鄙系有一门很著名的课,《计算机组成原理》,教你三周造台计算机。我们组今年眼瞎,选了挑战性课程,也就是教你一学期造台32位MIPS架构的计算机。前段时间全组人都被软工和编译原理所困扰(实际上,今天是编译原理第二次大作业的deadline,但我还没做完,但是我仍然在这里悠闲地写文章……),因此并未开始,直到昨天(第八周的周五)才开始研究软件的基本使用……
研究之后决定,主要仿照《自己动手写CPU》这本书的结构来进行编写和仿真。今天暂且先进行PC模块的简单实现和仿真。
参考文献
- 自己动手写处理器之第二阶段(4)——电路设计举例
- 自己动手写处理器之第二阶段(5)——ModelSim电路仿真
- Xilinx Vivado的使用详细介绍(1):创建工程、编写代码、行为仿真、Testbench
- 无数eda论坛和stackoverflow上的帖子
硬件和编译软件
我们使用的FPGA芯片是Xlinx的,具体型号是:Xilinx Artix-7系列FPGA: XC7A100TFGG676-2L,对应的编译软件是Xlinx的Vivado v2017.1 (64-bit)(当然,某些别的版本和平台的Vivado应该也可以)。
Vivado的详细使用方法可以参见这篇文章,虽然讲的是Verilog语言的编写和测试方法,但是VHDL也差不多。
简单PC模块的实现
完整代码的git仓库见这里。
这一部分的代码基本翻译自《自己动手写CPU》的2.7-2.8节,原文请参见书或作者专栏。
pc_reg.vhd
这一部分的实现十分简单,只需要在clk的上升沿给出ce的值,并且在使能的时候不断增加pc的值即可。需要注意的是,和Verilog不同,VHDL不能读输出端口的值,所以需要增加一个signal。
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_SIGNED.ALL;
entity pc_reg is
Port ( rst : in STD_LOGIC;
clk : in STD_LOGIC;
pc : out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(5 downto 0);
ce : out STD_LOGIC);
end pc_reg;
architecture Behavioral of pc_reg is
signal ce_o : STD_LOGIC;
signal pc_o : STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(5 downto 0);
begin
process (clk'event)
begin
if rising_edge(clk) then
if rst = '1' then
ce <= '0';
ce_o <= '0';
else
ce <= '1';
ce_o <= '1';
end if;
end if;
end process;
process (clk'event)
begin
if rising_edge(clk) then
if ce_o = '0' then
pc <= b"000000";
pc_o <= b"000000";
else
pc_o <= pc_o + b"000001"; -- STD_LOGIC_SIGNED library
pc <= pc_o;
end if;
end if;
end process;
end Behavioral;
rom.vhd
为了实现VHDL在模拟时读取文件数据,在这里debug了好久……显然VHDL比Verilog麻烦得多。花了好久才找到从文件读16进制数据后转换成STD_LOGIC_VECTOR的方法。
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
use IEEE.NUMERIC_STD.ALL;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_UNSIGNED.ALL;
use STD.TEXTIO.ALL;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_TEXTIO.ALL;
entity rom is
Port ( ce : in STD_LOGIC;
addr : in STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(5 downto 0);
inst : out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 downto 0));
end rom;
architecture Behavioral of rom is
begin
process
type rom_array_type is array(63 downto 0) of STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 downto 0);
variable rom_array : rom_array_type;
file filein : text;
variable fstatus : FILE_OPEN_STATUS;
variable buf : LINE;
variable output : LINE;
variable data : STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 downto 0);
variable index : STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(5 downto 0) := "000000";
begin
-- 在process中,先打开文件
file_open(fstatus, filein, "/home/zhanghuimeng/Computer_Architecture/TestThinpadProject/rom.data", read_mode);
-- 这里给出的是绝对地址,因为我也不知道如果用相对地址,应该把文件放在哪里……
while not endfile(filein) loop
readline(filein, buf);
-- 正常情况下,endfile(filein)就可以了,但是这里需要单独判断buf有没有读到内容
-- 否则会报错:Error: STD_LOGIC_ll64.HREAD End of String encountered
if buf'length = 0 then
exit;
end if;
hread(buf, data);
rom_array(to_integer(unsigned(index))) := data;
-- 打印rom_array(index)的值
-- 这些并不是必须的,但调试的时候比较方便。
deallocate(output);
write(output, string'("rom_array("));
write(output, integer'(to_integer(unsigned(index))));
write(output, string'(") = "));
write(output, rom_array(to_integer(unsigned(index))));
report output.all;
index := index + "000001";
end loop;
-- 等待ce和addr变化
-- 正常情况下是写在process的敏感信号中,但此处需要读完rom_array的初始数据后再开始等待
loop
wait on ce, addr;
if (ce = '0') then
inst <= x"00000000";
else
inst <= rom_array(to_integer(unsigned(addr)));
end if;
end loop;
end process;
end Behavioral;
顶层文件inst_fetch.vhd
除了把端口都连起来之外没有什么需要特别注意的。不过,VHDL中,在map端口的时候,属于实体的端口名写在前面,属于顶层文件的端口名和信号名写在后面。
library IEEE;
use IEEE.STD_LOGIC_1164.ALL;
entity inst_fetch is
Port ( rst : in STD_LOGIC;
clk : in STD_LOGIC;
inst_o : out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 downto 0));
end inst_fetch;
architecture Behavioral of inst_fetch is
component pc_reg
Port ( rst : in STD_LOGIC;
clk : in STD_LOGIC;
pc : out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(5 downto 0);
ce : out STD_LOGIC);
end component;
component rom is
Port ( ce : in STD_LOGIC;
addr : in STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(5 downto 0);
inst : out STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(31 downto 0));
end component;
signal pc_to_addr : STD_LOGIC_VECTOR(5 downto 0);
signal ce_to_ce : STD_LOGIC;
begin
pc_reg_0: pc_reg port map(rst => rst, clk => clk, pc => pc_to_addr, ce => ce_to_ce);
rom_0: rom port map(ce => ce_to_ce, addr => pc_to_addr, inst => inst_o);
end Behavioral;
建立Testbench和仿真
仿真文件rom.data
00000000
01010101
02020202
03030303
04040404
05050505
...
仿真文件inst_fetch_testbench.v
因为VHDL写起来太过麻烦所以就直接用Verilog写(抄)《自己动手写CPU》了。(Vivado仿真器支持VHDL和Verilog的混合使用,详情见Vivado 仿真器— 使用混合语言仿真)
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
module inst_fetch_testbench;
reg clk;
reg rst;
wire[31:0] inst;
initial begin
clk = 1'b0;
forever #10 clk = ~clk;
end
initial begin
rst = 1'b1;
#195 rst = 1'b0;
#1000 $stop;
end
inst_fetch inst_fetch_0(
.clk(clk),
.rst(rst),
.inst_o(inst)
);
endmodule
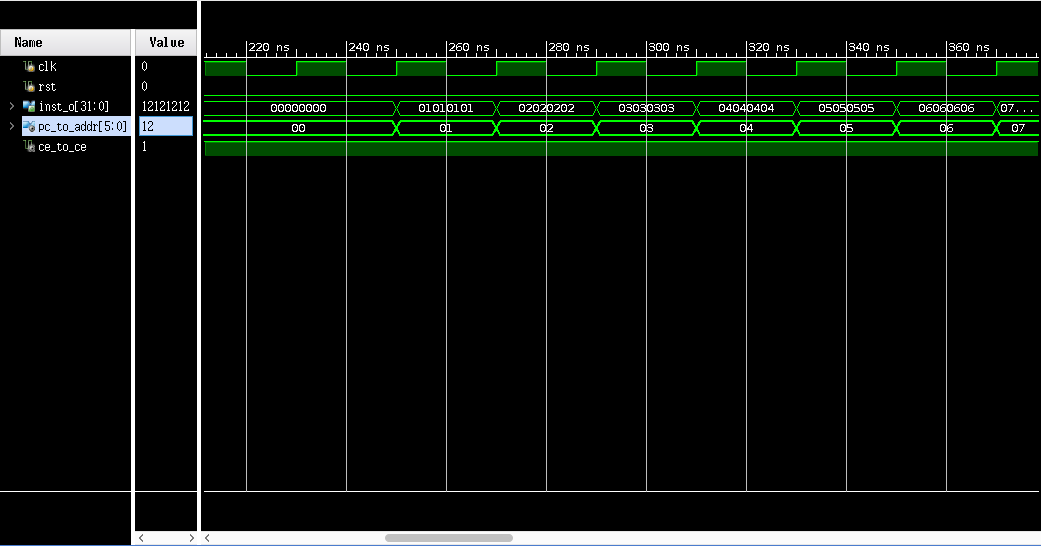
Behavioral Simulation 结果
这说明实现是正确的。