Vue 3 学习 五、Vite 模拟实现原理
Vite 核心功能
- 静态 Web 服务器
- 编译单文件组件
- 拦截浏览器不识别的模块,并处理
- HMR
当启动 Vite 的时候,首先会将当前项目目录作为静态 web 服务器的根目录。
静态 web 服务器会拦截部分请求,例如当请求单文件组件的时候会实时编译,以及处理其他浏览器不能识别的模块(非 JS 模块)。
通过 web socket 实现 HMR(暂不模拟)。
创建项目
首先创建一个基于 Vue 3 的项目,用于测试模拟的 vite-cli 工具。
可以使用 vite-app 快速创建:
npm init vite-app vue3-demo
cd vue3-demo
npm install
创建 vite-cli 目录
# 创建 vite 工具文件夹 vite-cli
mkdir vite-cli
# 进入目录
cd ./vite-cli
# npm 初始化
npm init -y
静态 Web 服务器
Vite 内部使用 Koa 开启静态 Web 服务器。
# 安装依赖,koa-send:静态文件处理的中间件
npm i koa koa-send
配置 bin 字段,默认执行的 js 文件的路径:
vite-cli/package.json:
{
"name": "vite-cli",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"bin": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"koa": "^2.13.0",
"koa-send": "^5.0.1"
}
}
添加 index.js 文件,因为要开发的是基于 Node 的命令行工具,需要在文件顶部配置运行 node 的位置。
使用koa开发静态文件服务器,默认返回根目录中的index.html
创建一个中间件,负责处理静态文件,默认加载当前目录下(运行该命令行工具的目录中的index.html)。
vite-cli/index.js:
#!/usr/bin/env node
// /index.js
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
// 创建实例
const app = new Koa()
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
await send(ctx, ctx.path, {
root: process.cwd(),
index: 'index.html'
})
await next()
})
app.listen(3000)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:3000');
然后将 vite-cli 链接到 npm:
# vite-cli 根目录下运行
npm link
使用 vite-cli 运行 vue3-demo:
# 在 vue3-demo 根目录下运行
vite-cli
或者配置到 vue3-demo 的脚本中:
vue3-demo/package.json:
{
"scripts": {
"serve": "vite-cli",
"dev": "vite",
"build": "vite build"
},
}
打开浏览器访问 http://localhost:3000
加载第三方模块失败
此时访问页面发现有个报错:Uncaught TypeError: Failed to resolve module specifier "vue". Relative references must start with either "/", "./", or "../".
解析 vue 模块的时候失败,要求使用相对路径("/", "./", or "../")导入模块。
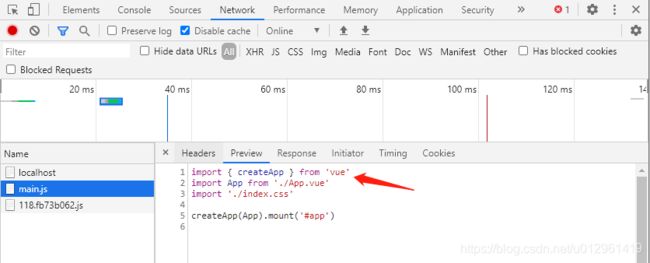
查看 main.js 源码:
在导入 vue 模块的时候,前面没有浏览器要求的相对路径地址("/", "./", or "../")。
这种方式的导入,期望的是从 node_modules 中加载模块,这是打包工具的默认行为,但是浏览器不支持。
接着查看 vite 中是如何处理的。
使用 vite 运行 vue3-demo 查看:
# vue3-demo目录下运行
npm run dev
# 当前3000端口被占用,web服务器端口分配为 3001
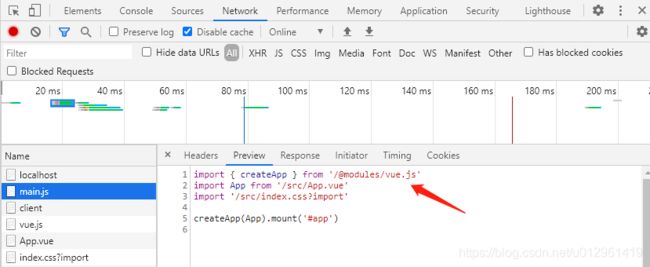
Vite 开启的 web 服务器在加载 main.js 时首先会处理第三方模块的 import 路径:vue => /@modules/vue.js
所以在服务器端要手动处理这个路径。
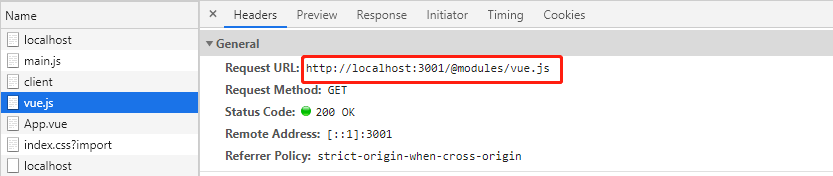
查看浏览器请求 main.js 的 Headers:
响应头 Response Headers 返回的 Content-Type 是 application/javascript,作用是告诉浏览器返回的文件是 JavaScript 文件。
所以要在 web 服务器输出之前,先判断一下当前返回的文件是否是 JS 文件。
如果是 JS 文件,再去处理里面第三方模块的路径。
然后在请求 /@modules/vue.js 时处理这个不存在的路径,去 node_modules 中寻找对应的文件。
所以下面要创建两个中间件,作用分别是:
- 修改第三方模块的
import路径,改为/@modules/[模块名](为了方便不添加.js后缀) - 判断请求路径中是否包含
/@modules/[模块名],如果有的话,去node_modules中加载对应的模块
修改第三方模块的路径
vite-cli/index.js:
#!/usr/bin/env node
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
// 创建实例
const app = new Koa()
// 流转化成字符串
// stream 读取的流
// 读取流是一个异步的过程,所以要返回一个 Promise
const streamToString = stream =>
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// chunks 存储读取到的 Buffer
const chunks = []
// 监听读取到的 Buffer
stream.on('data', chunk => chunks.push(chunk))
// 监听读取完毕,将 Buffer 转化成字符串
stream.on('end', () => resolve(Buffer.concat(chunks).toString('utf-8')))
// 监听读取失败
stream.on('error', reject)
})
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */})
// 2. 修改第三方模块的路径
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// 判断是否是 JS 文件
if (ctx.type === 'application/javascript') {
// ctx.body 是返回给浏览器的 JS 文件,是一个流,要转化成字符串处理
const contents = await streamToString(ctx.body)
// 替换路径并重新赋值 ctx.body
// 替换 `from '` 为 `from '/@modules/`
ctx.body = contents.replace(/(from\s+['"])(?![\.\/])/g, '$1/@modules/')
}
})
app.listen(3000)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:3000')
重启服务器:
# vue3-demo 项目下重新运行
npm run serve
加载第三方模块
vite-cli/index.js:
#!/usr/bin/env node
const path = require('path')
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
// 创建实例
const app = new Koa()
// 流转化成字符串
// stream 读取的流
// 读取流是一个异步的过程,所以要返回一个 Promise
const streamToString = stream =>
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
/* ... */}})
// 3. 加载第三方模块
// 在处理静态之前创建的中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// 判断路径是否是以 `/@odules/` 开头
if (ctx.path.startsWith('/@modules/')) {
// 截取模块名称
const moduleName = ctx.path.substr(10)
// 获取模块的入口文件(ESM模块的入口文件)
// 先找到这个模块的 package.json,再获取module字段的值
const pkgPath = path.join(process.cwd(), 'node_modules', moduleName, 'package.json')
const pkg = require(pkgPath)
ctx.path = path.join('/node_modules', moduleName, pkg.module)
}
await next()
})
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */}})
// 2. 修改第三方模块的路径
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */}})
app.listen(3000)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:3000')
重启服务。
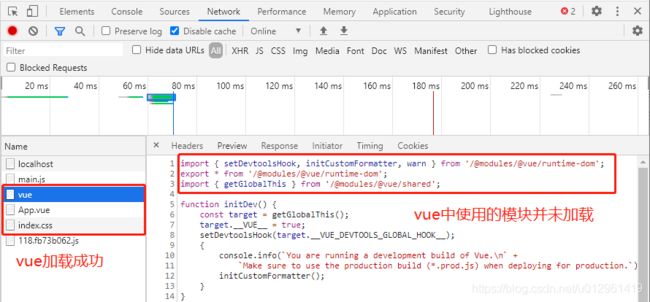
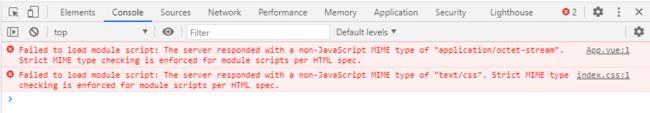
查看控制台报错,有两个浏览器不能识别的模块加载失败 App.vue 和 index.css。
编译单文件组件
Vite 编译单文件组件
浏览器只能处理 JS 模块,所以通过 import 加载的其他模块都需要在服务器端处理。
当请求单文件组件的时候,需要在服务器上把单文件组件编译成 JS 模块,然后返回给浏览器。
查看 vite 如何实现:
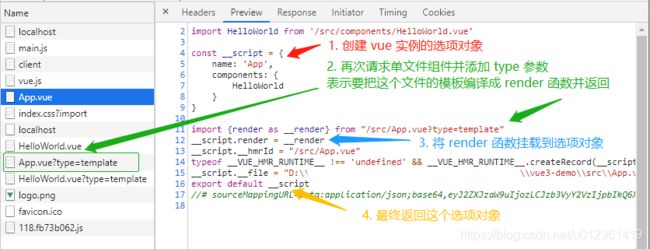
Vite 中处理单文件组件会发送两次请求:
- 第一次请求把单文件组件编译成对象
- 第二次请求编译单文件组件的模板,返回一个
render函数,并挂载到第一次请求编译的对象的render属性上
vite-cli 模拟实现第一次请求
安装 vue 3 编译单文件组件的模块 compiler-sfc
npm i @vue/compiler-sfc
#!/usr/bin/env node
const path = require('path')
const {
Readable } = require('stream')
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
const compilerSFC = require('@vue/compiler-sfc')
// 创建实例
const app = new Koa()
// 流转化成字符串
// stream 读取的流
// 读取流是一个异步的过程,所以要返回一个 Promise
const streamToString = stream =>
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
/* ... */}})
// 字符串转化成流
const stringToStream = text => {
const stream = new Readable()
stream.push(text)
// 标识 stream 已写完
stream.push(null)
return stream
}
// 3. 加载第三方模块
// 在处理静态之前创建的中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */}})
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */}})
// 4. 处理单文件组件
// 在获取文件之后,处理第三方模块之前
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// 判断是否是单文件组件
if (ctx.path.endsWith('.vue')) {
const contents = await streamToString(ctx.body)
// Vue 2 的 compiler 返回一个 AST 对象
// Vue 3 的 compiler 返回一个包含 descriptor 和 errors 的对象
const {
descriptor } = compilerSFC.parse(contents)
let code
if (!ctx.query.type) {
// 第一次请求
code = descriptor.script.content
// console.log(code)
// 改造code
code = code.replace(/export\s+default\s+/g, 'const __script = ')
// 拼接代码
code += `
import {render as __render} from "${
ctx.path}?type=template"
__script.render = __render
export default __script
`
}
// 告诉浏览器以 JS 方式识别该返回
ctx.type = 'application/javascript'
// 将code转换成流输出给浏览器
ctx.body = stringToStream(code)
}
await next()
})
// 2. 修改第三方模块的路径
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */}})
app.listen(3000)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:3000')
重启服务。
App.vue 编译成功,并发起第二次请求,但是第二次请求还没处理,所以没有返回内容。
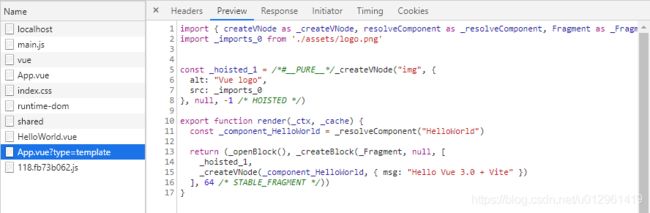
vite-cli 模拟实现第二次请求
#!/usr/bin/env node
const path = require('path')
const {
Readable } = require('stream')
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
const compilerSFC = require('@vue/compiler-sfc')
// 创建实例
const app = new Koa()
// 流转化成字符串
// stream 读取的流
// 读取流是一个异步的过程,所以要返回一个 Promise
const streamToString = stream =>
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
/* ... */}})
// 字符串转化成流
const stringToStream = text => {
const stream = new Readable()
stream.push(text)
// 标识 stream 已写完
stream.push(null)
return stream
}
// 3. 加载第三方模块
// 在处理静态之前创建的中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */}})
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */}})
// 4. 处理单文件组件
// 在获取文件之后,处理第三方模块之前
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// 判断是否是单文件组件
if (ctx.path.endsWith('.vue')) {
const contents = await streamToString(ctx.body)
// Vue 2 的 compiler 返回一个 AST 对象
// Vue 3 的 compiler 返回一个包含 descriptor 和 errors 的对象
const {
descriptor } = compilerSFC.parse(contents)
let code
if (!ctx.query.type) {
// 第一次请求
code = descriptor.script.content
// console.log(code)
// 改造code
code = code.replace(/export\s+default\s+/g, 'const __script = ')
// 拼接代码
code += `
import {render as __render} from "${
ctx.path}?type=template"
__script.render = __render
export default __script
`
} else if (ctx.query.type === 'template') {
// 第二次请求
const templateRender = compilerSFC.compileTemplate({
source: descriptor.template.content })
code = templateRender.code
}
// 告诉浏览器以 JS 方式识别该返回
ctx.type = 'application/javascript'
// 将code转换成流输出给浏览器
ctx.body = stringToStream(code)
}
await next()
})
// 2. 修改第三方模块的路径
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */}})
app.listen(3000)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:3000')
重启服务。
替换vue模块中的环境变量
当文件组件已经正常编译,但页面还是没有正常显示。
原因有两个:
- 其他浏览器不能识别的模块还没有处理
main.js中加载的./index.cssApp.vue中使用的图片./assets/logo.png
可以暂时注释这些模块来解决。
- vue 模块中使用了环境变量
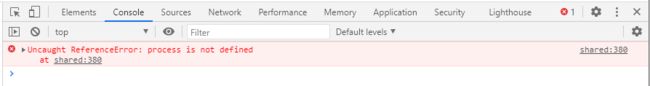
注释掉其他模块,刷新页面会发现一个报错:
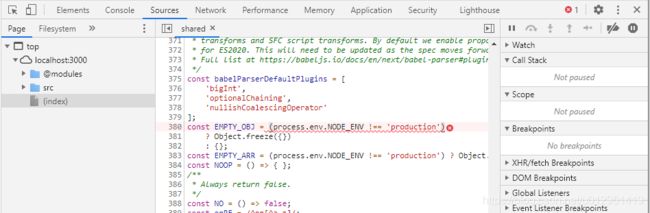
报错文件是 @vue/shared,查看源码:
源码中使用了 process.env.NODE_ENV。
当前代码是在浏览器环境下执行的,process是 node 环境的对象,浏览器环境没有这个对象,所以报错。
这段源码的作用是让打包工具根据环境变量分别进行生产环境或者开发环境的打包操作。
但是现在没有用打包工具,所以这句代码没有被处理,直接返回给了浏览器。
所以应该在服务器处理一下,在返回 JS 模块之前,应该把 JS 模块中所有process.env.NODE_ENV 都替换成 development(因为当前是开发环境下)。
#!/usr/bin/env node
const path = require('path')
const {
Readable } = require('stream')
const Koa = require('koa')
const send = require('koa-send')
const compilerSFC = require('@vue/compiler-sfc')
// 创建实例
const app = new Koa()
// 流转化成字符串
// stream 读取的流
// 读取流是一个异步的过程,所以要返回一个 Promise
const streamToString = stream =>
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
/* ... */})
// 字符串转化成流
const stringToStream = text => {
/* ... */}
// 3. 加载第三方模块
// 在处理静态之前创建的中间件
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */})
// 1. 开启静态文件服务器
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */})
// 4. 处理单文件组件
// 在获取文件之后,处理第三方模块之前
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
/* ... */})
// 2. 修改第三方模块的路径
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
// 判断是否是 JS 文件
if (ctx.type === 'application/javascript') {
// ctx.body 是返回给浏览器的 JS 文件,是一个流,要转化成字符串处理
const contents = await streamToString(ctx.body)
// 替换路径并重新赋值 ctx.body
// 替换 `from '` 为 `from '/@modules/`
ctx.body = contents
.replace(/(from\s+['"])(?![\.\/])/g, '$1/@modules/')
// 继续替换 process 对象
.replace(/process\.env\.NODE_ENV/g, '"development"')
}
})
app.listen(3000)
console.log('Server running @ http://localhost:3000')
重启服务,App.vue 文件的内容正常显示。