PL/SQL 是在我们常用语言上的扩展,使SQL语句有了结构化程序设计的特性,也就是我们常说的3种流程结构
- 顺序结构
- 分支结构
- 循环结构
这里我们不用存储过程,先单纯的用PL/SQL做连续,还是oracle pl/sql这本书上的例子
--创建个员工表
create table t_emp
(
id number(10) not null, --主键ID
name varchar2(10), --姓名
job varchar2(30), --工作
money number(10,2), --薪资
deptno number --部门编码
);
--定义主键
alter table t_emp add constraint emp_id primary key(id);
--创建自增长序列
create sequence seq_emp
increment by 1 --每次加1
start with 1 --开始于1
nomaxvalue --不设置最大值
minvalue 1--最小值1,可以设置nominvalue 无最小值
nocycle --不循环
cache 5 --缓存5
insert into t_emp (id,name,job,money,deptno) values (seq_emp.nextval,'张三','后台开发','1000',1);
insert into t_emp (id,name,job,money,deptno) values (seq_emp.nextval,'李四','前段','800',1);
insert into t_emp (id,name,job,money,deptno) values (seq_emp.nextval,'王五','测试','700',2);
insert into t_emp (id,name,job,money,deptno) values (seq_emp.nextval,'赵六','运维','600',3);
commit;
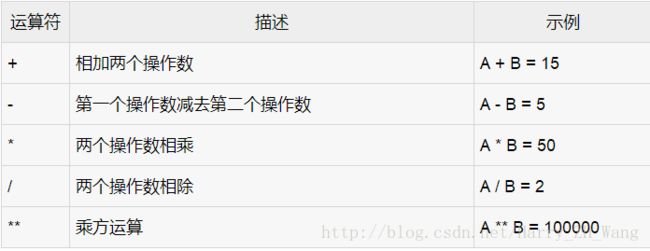
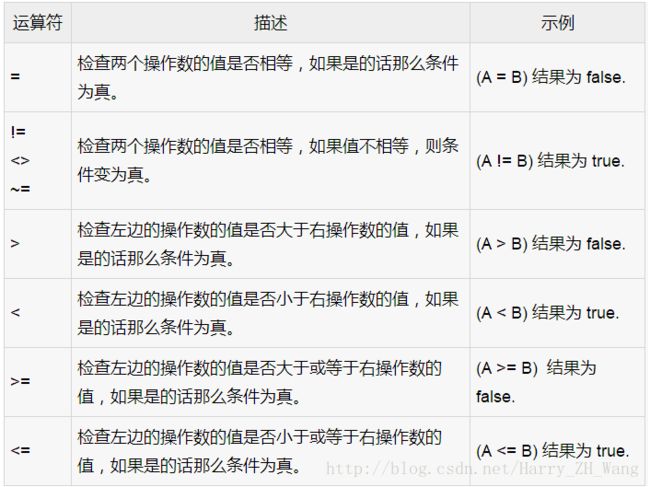
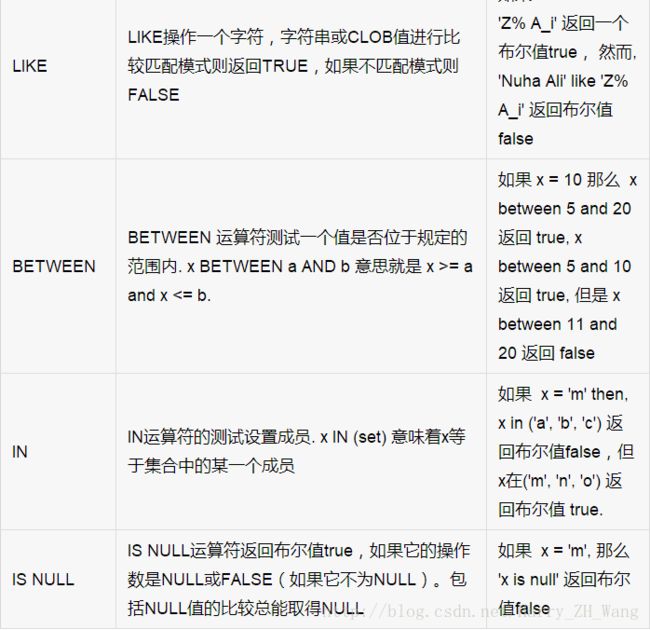
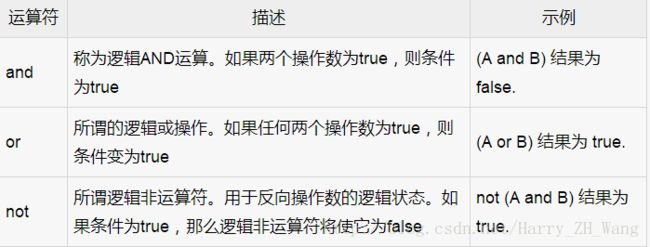
在流程之前普及下PL/SQL中的关系运算符
文章连接:http://www.yiibai.com/plsql/plsql_operators.html
算数运算符
关系运算符
比较运算符
逻辑运算符
这个是简单的顺序流程
--声明
declare
--定义变量
t_money1 number;
t_money2 number;
t_sumMoney number;
begin
--查询id为1的员工工资 赋值给变量t_money1
select money into t_money1 from t_emp where id = '1';
-- 查询id为2的员工工资,赋值给变量2
select money into t_money2 from t_emp where id = '2';
--plsql中 等号 用:= 计算两个员工的工资和
t_sumMoney := t_money1+t_money2;
--结果输出
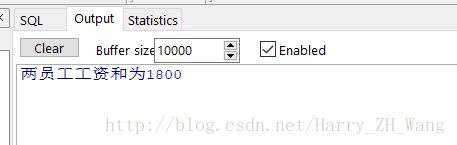
dbms_output.put_line('两员工工资和为'||t_sumMoney);
end;
输出结果
--查询指定员工,判断职务,如果是开发加薪20%,测试加薪10%,运维加薪10%,前段加薪15%
declare
-- constant表示常量,这里我们定义常量常量
add_kaifa constant number := 0.20;
add_ceshi constant number := 0.10;
add_yunwei constant number := 0.10;
add_qianduan constant number := 0.15;
v_job varchar2(50);
begin
select job into v_job from t_emp te where te.id = 1;
if v_job ='后台开发'
then
update t_emp te set te.money = te.money*(1+add_kaifa) where te.id = 1;
elsif v_job ='测试'
then
update t_emp te set te.money = te.money*(1+add_ceshi) where te.id = 1;
elsif v_job='运维'
then
update t_emp te set te.money = te.money*(1+add_yunwei) where te.id = 1;
elsif v_job='前段'
then
update t_emp te set te.money = te.money*(1+add_qianduan) where te.id = 1;
end if;
--显示处理的信息
dbms_output.put_line('id为:'||1||'员工加薪成功');
--定义异常
exception
when no_data_found
then
dbms_output.put_line('未找到员工');
end;
这里需要注意是elsif 不是elseif 或者else if
--正确的写法
if 条件 then 执行的方法 eslif 条件 then
PL/SQL中的循环大体有三种,loop. while-loop ,for-loop 。这里先展示一个loop
给所有员工按照职位进行加薪
-- loop 循环为员工加薪
declare
-- constant表示常量,这里我们定义常量常量
add_kaifa constant number := 0.20;
add_ceshi constant number := 0.10;
add_yunwei constant number := 0.10;
add_qianduan constant number := 0.15;
v_job varchar2(50);
--定义游标,游标查询后并不会对表数据进行锁表,如果使用了for update 就会对查询的数据锁表
cursor list_job is select job from t_emp for update;
begin
open list_job;--打开游标
loop
fetch list_job into v_job;--提取游标值
exit when list_job%notfound;--当循环到最后一个退出循环
if v_job ='后台开发'
then
update t_emp te set te.money = te.money*(1+add_kaifa) where current of list_job;--当需要更新或删除被update的数据需使用current of
elsif v_job ='测试'
then
update t_emp te set te.money = te.money*(1+add_ceshi) where current of list_job;
elsif v_job='运维'
then
update t_emp te set te.money = te.money*(1+add_yunwei) where current of list_job;
elsif v_job='前段'
then
update t_emp te set te.money = te.money*(1+add_qianduan) where current of list_job;
end if;
--输出提示
dbms_output.put_line ('职位为:'||v_job||'的员工加薪成功');
end loop;
--异常处理
close list_job;--关闭游标
exception
when no_data_found
then
dbms_output.put_line('未找到员工');
end;
在PL/SQL中能直接使用DDL语句进行增删查
--PL/SQL直接使用DDL语句
declare
v_job varchar2(50);
begin
select job into v_job from t_emp where id = '1';
dbms_output.put_line(v_job);
end;
但是不能直接使用DML语句进行建表等数据库操作,不过我们可以通过变量赋值的方式进行
--PL/SQL DML语句使用
declare
v_createTable varchar2(100) :=
'
create table t_emp
(
id number(10) not null,
name varchar2(10),
job varchar2(30),
money number(10,2),
deptno number
);
'
begin
execute immediate v_createTable;--执行DML语句
end;