spring mvc运行流程源码深度解析(同步debug效果更佳)
本文目录
-
- 分析Servlet之init()
- initWebApplicationContext()
- springMvc容器的初始化
- 分析Servlet之Service()
- springMvc核心代码之doDispatch()
- doDispatch之getHandler()
- getHandler()
-
- getHandlerInternal()
-
- lookupHandlerMethod()
-
- addMatchingMappings
-
- getMatchingMapping()
- createWithResolvedBean()
- getHandlerExecutionChain()
- getHandlerAdapter
- springmvc执行前置拦截器(preHandle)
- ha.handle()
-
- invokeHandlerMethod(调用接口、返回视图)
-
- invokeAndHandle(调用接口、处理返回值)
- springmvc调用接口过程
-
- getMethodArgumentValues(获取参数)
-
- resolveArgument(解析参数返回)
- doInvoke(真正调用)
- springmvc处理返回值过程
-
- handleReturnValue(解析返回值)
- springmvc封装视图(getModelAndView)
- springmvc执行中置拦截器
- springmvc视图渲染
-
- processDispatchResult
-
- render()
- springmvc执行后置拦截器
- 到此springMvc运行流程源码分析over
前言:Spring Mvc的设计主要围绕着DispatcherServlet来展开的,直接分析DispatcherServlet即可。个人理解SpringMvc其实就是一个Servelt Plus 。
观察DispatcherServlet继承关系可以得出如下结论:
- DispatcherServlet其实就是一个Servlet,而 一个Servelt完整生命周期必然少不了 init()、service()、destory() 这几个步骤
- DispatcherServlet 继承到 HttpServletBean这里是由Spring实现的,再往上的HttpServlet不关Spring的事。故我们只需分析DispatcherServlet、FrameworkServlet、HttpServletBean 即可

分析Servlet之init()
仔细观察DispatcherServlet、FrameworkServlet、HttpServletBean这三个类,只有 HttpServletBean 中有init()方法。点进 init()
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
//点进去
initServletBean();
}
上述的 init()方法有很多杂七杂八的代码,关注 initServletBean() 即可,点进去 initServletBean() 来到了FrameworkServlet类中的 initServletBean(),点进去 initWebApplicationContext();
initWebApplicationContext()
代码很多,initWebApplicationContext()方法主要做了俩件事。
- 设置父子容器。springMvc容器:ConfigurableWebApplicationContext、spring容器:WebApplicationContext。本质俩个容器都是WebApplicationContext类型的
- springMvc容器的初始化
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
/**
* spring容器
*/
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
/**
* springmvc容器
*/
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
/**
* 设置父子容器
*/
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
/**
* 里面都是对应父子容器的设置
*/
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
/**
* 设置父子容器
*/
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
/**
* springmvcrong容器初始化
*/
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
springMvc容器的初始化
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
/**
* 初始化上下文,在启动时期执行
*/
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
/**
* 初始化映射器
*/
initHandlerMappings(context);
/**
* 初始化handler适配器
*/
initHandlerAdapters(context);
/**
*
*/
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
springMvc容器的初始化代码如上,个人感觉和spring源码类似啊,短短几行铺开了分析简直不要太爽,本文中的源码分析主要和图中标注箭头的几个方法有关哦,现在还只是开胃小菜,真正的springMvc运行流程源码分析现在开始
分析Servlet之Service()
仔细观察DispatcherServlet、FrameworkServlet、HttpServletBean这三个类,只有FrameworkServlet中有service()方法,但是里面调用的是HttpServlet中的service(),不关我们SpringMvc的事。
super.service(request, response);
难道这样就能阻止我们分析源码了吗?不存在的,点开doGet()
springMvc核心代码之doDispatch()
doService() 代码这里就不贴了,里面核心调用代码为doDispatch(),里面的代码重点看!
/**
* 当前springmvc核心代码
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
/**
* 检查多媒体文件类型,验证当前请求
*/
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
/**
* 获取HandlerExecutionChain对象,根据请求的不一样,返回的HandlerExecutionChain对象也不一样
*/
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
/**
* handler:handlerMethod
* mappedHandler:new HandlerExecutionChain(handler)
* mappedHandler.getHandler():我们的handlerMethod对象
* 获取相应HandlerExecutionChain对象的适配器(简单)
*/
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
/**
* 顺序遍历拦截器,执行相应的前置通知
* 方法返回false,将不会执行如下的逻辑了。
*/
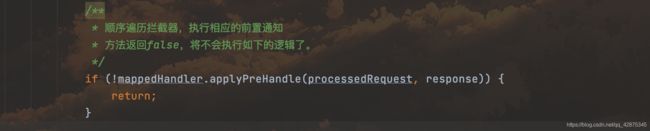
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
/**
* 处理适配器,返回值modeAndView,开始执行调用我们的controller方法
* processedRequest:request
* response:response
* mappedHandler.getHandler():handlerMethod
*/
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
/**
* 倒叙遍历拦截器执行里面的postHandle()方法
*/
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
} catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
} catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
/**
* 1:当执行controller出现异常的时候,dispatchException会存在值,由于异常没有抛出去,还会接着执行这行代码
* 代码与@ControllerAdvice的执行有关
* 2:视图渲染 rend()
*/
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
/**
* 当执行controller出现异常的时候,调用拦截器中的AfterCompletion方法
*/ catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
} catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
} finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
} else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
doDispatch之getHandler()
遍历所有的handlerMappings进行getHandler操作()直至能获取到HandlerExecutionChain对象为止。不知道读者看如下的代码是否有如下疑惑?
- this.handlerMappings 的值从哪里来的?
答:在我们初始化springMvc容器的时候,已经对这些值初始化过了
@Nullable
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
/**
* handlerMappings 遍历如下5个handler,依据合适handlerMappings获取合适的HandlerExecutionChain对象
*
* requestMappingHandlerMapping 基于注解方式处理handler
* beanNameHandlerMapping
* routerFunctionMapping
* resourceHandlerMapping
* welcomePageHandlerMapping
*/
if (this.handlerMappings != null) {
for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {
/**
* 获取HandlerExecutionChain
* HandlerExecutionChain为handlerMethod的包装对象,
* HandlerExecutionChain里面包含controller对应的bean对象、HandlerInterceptor类型的拦截器
*/
HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
}
return null;
}
getHandler()
getHandler方法主要做了如下事情:
- 获取handlerMethod对象: Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
- 将handlerMethod对象+拦截器封装成一个HandlerExecutionChain 对象:HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
- 返回HandlerExecutionChain 对象:return executionChain;
@Override
@Nullable
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
/**
* 根据请求对象,获取对应的handlerMethod对象
*/
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
//如果获取不到handlerMethod对象直接返回我们默认的handler对象
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
//默认的也获取到,返回null
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
//如果此时的handler还是字符串,进行getBean()操作
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// Ensure presence of cached lookupPath for interceptors and others
if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) {
initLookupPath(request);
}
/**
* handlerMethod强转为HandlerExecutionChain类型,同时给HandlerExecutionChain添加HandlerInterceptor类型的拦截器
*/
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !DispatcherType.ASYNC.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);
config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config);
}
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
}
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
/**
* 返回我们的HandlerExecutionChain对象
*/
return executionChain;
}
getHandlerInternal()
getHandlerInternal方法干了些啥?
- 根据 request 获取url (不做重点分析)
- lookupHandlerMethod():获取HandlerMethod对象(着重分析)
- 给获取到的HandlerMethod对象进一步包装,填充我们的controller这个bean属性到HandlerMethod中,最终返回。handlerMethod对象
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
/**
* 初始化查找路径
*/
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
/**
* 对映射关系中获取HandlerMethod对象
*/
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
/**
* handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean():
* 有可能被调用接口的controller此时还是一个字符串,从ioc容器中先getBean()此controller,
* 然后重新包装HandlerMethod,最终返回的HandlerMethod包含了controller的bean对象
*/
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
} finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
lookupHandlerMethod()
lookupHandlerMethod做了些什么工作?
- 获取符合条件的url对应接口上的@RequestMapping注解中的信息封装成一个RequestMappingInfo对象,将RequestMappingInfo+从映射关系中获取到的handlerMethod对象 封装进一个match对象中并添加进matches集合
- 最终返回Macth对象中的handlerMethod
就是各种封装绕来绕去, 总而言之lookupHandlerMethod能获取到我们需要的handlerMethod 。获取过程具体是怎么获取的看下文
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
/**
* 获取符合条件的url对应接口上的@RequestMapping注解中的信息,将这些信息封装成一个match对象添加进matches中
* 我们封装的match对象构成:(requestMappingInfo、handlerMethod)
* spring中的match对象构造方法(T mapping, MappingRegistration registration)
*/
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
/**
* 如果有俩个一样的接口那么会报错
*/
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
for (Match match : matches) {
if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
}
} else {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
}
/**
* 向request中设置一个属性(key:BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE,value:HandlerMethod)
*/
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
/**
* bestMatch.mapping:handlerMethod
* lookupPath:url
* request:request请求
* 往request中设置一些属性,不用管
*
*/
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
/**
* 返回handlerMethod对象
*/
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
} else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
addMatchingMappings
addMatchingMappings干了些什么?
- 往matches集合中添加我们封装的Match对象。
- matches集合:合法的@RequestMapping请求包装的Match对象的集合
- 本质Match对象是requestMappingInfo+handlerMethod的包装类型
小结addMatchingMappings:总而言之addMatchingMappings把Match对象添加进了matches集合中
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
/**
* mappings: 装的是requestMappingInfo信息的对象的集合
*/
for (T mapping : mappings) {
/**
* getMatchingMapping:获取当前请求接口上的@RequestMapping注解上的所有东西包装成一个requestMappingInfo对象返回
* getMatchingMapping返回值:requestMappingInfo对象
*/
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
/**
* match:requestMappingInfo对象,只有匹配的请求才会走到这
* this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().get(mapping):从映射关系中获取handlerMethod
* ⚠️ matches集合为入参,Match对象组成:requestMappingInfo+handlerMethod
*/
matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().get(mapping)));
}
}
}
Match对象构造
- 通过Match对象能获取handlerMethod对象
MappingRegistration可以强转为HandlerMethod对象!!!!!!!!
getMatchingMapping()
getMatchingMapping点进去本质是调用getMatchingCondition方法,getMatchingCondition作用是什么?
- 获取匹配的请求上的@RequestMapping注解信息,封装成一个RequestMappingInfo对象返回
public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
/**
* @RequestMapping中各种参数拦截生效
*/
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (methods == null) {
return null;
}
/**
* paramsCondition:@RequestMapping注解中的param属性
*/
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (params == null) {
return null;
}
/**
* paramsCondition:@RequestMapping注解中的header属性
*/
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (headers == null) {
return null;
}
/**
* paramsCondition:@RequestMapping注解中的onsumes属性
*/
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (consumes == null) {
return null;
}
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (produces == null) {
return null;
}
PathPatternsRequestCondition pathPatterns = null;
if (this.pathPatternsCondition != null) {
pathPatterns = this.pathPatternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (pathPatterns == null) {
return null;
}
}
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = null;
if (this.patternsCondition != null) {
patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (patterns == null) {
return null;
}
}
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (custom == null) {
return null;
}
/**
* 获取当前请求@RequestMapping注解中的各个参数封装成一个RequestMappingInfo对象返回
*/
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, pathPatterns, patterns,
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom, this.options);
}
getMatchingCondition()这个方法就是处理这些参数的,如果请求中没有携带这些参数,getMatchingCondition()方法将会返回null,返回null也就意味着找不到合适的接口来处理此次请求。
小结getMatchingCondition:总而言之getMatchingCondition查找到了我们需要@RequestMapping这个注解上的信息,并且包装成一个RequestMappingInfo对象返回了
分析到这里着实有些绕啊,分析到这只是为例向读者阐述lookupHandlerMethod获取handlerMethod对象的过程哦。到此handlerMethod已经获取到了,但是最终的handlerMethod还需经过createWithResolvedBean这一步呀!
createWithResolvedBean()
向handlerMethod中填充我们的controller属性,如果此时controller还是一个字符串,先进行getBean操作(这个涉及到spring的源码了,可以阅读我写的spring源码解读哦)。
最终getHandlerInternal可算获取到了我们的handlerMethod对象,接着来分析getHandlerExecutionChain()
getHandlerExecutionChain()
将handlerMethod包装成我们的HandlerExecutionChain对象,同时将匹配的拦截器添加进HandlerExecutionChain然后最终的return。
到此我们的getHandler()算是彻彻底底的获取到了我们所需的HandlerExecutionChain对像了,获取到了我们的handlerMethod对象,然后就是开始获取对应的适配器了
getHandlerAdapter
利用策略模式循环遍历查找出匹配我们handler的适配器然后返回。适配器用于执行我们的具体接口中的逻辑
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {
if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {
for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {
/**
* 查找当前handler的适配器
*/
if (adapter.supports(handler)) {
return adapter;
}
}
}
}
springmvc执行前置拦截器(preHandle)
在调用请求接口之前,先执行HandlerExecutionChain中的拦截器中的preHandle()方法
执行preHandle()就是挨个顺序遍历HandlerExecutionChain中的拦截器依次调用preHandle()方法
ha.handle()

handle嵌套了很多层,本质是调用到了handleInternal()方法,点进来handleInternal,发现视图的处理逻辑在invokeHandlerMethod方法中,点进去invokeHandlerMethod方法
invokeHandlerMethod(调用接口、返回视图)
里面有很多没有用的代码,看重要的代码就是了
点进去分析invokeAndHandle方法还有getModelAndView方法就好了
invokeAndHandle(调用接口、处理返回值)
invokeAndHandle主要做了俩件事:
- invokeAndHandle里面涉及到真正的接口调用逻辑(invokeForRequest)
- 对我们接口返回值的处理(this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue)
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
/**
* 重点
*/
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
/**
* 接口返回值的处理
*/
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
springmvc调用接口过程
invokeForRequest()执行步骤:
- 获取方法上的执行参数的值:getMethodArgumentValues()
- 开始调用方法:doInvoke()
@Nullable
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
/**
* 获取方法参数列表
*/
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
/**
* 进行调用方法
*/
return doInvoke(args);
}
getMethodArgumentValues(获取参数)
getMethodArgumentValues主要做了一件事:解析接口的参数值放到参数数组中,然后返回参数数组。关键看springMvc是如何为我来进行解析参数的,点进去this.resolvers.resolveArgument()。
protected Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
/**
* 获取方法上的参数,从handlerMethod对象中直接获取参数
*/
MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters();
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parameters)) {
return EMPTY_ARGS;
}
Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {
MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i];
parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
args[i] = findProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs);
if (args[i] != null) {
continue;
}
/**
* 策略模式获取参数解析器
*/
if (!this.resolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(formatArgumentError(parameter, "No suitable resolver"));
}
try {
/**
* 参数解析器解析参数
*/
args[i] = this.resolvers.resolveArgument(parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Leave stack trace for later, exception may actually be resolved and handled...
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String exMsg = ex.getMessage();
if (exMsg != null && !exMsg.contains(parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString())) {
logger.debug(formatArgumentError(parameter, exMsg));
}
}
throw ex;
}
}
/**
* 返回解析到的参数列表
*/
return args;
}
resolveArgument(解析参数返回)
主要还是先获取相应的解析类然后开始真正的参数解析,点进去resolveArgument()
解析类有很多下面列举常见的@RequestParam解析
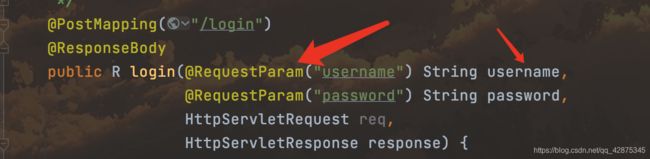
先是解析name,然后根据name解析value
解析value本质其实就是request.getParameterValues(name);
最终我们得到了我们方法的参数value值,还记得我们是从何处开始获取参数值的嘛,回顾一下是从invokeForRequest这开始获取的哦,获取到了参数value,然后开始调用接口了,点开doInvoke()
doInvoke(真正调用)
反射来进行调用方法,到此方法是调用成功了,但是有些方法是有返回值的呀,我们还需要对返回值进行处理
springmvc处理返回值过程
回到invokeAndHandle中我们点开handleReturnValue()方法看是如何处理返回值的
handleReturnValue(解析返回值)
先获取能处理这种类型的返回值的适配器,然后开始真正的处理返回值,看适配器都是一个套路,策略模式挨个遍历spring写好的适配器,遍历到合适的然后返回,点开handleReturnValue看是如何解析的
解析过程很简单,返回参数如果是map类型的直接强转为map类型,然后添加到modelAndView容器中
springmvc封装视图(getModelAndView)
最终到这接口的调用过程算是完成了,然后就是返回视图了,主要做法就是新建一个modelAndView对象,属性填充从modelAndView容器中的获取
private ModelAndView getModelAndView(ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
ModelFactory modelFactory, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
modelFactory.updateModel(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
return null;
}
/**
* 从modelAndView容器中获取model
*/
ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel();
/**
* 创建modeAndView
* model:一个map
* mavContainer.getViewName():视图名字
* mavContainer.getStatus():视图状态码
*/
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, mavContainer.getStatus());
if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) {
mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView());
}
if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes) {
Map<String, ?> flashAttributes = ((RedirectAttributes) model).getFlashAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = webRequest.getNativeRequest(HttpServletRequest.class);
if (request != null) {
RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes);
}
}
/**
* 返回视图
*/
return mav;
}
最终我们的ha.handle()就成功获取到了我们的视图了
springmvc执行中置拦截器
执行流程也是很简单就是倒叙遍历 HandlerExecutionChain中的拦截器挨个调用postHandle()方法
springmvc视图渲染
processDispatchResult
processDispatchResult干了俩件很重要的事情
- 视图的渲染(render)
- 处理springmvc执行过程中抛出的异常(processHandlerException),里面对应着@ControllerAdvice注解的执行逻辑。本文太长了,改天写一篇新的文章分析。
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
} else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
/**
* 处理@ControllerAdvice注解
*/
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
/**
* 渲染视图
*/
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
} else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
render()
此方法主要负责视图的渲染
视图种类有很多种(renderMergedOutputModel有很多个实现类),本文就挑jsp视图解析着重分析一下。jsp视图解析其实和我们的servlet操作一摸一样就是
request.getRequestDispatcher(path).forward(request,reponse)。最终
/**
* jsp视图响应
*/
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Expose the model object as request attributes.
/**
* 把model中的值写入到request对象中
*/
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);
// Expose helpers as request attributes, if any.
exposeHelpers(request);
// Determine the path for the request dispatcher.
/**
* 拿到我们的响应地址
*/
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response);
// Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP).
/**
* 转发
*/
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath);
if (rd == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() +
"]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!");
}
// If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward.
if (useInclude(request, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Including [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.include(request, response);
}
else {
// Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
/**
* 视图响应
*/
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
springmvc执行后置拦截器
最后只剩下分析doDispatch()中的triggerAfterCompletion()方法了,执行后置拦截器的时机:
- 当调用接口的过程中抛出了异常
- 中置拦截器执行过程中抛出异常
- 前置拦截器 return false,可能触发后置拦截器的执行