深度解析XML的结构与类映射
- XML概述
可扩展标记语言 (Extensible Markup Language, XML) ,用于标记电子文件使其具有结构性的标记语言,可以用来标记数据、定义数据类型,是一种允许用户对自己的标记语言进行定义的源语言。 XML是标准通用标记语言 (SGML) 的子集,非常适合 Web 传输。XML 提供统一的方法来描述和交换独立于应用程序或供应商的结构化数据。我经常用它来保存一些数据,或者是一些配置参数。
-
- XmlElement
节点元素
-
- XmlAttribute
-
- InnerText
节点文本内容
- 类型定义与XML结构的映射
-
- XmlElement
默认情况下(不加任何Attribute),类型中的属性或者字段,都会生成XmlElement。
-
- XmlAttribute
如果希望类型中的属性或者字段生成XmlAttribute,需要在类型的成员上用[XmlAttribute]来指出。
public class Class2 {
[XmlAttribute]
public int IntValue { get; set; }
[XmlElement]
public string StrValue { get; set; }
}
|
-
- InnerText
如果希望类型中的属性或者字段生成InnerText,需要在类型的成员上用[XmlText]来指出。
public class Class3 {
[XmlAttribute]
public int IntValue { get; set; }
[XmlText]
public string StrValue { get; set; }
}
|
-
- 重命名节点名称
如果希望类型中的属性或者字段生成InnerText,需要在类型的成员上用[XmlText]来指出。
[XmlType("c4")]
public class Class4 {
[XmlAttribute("id")]
public int IntValue { get; set; }
[XmlElement("name")]
public string StrValue { get; set; }
}
|
-
- 列表和数组的序列化
数组和列表都能直接序列化,如果要重命名根节点名称,需要创建一个新类型来实现。根节点重命名需要用[XmlRoot]来指出。
[XmlRoot("c4List")]
public class Class4List : List<Class4> { }
|
-
- 列表和数组的做为数据成员的序列化
数组和列表都在序列化时,默认情况下会根据类型中的数据成员名称生成一个节点,列表项会生成子节点,如果要重命名,可以使用[XmlArrayItem]和[XmlArray]来实现。还可以直接用[XmlElement]控制不生成列表的父节点。
public class Root {
public Class3 Class3 { get; set; }
[XmlArrayItem("c2")]
[XmlArray("cccccccccccc")]
public List<Class2> List { get; set; }
}
|
public class Root {
public Class3 Class3 { get; set; }
[XmlElement("c2")]
public List<Class2> List { get; set; }
}
|
-
- 类型继承与反序列化
列表元素可以是同一种类型,也可以不是同一种类型(某个类型的派生类)。同时为列表成员指定多个[XmlArrayItem(typeof(XXX))]可实现多种派生类型混在一起输出。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<XRoot xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<List>
<x1 aa="1" bb="2" />
<x1 aa="3" bb="4" />
<x2>
<cc>ccccccccccc</cc>
<dd>dddddddddddd</dd>
</x2>
</List>
</XRoot>
|
public class XBase { }
[XmlType("x1")]
public class X1 : XBase {
[XmlAttribute("aa")]
public int AA { get; set; }
[XmlAttribute("bb")]
public int BB { get; set; }
}
[XmlType("x2")]
public class X2 : XBase {
[XmlElement("cc")]
public string CC { get; set; }
[XmlElement("dd")]
public string DD { get; set; }
}
public class XRoot {
[XmlArrayItem(typeof(X1)),
XmlArrayItem(typeof(X2))]
public List<XBase> List { get; set; }
}
|
-
- 排除不需要序列化的成员
默认情况下,类型的所有公开的数据成员(属性,字段)在序列化时都会被输出,如果希望排除某些成员,可以用[XmlIgnore]来指出。
public class TestIgnore {
[XmlIgnore] // 这个属性将不会参与序列化 public int IntValue { get; set; }
public string StrValue { get; set; }
public string Url;
}
|
-
- 强制指定成员的序列化顺序
使用Order指定元素的排序。
public class TestIgnore {
[XmlElement(Order = 1)]
public string StrValue { get; set; }
[XmlElement(Order = 2)]
public string Url;
}
|
-
- 反序列化
如果XML是由类型序列化得到那的,那么反序列化的调用代码是很简单的,反之,如果要面对一个没有类型的XML,就需要我们先设计一个(或者一些)类型出来,这是一个逆向推导的过程,请参考以下步骤:
- 首先要分析整个XML结构,定义与之匹配的类型。
- 如果XML结构有嵌套层次,则需要定义多个类型与之匹配。
- 定义具体类型(一个层级下的XML结构)时,请参考以下表格。
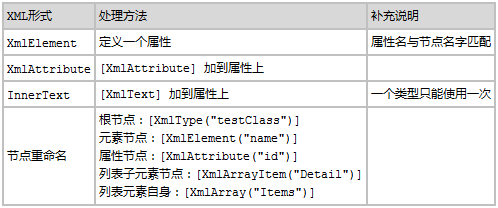
- XML数据读写代码示例
如果只是为了保存和读取数据而不关心xml文件结构的话,可以使用序列化的方式来读写xml,这样做操作相当的简单。
// 1. 首先要创建或者得到一个数据对象 Order order = GetOrderById(123);
// 2. 用序列化的方法生成XML string xml = XmlHelper.XmlSerialize(order, Encoding.UTF8);
// 3. 从XML读取数据并生成对象 Order order2 = XmlHelper.XmlDeserialize<Order>(xml, Encoding.UTF8);
|
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Xml.Serialization; using System.IO; using System.Xml; /// <summary> /// 将一个对象序列化 /// </summary>
private static void XmlSerializeInternal(Stream stream, object o, Encoding encoding)
{
if( o == null )
throw new ArgumentNullException("o");
if( encoding == null )
throw new ArgumentNullException("encoding");
XmlSerializer serializer = new XmlSerializer(o.GetType());
XmlWriterSettings settings = new XmlWriterSettings();
settings.Indent = true;
settings.NewLineChars = "\r\n";
settings.Encoding = encoding;
settings.IndentChars = " ";
using( XmlWriter writer = XmlWriter.Create(stream, settings) ) {
serializer.Serialize(writer, o);
writer.Close();
}
}
/// <summary> /// 将一个对象序列化为XML字符串 /// </summary> /// <param name="o">要序列化的对象</param> /// <param name="encoding">编码方式</param> /// <returns>序列化产生的XML字符串</returns> public static string XmlSerialize(object o, Encoding encoding)
{
using( MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream() ) {
XmlSerializeInternal(stream, o, encoding);
stream.Position = 0;
using( StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(stream, encoding) ) {
return reader.ReadToEnd();
}
}
}
/// <summary> /// 将一个对象按XML序列化的方式写入到一个文件 /// </summary> /// <param name="o">要序列化的对象</param> /// <param name="path">保存文件路径</param> /// <param name="encoding">编码方式</param> public static void XmlSerializeToFile(object o, string path, Encoding encoding)
{
if( string.IsNullOrEmpty(path) )
throw new ArgumentNullException("path");
using( FileStream file = new FileStream(path, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write) ) {
XmlSerializeInternal(file, o, encoding);
}
}
/// <summary> /// 从XML字符串中反序列化对象 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">结果对象类型</typeparam> /// <param name="s">包含对象的XML字符串</param> /// <param name="encoding">编码方式</param> /// <returns>反序列化得到的对象</returns> public static T XmlDeserialize<T>(string s, Encoding encoding)
{
if( string.IsNullOrEmpty(s) )
throw new ArgumentNullException("s");
if( encoding == null )
throw new ArgumentNullException("encoding");
XmlSerializer mySerializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(T));
using( MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(encoding.GetBytes(s)) ) {
using( StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(ms, encoding) ) {
return (T)mySerializer.Deserialize(sr);
}
}
}
/// <summary> /// 读入一个文件,并按XML的方式反序列化对象。 /// </summary> /// <typeparam name="T">结果对象类型</typeparam> /// <param name="path">文件路径</param> /// <param name="encoding">编码方式</param> /// <returns>反序列化得到的对象</returns> public static T XmlDeserializeFromFile<T>(string path, Encoding encoding)
{
if( string.IsNullOrEmpty(path) )
throw new ArgumentNullException("path");
if( encoding == null )
throw new ArgumentNullException("encoding");
string xml = File.ReadAllText(path, encoding);
return XmlDeserialize<T>(xml, encoding);
}
}
|