Spring Boot学习笔记(二)——yaml语法
properties和yaml语法
在创建一个SpringBoot项目时,默认会在resources目录下创建一个application.properties的配置文件,在SpringBoot项目中,其实也可以使用application.yaml这样的配置文件代替,都可以进行配置,但两者在使用语法上有一定的区别。

从上面我们可以发现,yaml语法是阶梯呈现的:
- 在properties文件里面的 " . " 连接在yaml文件里面全部换成 " : " 进行连接,并且每一级之间必须换行,在第二级开始应该进行一个Tab键的缩进,当然如果是同级的就不需要进行缩进
- 在yml文件里面如果是需要进行赋值那么必须是要在 " : " 后面进行一个空格键的缩进
- 在yml文件里面所有的配置,相同级别只能出现一次
读取yaml文件中的内容
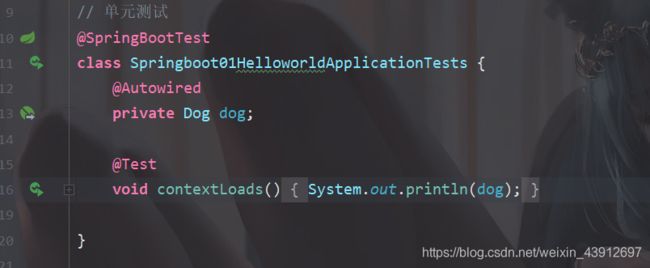
创建两个实体类:
@Component
public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Dog() {
}
public Dog(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean flag;
private Date birthday;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, Integer age, Boolean flag, Date birthday, Map<String, Object> maps, List<Object> lists, Dog dog) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.flag = flag;
this.birthday = birthday;
this.maps = maps;
this.lists = lists;
this.dog = dog;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Boolean getFlag() {
return flag;
}
public void setFlag(Boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
return maps;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public List<Object> getLists() {
return lists;
}
public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", flag=" + flag +
", birthday=" + birthday +
", maps=" + maps +
", lists=" + lists +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
}
}
编写application.yaml文件:
person:
name: 周杰伦
age: 21
flag: false
birthday: 2000/01/01
maps: {
k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- 稻香
- 晴天
- 七里香
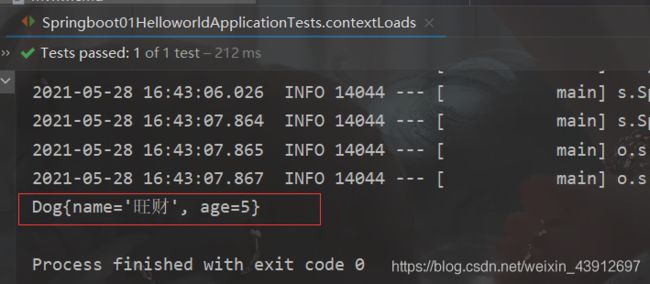
dog:
name: 旺财
age: 3
person类上的注解必须指向yaml中指定的对象

在test中测试:
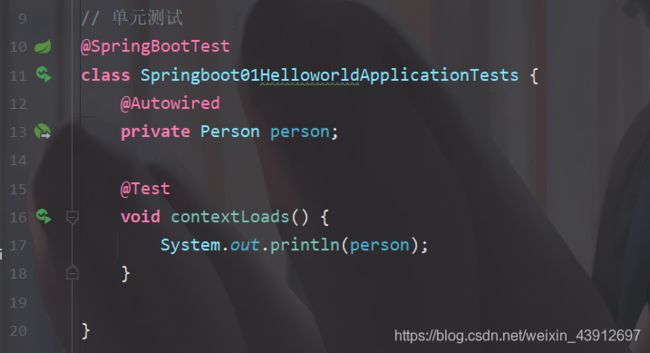
输出结果:

@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”)默认加载的是名字为application的配置文件,当你想使用其他名字的配置文件时

通过 @PropertySource(value = “classpath:dog.properties”) 加载指定的配置文件
JSP303校验
当我们在类上加上 @Validated注解,就可以在当前类上的属性上加上一些注解来后端验证当前属性值的正确性。
比如我们在Person类上加上 @Validated,在name属性上加上 @Email(),给name注入的值就必须是email类型,否则会报错!

常用的JSP303校验类型:
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) Validates that the annotated string is between min and max included
日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
数值检查,建议使用在Stirng,Integer类型,不建议使用在int类型上,因为表单值为“”时无法转换为int,但可以转换为Stirng为"",Integer为null
@Min 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否大等于指定的值
@Max 验证 Number 和 String 对象是否小等于指定的值
@DecimalMax 被标注的值必须不大于约束中指定的最大值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最大值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
@DecimalMin 被标注的值必须不小于约束中指定的最小值. 这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最小值的字符串表示.小数存在精度
@Digits 验证 Number 和 String 的构成是否合法
@Digits(integer=,fraction=) 验证字符串是否是符合指定格式的数字,interger指定整数精度,fraction指定小数精度。
@Range(min=, max=) 检查数字是否介于min和max之间
@Valid 递归的对关联对象进行校验, 如果关联对象是个集合或者数组,那么对其中的元素进行递归校验,如果是一个map,则对其中的值部分进行校验.(是否进行递归验证)
@CreditCardNumber信用卡验证
@Email 验证是否是邮件地址,如果为null,不进行验证,算通过验证。
@ScriptAssert(lang= ,script=, alias=)
@URL(protocol=,host=, port=,regexp=, flags=)
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_33446857/article/details/84932631.