声明:
1.本节将会通过Spring Cloud Bus来将配置更新的事件进行发布,从而达到在更新配置后,使得所有服务都去更新配置的效果,由于配置中心集成在Eureka中,且会以Kafka作为Spring Cloud Bus的基础,所以本节将会使用Spring Cloud Netflix Eureka + Spring Cloud Config + Spring Cloud Bus + Spring Kafka来完成本节内容,Kafka也需要Zookeeper的环境基础,所以你还得整个Zookeeper。
2.入门级文档,更多内容会持续更新,不足之处,望不吝指点
一、Spring Cloud Bus介绍
Spring Cloud Bus就是一个消息总线,也就是一个广播,任何对象都可以接收这条总线上的任何广播消息,同样也可以发布消息出去。内部是使用Spring Cloud Stream来实现,也就是说Spring Cloud Bus不过是Spring Cloud Stream的一个广播性用法,主要用于在服务间共享事件,使得一个事件不单单只在一个服务上被处理,而是可以扩大到整个分布式应用上去。
目前Spring Cloud Bus支持RabbitMQ和Kafka两种消息中间件。
二、Spring Cloud Bus自带事件
-
Spring Cloud Bus内部自带了几个比较重要的事件:-
RemoteApplicationEvent这是Spring Cloud Bus支持的远程事件的超类,只有继承该类的事件类才能够被发布到消息队列中去,本身是一个抽象类,无法实例化。 -
RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent这是配置刷新事件,父类是RemoteApplicationEvent,其他服务如果接收到这个事件,并且确定是自己应收的,就会自动进行配置的刷新 -
EnvironmentChangeRemoteApplicationEvent环境变化事件,父类是RemoteApplicationEvent
-
- 其他事件:
-
AckRemoteApplicationEvent确认接收事件,当服务确实接收到一个事件后(指自己应当接收的),就会回返一条消息告诉发送者我接收了这个事件。 -
UnknownRemoteApplicationEvent,未知远端事件,当服务接收到一条消息,并尝试反序列化该事件时发现这个事件它不认识,就会产生该事件。 -
SentApplicationEvent当在发送一个事件的时候产生该事件。
-
三、事件接收者
事件接收者指这个事件应当被哪个服务接收,这与广播机制并不冲突,就比如,我在广播中找“李四”,那么只有“李四”听到了消息应当回应,其他人其实也听得到,但是因为不是“李四”,所有没有必要回应罢了。
事件接收者和事件的发送者在Spring Cloud Bus中都由一串特殊的字符串构成,其格式为app:index:id,其中:
app指的是vcap.application.name或者是spring.application.name(写在前的优先级高)
index是vcap.application.instance_index或spring.application.index或local.server.port或server.port或0
id是vcap.application.instance_id或者是一个不重复的随机值
注:**是通配符
例如:service:**表示事件的接收者是叫service服务的所有实例
四、端点
Spring Cloud Bus一共开了4个端点,分别是/bus/refresh,/bus/env,/actuator/bus-refresh和/actuator/bus-env,它们都只接受Post请求,后两者需要使用management.endpoints.web.exposure.include来开启。它们会分别触发RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent和EnvironmentChangeRemoteApplicationEvent事件。
附:
/actuator/bus-env可以接受一个Json格式的数据来进行环境的变更,其格式如下:
{
"name": "key1",
"value": "value1"
}
五、发布你的自定义事件
你肯定不满足只发布自带的那几个事件,你可能想发布自己的事件
- 创建你自己的事件并使其继承
RemoteApplicationEvent,并且保证公有的无参构造方法存在,例如:
public class TestRemoteEvent extends RemoteApplicationEvent {
public TestRemoteEvent(){}
public TestRemoteEvent(Object source, String originService, String destinationService){
super(source , originService , destinationService);
}
}
- 在需要接受该方法的服务中将该事件注册给
Spring Cloud Bus
这时候你需要使用到@RemoteApplicationEventScan注解,该注解使用方法同@ComponentScan,把该事件所在的包名配置上即可
注意:事件的发送者和接受者都要有这个事件,唯一不同的是,发送者(如果不需要的话)可以不用注册该事件给Spring Cloud Bus
六、配置
#开启Spring Cloud Bus
spring.cloud.bus.enabled=true
#消息发送与接收的频道
spring.cloud.bus.destination=SpringCloudBus
#更多配置可以尝试spring.cloud.stream
#kafka使用者可以使用下列配置
spring.kafka.bootstrap-servers=localhost:9092
七、使用Spring Cloud Bus实现配置自动刷新功能
- 实现原理:
由于访问/actuator/bus-refresh可以发布配置更新事件,所以我们就需要实现在Git仓库更新时,让其访问/actuator/bus-refresh就行了。 - 依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-bus-kafka
- 配置
- 服务中心(其他配置不列出)
spring: kafka: # kafka的地址,我的启动在本地9093端口 bootstrap-servers: localhost:9093 cloud: bus: refresh: #服务中心接收事件,但不响应刷新 enabled: false env: #服务中心接收事件,但不响应环境变化 enabled: false #开启spring cloud bus enabled: true- 远端配置(application.yaml)
management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: health , info spring: kafka: bootstrap-servers: localhost:9093 - Git远端仓库WebHook配置
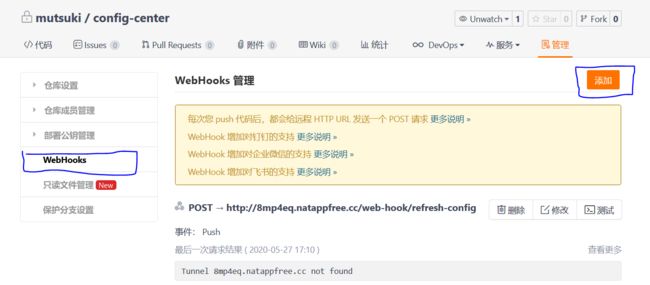
WebHook配置是各大远端仓库(Github、Gitee等)的基本功能,其作用是在仓库更新时自动调用一个接口,此处我将以Gitee作为示例:
注意:回调地址应当配置为触发RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent刷新事件的地址,所以应当为http://host:port/xxx/actuator/bus-refresh,xxx代表server.servlet.context-path。但是!!!由于Gitee的回调会附带一大串Json格式的信息,所以直接使用actuator/bus-refresh接口会报无法正常解析Json的问题,但是由于Gitee回调附带的信息中包含了commit的信息,所以我们可以自己开一个接口,对回调的数据进行解析,根据解析出来的文件修改信息,我们可以实现对指定服务进行事件的发布,而不是一股脑的全部发布。比如本次提交中修改了service1.properties那么我便将事件的目标设为service1:**,如果我修改了application.yaml那么我便将事件的目标设为** - 针对Gitee的特殊回调接口
/**
* @author mtk
* 针对WebHook的回调接口
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/web-hook")
public class WebHookController {
//自定义的Bus远端事件发布工具类
private BusRemoteEventPublisher busRemoteEventPublisher;
@Autowired
public WebHookController(BusRemoteEventPublisher busRemoteEventPublisher){
this.busRemoteEventPublisher = busRemoteEventPublisher;
}
/**
* 针对Gitee的WebHook的回调接口
* @param jsonInfo 回调数据
* @return 简易的执行结果
*/
@PostMapping("/refresh-config")
public String refreshBus(@RequestBody Map jsonInfo){
//解析json
List - 到此为止,基本上就已经完成了,如果你想看到效果,你可以给需要刷新配置的地方加上@RefreshScope注解,比如:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@RefreshScope
public class HelloController {
@Value("${cn.mtk.hello}")
private String hello;
@GetMapping("/ph")
public String printHello(){
return hello;
}
}
如果你变更过远端仓库上的配置文件,并修改了
cn.mtk.hello这一项配置,那么你将会在/hello/ph上看到更新后的结果
注意:如果你发现配置并没有刷新,但所有步骤都没有问题,那么你得考虑下是不是消费者没有正常连接到Kafka,你可以通过调整日志等级为来查看是否有隐藏掉的错误日志logging.level.root=DEBUG,或者开启一个Kafka消费者控制台来查看消息的发送情况(如果一切都是默认配置的话)kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --from-beginning --topic SpringCloudBus --partition 0,如果发现确实是Kafka问题,并且各种重启无效后,你可以尝试删除SpringCloudBus这个话题。
$ zkcli
$ rmr /brokers/topics/SpringCloudBus
$ quit
附:
- BusRemoteEventPublisher
/**
* @author mtk
* 便捷的bus远端事件发布工具
*/
public class BusRemoteEventPublisher {
private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
private BusProperties busProperties;
public BusRemoteEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher , BusProperties busProperties){
this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;
this.busProperties = busProperties;
}
public void publish(Class eventClass, String destinationService){
try{
RemoteApplicationEvent event = eventClass.getDeclaredConstructor(Object.class , String.class , String.class).newInstance(this , busProperties.getId() , destinationService);
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
参考文档:
[1] Spring Cloud Bus