A:牛牛与牛妹的RMQ | 2021牛客寒假算法基础集训营2
链接:https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/9982/A
时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒
空间限制:C/C++ 262144K,其他语言524288K
题目描述
某天,牛妹来找牛牛学习RMQ算法(Range Minimum/Maximum Query),即区间最值查询。也就是给定一个数组区间[L,R],查询该子区间的最大值。
假设子数组的两端点下标分别为L,R的话RMQ(L,R)就表示数组区间[L,R]的最大值。
因为牛妹学会了RMQ算法,所以牛牛准备和她玩个游戏验证她真的学会了。
牛牛有一个长度大小为n的全排列数组,即数组中的数字是1~n,且每个数字仅出现1次。
她们一共玩了m轮游戏,在每轮游戏中,牛牛都准备了k个不同的下标。
然后牛牛和牛妹各自随机选出一个下标,并且两人所选下标可以是相同的。
假设牛牛选出的下标为a,牛妹选出的下标为b的话,那么本轮游戏的得分就是RMQ(min(a,b),max(a,b))。
请你告诉牛牛,对于每轮游戏可能的得分都有哪几种情况,以及这些情况出现的概率各是多大?

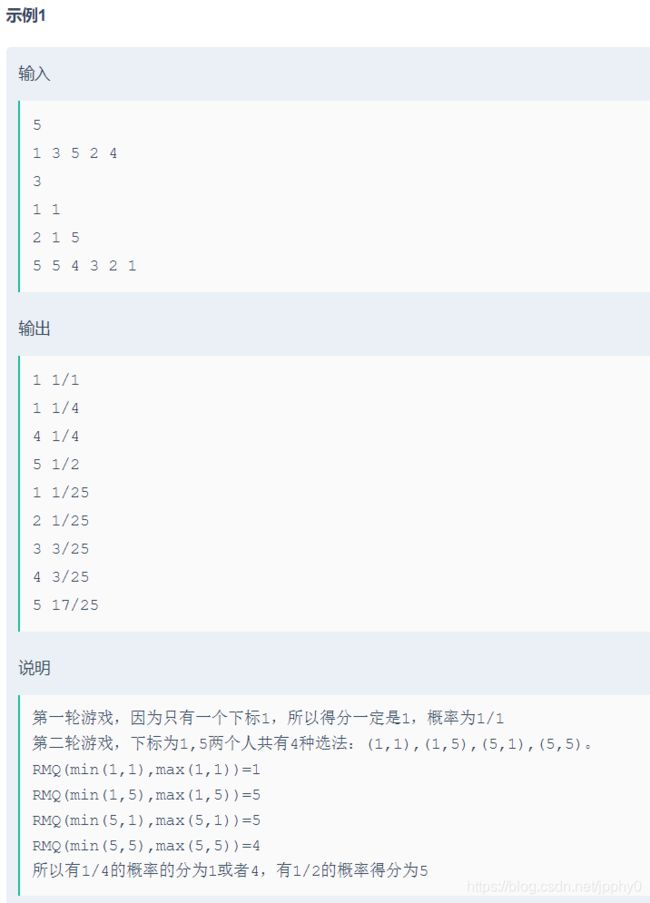
分析
关键:如何遍历?
- 遍历所有可能区间?超时不可行。(因为:p序列有k个元素,对这k个元素排序后,容易计算出这些元素可以产生k^2个可能区间)
- 将k2个区间按得分进行分类,遍历所有的分类?最多2k-1个分类,可行且有效。设arr序列为(1,3, 5, 2, 4),则
例1:如果p序列为(1,2,4,5),那么p序列的p1, p4对应arr序列的区间[1,5],它的最大值为5(即arr3,下标i=3),因为i= 3在p序列中介于p2和p3间,借用下界的概念,最大值在p中的位置用p的下标3表示,因此有(3-1)(5-3) = 4个区间的得分为5(即arr3),出现5这个得分的次数为 2 (3-1)(5-3)=8次。到此,一个分类整体解决。
例2:如果p序列为(1,3,4,5),那么p序列的p1, p4对应arr序列的区间[1,5],它的最大值为5(即arr3,下标i=3),因为i= 3在p序列中等于p2,借用下界的概念,最大值在p中的位置用p的下标2表示,因此有(2-1+1)(5-3+1)-1 = 5个区间的得分为5(即arr3),出现5这个得分的次数为 2 ((2-1+1)(5-3+1)-1)=10次,此外还有[p2,p2]单独1次,共11次。 - 问题的主要任务就是如何找出这些分类?或者说某个得分在哪些区间是有效的?可以尝试二分搜索 和 单调栈两种方法。
思路
-
st表存储下标,st表查询返回下标
-
对p序列按升序排序
二分处理 -
按最大得分将整个区间二分,然后再对子区间二分处理,……,每个区间的最大值通过二分搜索确定
单调栈 -
对于一个最小区间的得分,它有可能向两侧扩展从而获得这个得分的有效区间。例如:当与它相邻的区间的得分比它的得分小,就可以扩展。遍历最小的区间可以扩展出所有区间。但扩展时,左侧边界的信息出现在已遍历的区间中,而右侧边界的信息将会出现在将要遍历的区间中,即:与过去相关,与未来相关。这时单调栈发挥作用,新区间的得分比栈顶区间得分小则入栈,且扩展新区间的左边界为栈顶区间的有边界;若新区间的得分比栈顶得分大,则弹出栈顶区间,且被弹出区间的有边界为新区间的左边界。被弹出的区间是左右边界都确定的,故这个区间对应的得分出现次数是可计算的。
-
区间出现的次数存储在map中
-
L==R的区间(L,R)出现的1次单独处理
代码
使用单调栈
#include 使用stl的lower_bound
#include 自定义二分
#include