springboot源码分析 (一)启动流程及内嵌tomcat源码
本来想一篇分析完springboot核心源码的,发现内容有点多,就拆分为多个章节。
按照个人理解,springboot核心有这么几个(相对于spring来说):
1.tomcat是如何内嵌的
2.自动装配原理 自动装配稍微分析了一下,可能不是很详细 自定义starter及自动配置源码分析
3.事件驱动机制 4.配置文件怎么被加载的
5.热部署原理
这一章作为起点,先分析一下springboot启动流程和tomcat是如何被内嵌的,不对其他问题做过多分析。
springboot启动流程源码分析
首先我们以这个方法为起点,开始分析springboot启动流程源码。
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(xxx.class, args);
}向里面走两层,到这一个方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}先看一下这个构造方法:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
//可以自定义加载器
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//记录配置源
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//推断web类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//初始化classpath下 META-INF/spring.factories中配置的ApplicationContextInitializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//初始化classpath下 META-INF/spring.factories中配置的ApplicationContextInitializer
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//记录主类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}进入getSpringFactoriesInstances()查看
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type, Class[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// 从META-INF/spring.factories中获取资源
Set names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
//整个 springBoot 框架中获取factories的统一方法
List instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
} 构造方法分析完成,主要是初始化一些内容,然后继续执行new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); //记录运行时间
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//java.awt.headless是J2SE的一种模式用于在缺少显示屏、键盘或者鼠标时的系统配置,很多监控工具如jconsole
// 需要将该值设置为true,系统变量默认为true
configureHeadlessProperty();
//从META-INF/spring.factories中获取监听器 SpringApplicationRunListeners
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();//遍历回调SpringApplicationRunListeners的starting方法
try {
//封装命令行参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//构造应用上下文环境,完成后回调SpringApplicationRunListeners的environmentPrepared方法
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);//处理需要忽略的Bean
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);//打印banner
//根据是否web环境创建相应的IOC容器
context = createApplicationContext();
//实例化SpringBootExceptionReporter,用来支持报告关于启动的错误
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
//准备上下文环境,将environment保持到IOC容器中
//执行applyInitializers,遍历回调ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法
//遍历回调SpringApplicationRunListeners的contextPrepared方法
//遍历回调SpringApplicationRunListeners的contextLoaded方法
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);//刷新应用上下文,组件扫描、创建、加载,同spring的refresh方法
//从IOC容器获取所有的ApplicationRunner(先调用)和CommandLinedRunner进行回调
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();//时间记录停止
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);//发布容器启动完成事件
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
} 这个run方法已经做完了所有启动的工作,这章我们先来分析tomcat怎么被内嵌的。
tomcat内嵌源码分析
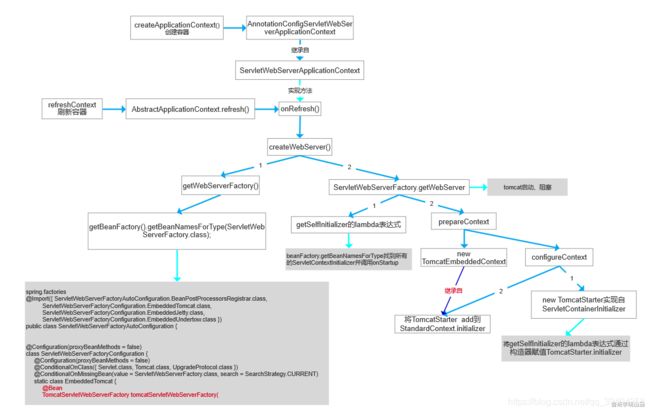
先来看一张流程图
回到run方法中,查看createApplicationContext()方法
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
//servlet方式:加载org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
//reactive方式:加载org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
//不是以上两种方式,加载org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(spring的非web容器)
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
//去得到一个ConfigurableApplicationContext对象
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}因为获取contextClass这个实例,目前我们只分析contextClass=org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。
执行AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext无参构造器,先执行父类的构造,然后一层一层向下执行,其中会在GenericApplicationContext的构造方法中创建一个DefaultListableBeanFactory的beanFactory。
接着回到run方法继续走,进入到refreshContext()方法,一直到spring的refresh()方法。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
prepareRefresh();
// 刷新BeanFactory,得到一个空的BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 准备BeanFactory
// 1. 设置BeanFactory的类加载器、表达式解析器、类型转化注册器
// 2. 添加三个BeanPostProcessor,注意是具体的BeanPostProcessor实例对象
// 3. 记录ignoreDependencyInterface
// 4. 记录ResolvableDependency
// 5. 添加三个单例Bean
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 子类可以对BeanFactory进行进一步初始化
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// BeanFactory准备好了之后,执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor,开始对BeanFactory进行处理
// 默认情况下:
// 此时beanFactory的beanDefinitionMap中有6个BeanDefinition,5个基础BeanDefinition+AppConfig的BeanDefinition
// 而这6个中只有一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
// 这里会执行ConfigurationClassPostProcessor进行@Component的扫描,扫描得到BeanDefinition,并注册到beanFactory中
// 注意:扫描的过程中可能又会扫描出其他的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,那么这些BeanFactoryPostProcessor也得在这一步执行
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 从BeanFactory找出扫描得到得BeanPostProcessor,实例化并注册到BeanFactory中
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 初始化MessageSource,如果配置了一个名字叫做“messageSource”的BeanDefinition
// 就会把这个Bean创建出来,并赋值给ApplicationContext的messageSource属性
// 这样ApplicationContext就可以使用国际化的功能了
initMessageSource();
// 设置ApplicationContext的applicationEventMulticaster
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 钩子方法,父类没做任何实现,交给子类去实现,执行子类的onRefresh方法
onRefresh();
// 注册Listener
registerListeners();
// 完成beanFactory的初始化(实例化非懒加载的单例bean)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 发布事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}该方法和spring的refresh()一样。而当初spring留给子类扩展的onRefresh()方法就需要用到了。执行到onRefresh()方法,这时就会进入到ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefresh()方法
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
createWebServer();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex);
}
}进入到 createWebServer()
private void createWebServer() {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
//获取servlet上下文
ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) {
//从beanFactory中获取接口为ServletWebServerFactory的类,也就是TomcatServletWebServerFactory
ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory();
//执行getWebServer,也就是tomcat启动
this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer());
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown",
new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer));
getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop",
new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer));
}
else if (servletContext != null) {
try {
getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex);
}
}
initPropertySources();
}先记下这个方法getSelfInitializer(),是一个点,后面分析。
在getWebServerFactory()方法中会获取到一个接口为ServletWebServerFactory的实现类,也就是TomcatServletWebServerFactory,这个TomcatServletWebServerFactory实现类是何时加入到springboot里面的呢,这里就用到了自动装配。会引入ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration配置类,然后又@import了ServletWebServerFactoryConfiguration.EmbeddedTomcat.class.在这里创建了TomcatServletWebServerFactory的bean。
进入到getWebServer()方法中看tomcat是如何启动的。该方法设置了一些tomcat基本配置
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
//准备容器
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//获得tomcat服务
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}继续进入getTomcatWebServer()方法,直到执行到initialize()中的this.tomcat.start()方法,到这里就进入了tomcat的逻辑。
private void initialize() throws WebServerException {
logger.info("Tomcat initialized with port(s): " + getPortsDescription(false));
synchronized (this.monitor) {
try {
addInstanceIdToEngineName();
Context context = findContext();
context.addLifecycleListener((event) -> {
if (context.equals(event.getSource()) && Lifecycle.START_EVENT.equals(event.getType())) {
// Remove service connectors so that protocol binding doesn't
// happen when the service is started.
removeServiceConnectors();
}
});
// 启动tomcat
this.tomcat.start();
// We can re-throw failure exception directly in the main thread
rethrowDeferredStartupExceptions();
try {
ContextBindings.bindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader());
}
catch (NamingException ex) {
// Naming is not enabled. Continue
}
//阻塞tomcat,不让其关闭
startDaemonAwaitThread();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
stopSilently();
destroySilently();
throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat", ex);
}
}
}tomcat源码本篇不做过多分析,springboot内嵌tomcat的过程到这里就分析完了。
DispatcherServlet怎么被注入进来的
回到getWebServer()方法中,
public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) {
Registry.disableRegistry();
}
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat");
tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath());
Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol);
connector.setThrowOnFailure(true);
tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector);
customizeConnector(connector);
tomcat.setConnector(connector);
tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false);
configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine());
for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) {
tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector);
}
//准备容器
prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers);
//获得tomcat服务
return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat);
}查看 prepareContext()方法
protected void prepareContext(Host host, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) {
//设置一些参数
File documentRoot = getValidDocumentRoot();
TomcatEmbeddedContext context = new TomcatEmbeddedContext();
if (documentRoot != null) {
context.setResources(new LoaderHidingResourceRoot(context));
}
context.setName(getContextPath());
context.setDisplayName(getDisplayName());
context.setPath(getContextPath());
File docBase = (documentRoot != null) ? documentRoot : createTempDir("tomcat-docbase");
context.setDocBase(docBase.getAbsolutePath());
context.addLifecycleListener(new FixContextListener());
context.setParentClassLoader((this.resourceLoader != null) ? this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader()
: ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
resetDefaultLocaleMapping(context);
addLocaleMappings(context);
try {
context.setCreateUploadTargets(true);
}
catch (NoSuchMethodError ex) {
// Tomcat is < 8.5.39. Continue.
}
configureTldSkipPatterns(context);
WebappLoader loader = new WebappLoader();
loader.setLoaderClass(TomcatEmbeddedWebappClassLoader.class.getName());
loader.setDelegate(true);
context.setLoader(loader);
if (isRegisterDefaultServlet()) {
addDefaultServlet(context);
}
if (shouldRegisterJspServlet()) {
addJspServlet(context);
addJasperInitializer(context);
}
context.addLifecycleListener(new StaticResourceConfigurer(context));
ServletContextInitializer[] initializersToUse = mergeInitializers(initializers);
host.addChild(context);
//重点看这里
configureContext(context, initializersToUse);
postProcessContext(context);
}进入configureContext方法
protected void configureContext(Context context, ServletContextInitializer[] initializers) {
TomcatStarter starter = new TomcatStarter(initializers);
if (context instanceof TomcatEmbeddedContext) {
TomcatEmbeddedContext embeddedContext = (TomcatEmbeddedContext) context;
embeddedContext.setStarter(starter);
embeddedContext.setFailCtxIfServletStartFails(true);
}
//重点,
context.addServletContainerInitializer(starter, NO_CLASSES);
for (LifecycleListener lifecycleListener : this.contextLifecycleListeners) {
context.addLifecycleListener(lifecycleListener);
}
for (Valve valve : this.contextValves) {
context.getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
for (ErrorPage errorPage : getErrorPages()) {
org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.ErrorPage tomcatErrorPage = new org.apache.tomcat.util.descriptor.web.ErrorPage();
tomcatErrorPage.setLocation(errorPage.getPath());
tomcatErrorPage.setErrorCode(errorPage.getStatusCode());
tomcatErrorPage.setExceptionType(errorPage.getExceptionName());
context.addErrorPage(tomcatErrorPage);
}
for (MimeMappings.Mapping mapping : getMimeMappings()) {
context.addMimeMapping(mapping.getExtension(), mapping.getMimeType());
}
configureSession(context);
new DisableReferenceClearingContextCustomizer().customize(context);
for (TomcatContextCustomizer customizer : this.tomcatContextCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(context);
}
}查看 context.addServletContainerInitializer(starter, NO_CLASSES);里面就是将ServletContainerInitializer放入到了initializers中
public void addServletContainerInitializer(
ServletContainerInitializer sci, Set> classes) {
initializers.put(sci, classes);
} 而当tomcat启动时会调用StandardContext.startInternal()方法,而startInternal()方法中有这么一段代码
for (Map.Entry>> entry :
initializers.entrySet()) {
try {
//获取到ServletContainerInitializer的bean,调用其onStartup()方法
entry.getKey().onStartup(entry.getValue(),
getServletContext());
} catch (ServletException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.sciFail"), e);
ok = false;
break;
}
} 这时会调用到TomcatStarter的onStartup方法
public void onStartup(Set> classes, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
try {
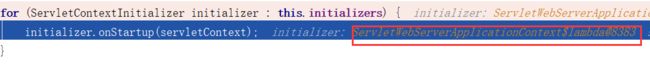
for (ServletContextInitializer initializer : this.initializers) {
initializer.onStartup(servletContext);
}
//省略
}
} 循环到这里时是个lambda表达式,这里为什么是lambda表达式呢?这时我们就要把上面getSelfInitializer()这个点说一下了。
getSelfInitializer()返回的是一个lambda表达式
return this::selfInitialize;对这个方法进行了引用
private void selfInitialize(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
prepareWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
registerApplicationScope(servletContext);
WebApplicationContextUtils.registerEnvironmentBeans(getBeanFactory(), servletContext);
for (ServletContextInitializer beans : getServletContextInitializerBeans()) {
beans.onStartup(servletContext);
}
}当这个lamdba被真实调用时,执行 beans.onStartup()方法,进入到RegistrationBean.register()->DynamicRegistrationBean.register()方法
protected final void register(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
D registration = addRegistration(description, servletContext);
if (registration == null) {
logger.info(StringUtils.capitalize(description) + " was not registered (possibly already registered?)");
return;
}
configure(registration);
}进入到ServletRegistrationBean.addRegistration()方法
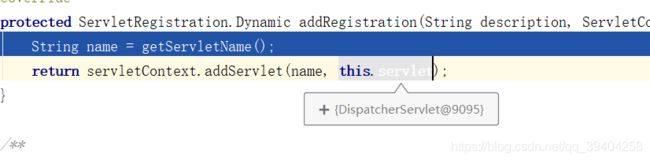
protected ServletRegistration.Dynamic addRegistration(String description, ServletContext servletContext) {
String name = getServletName();
return servletContext.addServlet(name, this.servlet);
}看servletContext.addServlet(name, this.servlet);这句代码,这个this.servlet是什么,我们查看一下。
这个this.servlet什么时候就是dispatcherServlet了?我们来看一下这个dispatcherServlet是怎么来的。
这时就又用到了自动装配了。
进入这个配置类中查看这个方法dispatcherServletRegistration()
@Bean(name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_REGISTRATION_BEAN_NAME)
@ConditionalOnBean(value = DispatcherServlet.class, name = DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME)
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean dispatcherServletRegistration(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet,
WebMvcProperties webMvcProperties, ObjectProvider multipartConfig) {
//将dispatcherServlet注入进来
DispatcherServletRegistrationBean registration = new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet,
webMvcProperties.getServlet().getPath());
registration.setName(DEFAULT_DISPATCHER_SERVLET_BEAN_NAME);
registration.setLoadOnStartup(webMvcProperties.getServlet().getLoadOnStartup());
multipartConfig.ifAvailable(registration::setMultipartConfig);
return registration;
} 查看DispatcherServletRegistrationBean构造方法,
public DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(DispatcherServlet servlet, String path) {
super(servlet);
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.path = path;
super.addUrlMappings(getServletUrlMapping());
}调用了super(servlet);继续查看父类的构造方法
public ServletRegistrationBean(T servlet, boolean alwaysMapUrl, String... urlMappings) {
Assert.notNull(servlet, "Servlet must not be null");
Assert.notNull(urlMappings, "UrlMappings must not be null");
//this就是ServletRegistrationBean
this.servlet = servlet;
this.alwaysMapUrl = alwaysMapUrl;
this.urlMappings.addAll(Arrays.asList(urlMappings));
}这个dispatcherServlet就被设置进来了。