get_longest_str(str_list):
pat = re.compile(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5A-Za-z]+')
str = max(str_list, key=hanzi_len)
result = pat.findall(str)
return ''.join(result)
def hanzi_len(item):
pat = re.compile(r'[\u4e00-\u9fa5]+')
sum = 0
for i in item:
if pat.search(i):
sum += 1
return sum
# 遍历某个文件夹下所有图片
def query_picture(dir_path):
pic_path_list = []
for filename in os.listdir(dir_path):
pic_path_list.append(dir_path + filename)
return pic_path_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
pic_list = query_picture(pic_dir)
if len(pic_list) > 0:
for i in pic_list:
img_to_str(i)
运行程序,结果如下图所示:
