个人博客系统之框架搭建
1、写在前面
本篇博客是个人博客系统系列第二篇,以下是其他博客的链接:
- 个人博客系统整体介绍
2、新建项目
2.1 创建SpringBoot项目
首先新建一个SpringBoot项目,项目信息大家可以随便填,不过为了开发方便,最好跟我的截图保持一致:
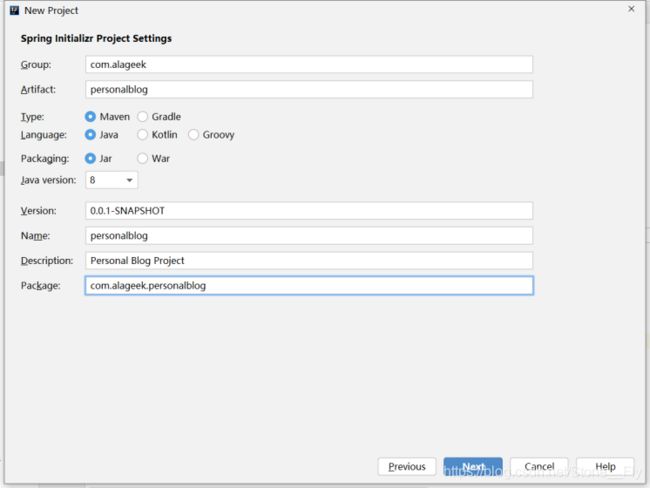
2.2 添加依赖
点击下一步后选择依赖,其中:
- 必选依赖:
- Thymeleaf
- Spring Security
- MyBatis Framework
- MySQL Driver
- Lombok【这个依赖其实也非必选,不过加了可以少写很多代码】
- 非必选依赖:
- Spring Boot DevTools【这个依赖用于热部署,可以不重启服务器部署项目,不过我没咋用,可以不加】

一直点击下一步,直到项目创建完成,打开pom.xml文件,这里边有个线程池依赖(可以不加,我貌似没在项目上用到,不过后期优化可能会用到)在上边的截图中找不到,因此需要手动添加下:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.10version>
dependency>
2.3 创建多环境配置
在resources文件夹下创建一下四个文件:
- application.properties
- application-dev.properties
- application-test.properties
- application-prod.properties
当然我们这个项目用不到这么多配置,嫌麻烦的朋友也可以只创建第一个文件,我这边只是想尽量靠近企业开发。
其中application.properties文件内容如下:
spring.profiles.active=dev
表示启用开发环境的配置,开发环境配置在application-dev.properties文件中,内容如下:
# tomcat端口号
server.port=8080
# 线程池类型,前面线程池依赖没加的朋友,可以把这行代码去掉
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# 数据库配置,自行替换
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.203.128:3306/personal_blog?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
# 视图解析
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.html
# mapper.xml文件位置
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
# 在控制台打印SQL语句
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
# 日志级别
logging.level.root=info
# 因为是开发环境的配置,所以配置为debug,在开发测试环境中,可以相应的提高日志级别
logging.level.com.alageek.personalblog=debug
开发阶段,测试和生产的配置暂且不写,有兴趣的朋友可以复制开发的配置,修改下端口号试试。
3、异常处理
项目运行过程中肯定会有各种各样的异常抛出,我们期望将这些异常全部捕获,进行统一处理,并且在某些情况下,我们也期望抛出来的异常是我们自定义的异常,比如这里我们自定义一个博客未找到的异常:
/**
* 博客未找到异常
* @author AlaGeek
*/
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class BlogNotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3780352823465733637L;
public BlogNotFoundException() {
}
public BlogNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public BlogNotFoundException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}
当我们访问系统中不存在的博客时,将会返回一个404的http错误到前端,这里我们让其抛出博客未找到异常,从而能被我们的全局异常处理捕获,以便跳转到相应页面并做相应处理。
这边博客未找到异常只是做个演示,让大家明白下怎么自定义异常,在全局异常处理中我们还是先将所有异常都捕获,其代码如下:
/**
* 全局异常处理机制
* @author AlaGeek
*/
@Slf4j
@ControllerAdvice
public class ControllerExceptionHandler {
/**
* 异常处理
* @param e 异常对象
* @param request 请求对象
* @return 返回错误页面
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
public ModelAndView resolveException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
log.debug("Request URL: {}, Exception: {}", request.getRequestURL(), e);
if (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(e.getClass(), ResponseStatus.class) != null) {
throw e;
}
String viewName = "error/error";
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject(BlogConstant.ATTR_NAME_URL, request.getRequestURL());
modelAndView.addObject(BlogConstant.ATTR_NAME_EXCEPTION, e);
modelAndView.setViewName(viewName);
return modelAndView;
}
}
之前在尚筹网项目中有用到这个异常处理机制,如果不懂这个可以看看我的这篇博客:admin-component异常处理机制
上方代码表示异常被捕获后,将会跳转到error目录下的error.html页面【.html是前面配置的视图解析】,因此需要在resources/template目录下新建error文件夹,并在该文件夹下创建error.html文件,error.html页面长什么样无关紧要,不过需要在其中插入以下代码:
代码运用了thymeleaf模板,用于获取异常的具体信息,并且将这段异常信息放在页面的源码注释中,而不是展示在前端页面供用户查看,这样做的目的主要也是为了调试方便,开发的时候可以随时看控制台信息,不过测试环境或者生产环境,如果直接看源码就能看到异常信息的话,想必是非常方便的。
4、日志处理
有了异常处理,还想做的就是每次用户访问我这个博客系统的时候,就把这次访问的相关信息记下来,打印出日志。
对于访问日志,我希望能够记录以下信息:
- 请求url
- 请求ip
- 请求方法
- 请求参数
- 返回内容
我们不可能在每个controller的函数里都加上记录日志的代码,那样太麻烦了,因此需要用到spring框架的绝技——AOP,也就是面向切面编程。
首先引入AOP相关的依赖,在pom.xml中添加如下代码:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aopartifactId>
dependency>
然后新增一个日志记录类LogAspect,代码如下:
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.alageek.personalblog.web.*.*(..))")
public void log() {
}
@Before("log()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
if (attributes != null) {
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
String url = request.getRequestURL().toString();
String ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
String classMethod = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() + "." + joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
RequestLog requestLog = new RequestLog(url, ip, classMethod, args);
log.info("Request: {}", requestLog);
}
}
@AfterReturning(returning = "result", pointcut = "log()")
public void doAfterReturn(Object result) {
log.info("Result: {}", result);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
private static class RequestLog {
private String url;
private String ip;
private String classMethod;
private Object[] args;
}
}
5、写在后面
这部分为框架搭建,其实新建一个项目没有这么麻烦,idea鼠标点几下的事情,只是为了后续开发和调试方便,所以要做些相关配置,比如日志处理,比如异常处理。