介绍
接下来介绍bancor最核心的部分,也就是如何进行交易,因为篇幅很多,这里就只介绍核心部分
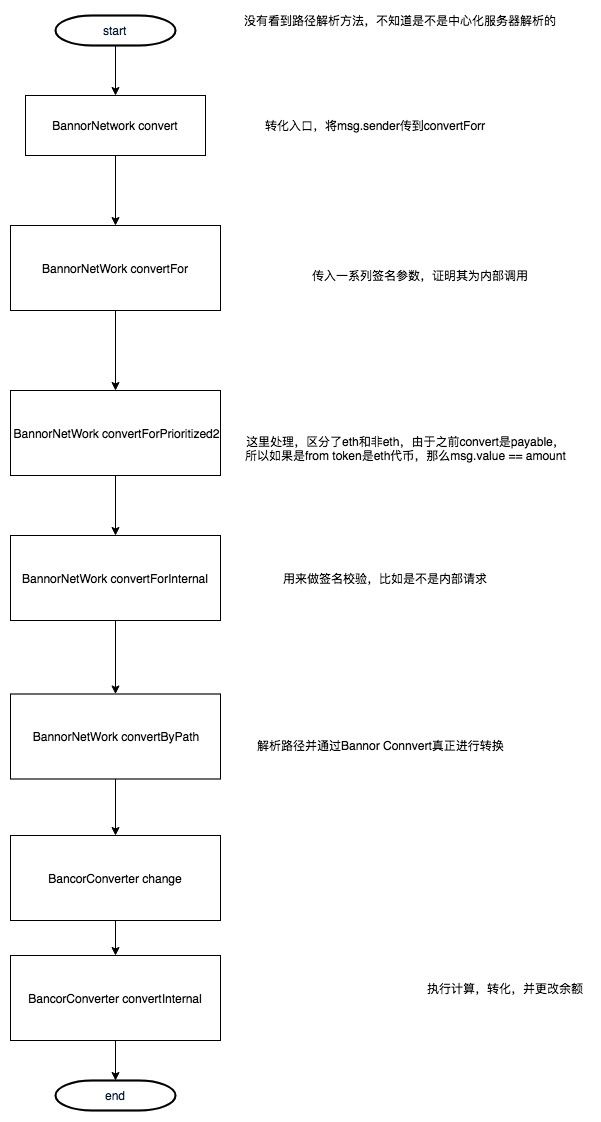
在合约上的流程图
这张流程图是一次交易合约调用方法的流程,前面的合约名,后面是合约方法。
注意这是内部调用的流程,也就是假定所有的币都已经在bancor网络上注册过了,bancor合约比较复杂,支持自己的钱包发起的交易,也支持第三方钱包钱包发起的交易,根据优先级不同,会收取不同的手续费
由于代码很多,这里就只挑几处重要的代码进行解析,有兴趣的同学可以跟着这个流程图去合约里慢慢研究
入口
@dev converts the token to any other token in the bancor network by following
a predefined conversion path and transfers the result tokens back to the sender
note that the converter should already own the source tokens
@param _path conversion path, see conversion path format above
@param _amount amount to convert from (in the initial source token)
@param _minReturn if the conversion results in an amount smaller than the minimum return - it is cancelled, must be nonzero
@return tokens issued in return
function convert(IERC20Token[] _path, uint256 _amount, uint256 _minReturn) public payable returns (uint256) {
return convertFor(_path, _amount, _minReturn, msg.sender);
}
当解析好转化路径后,就会调用这个函数,这里做的事很简单,就只是吧msg.sender当做参数传下去
兑换
/**
@dev executes the actual conversion by following the conversion path
@param _path conversion path, see conversion path format above
@param _amount amount to convert from (in the initial source token)
@param _minReturn if the conversion results in an amount smaller than the minimum return - it is cancelled, must be nonzero
@param _fromToken ERC20 token to convert from (the first element in the path)
@param _for account that will receive the conversion result
@return ERC20 token to convert to (the last element in the path) & tokens issued in return
*/
function convertByPath(
IERC20Token[] _path,
uint256 _amount,
uint256 _minReturn,
IERC20Token _fromToken,
address _for
) private returns (IERC20Token, uint256) {
ISmartToken smartToken;
IERC20Token toToken;
IBancorConverter converter;
// get the contract features address from the registry
IContractFeatures features = IContractFeatures(registry.addressOf(ContractIds.CONTRACT_FEATURES));
// 根据路径多次转换,最终换成目标代币
uint256 pathLength = _path.length;
for (uint256 i = 1; i < pathLength; i += 2) {
smartToken = ISmartToken(_path[i]);
toToken = _path[i + 1];
converter = IBancorConverter(smartToken.owner());
checkWhitelist(converter, _for, features);
// if the smart token isn't the source (from token), the converter doesn't have control over it and thus we need to approve the request
if (smartToken != _fromToken)
ensureAllowance(_fromToken, converter, _amount);
// 这里是真正执行转换的方法
_amount = converter.change(_fromToken, toToken, _amount, i == pathLength - 2 ? _minReturn : 1);
_fromToken = toToken;
}
return (toToken, _amount);
}
ContractFeatures里面存了如何计算价格需要的内容,真正的Bancor算法的合约名是BancorFormula。
在这个方法里我们看到了一个循环,非常的奇怪,每次循环都是加2。
这样做的原因是我们进行货币兑换的时候,我们的源货币跟目标货币,并不一定是经过一次转化就可以完成,因为我们所有代币的中轴是BNT,只要两个非BNT的代币兑换就会起码需要两次。
举个
假如我有两个代币,ERA和ERB,那么传进来的path会是
[ERA, ERABNT, BNT, ERBBNT, ERB]
这里只是伪代码,数组类型实际是IERC20类型的。
那么为什么要+2呢,前面我们说过了,BancorConverter是基于某一个智能代币的,可以直接兑换两个代币的值,所以,兑换一次,需要3个数[fromToken, smartToken, toToken]。
增加减少钱包的值
/**
@dev converts a specific amount of _fromToken to _toToken
@param _fromToken ERC20 token to convert from
@param _toToken ERC20 token to convert to
@param _amount amount to convert, in fromToken
@param _minReturn if the conversion results in an amount smaller than the minimum return - it is cancelled, must be nonzero
@return conversion return amount
*/
function convertInternal(IERC20Token _fromToken, IERC20Token _toToken, uint256 _amount, uint256 _minReturn)
public
bancorNetworkOnly
conversionsAllowed
greaterThanZero(_minReturn)
returns (uint256)
{
require(_fromToken != _toToken); // validate input
// conversion between the token and one of its connectors
if (_toToken == token)
return buy(_fromToken, _amount, _minReturn);
else if (_fromToken == token)
return sell(_toToken, _amount, _minReturn);
// conversion between 2 connectors
uint256 amount = getCrossConnectorReturn(_fromToken, _toToken, _amount);
// ensure the trade gives something in return and meets the minimum requested amount
require(amount != 0 && amount >= _minReturn);
// 更新源token连接器储备量
Connector storage fromConnector = connectors[_fromToken];
if (fromConnector.isVirtualBalanceEnabled)
fromConnector.virtualBalance = safeAdd(fromConnector.virtualBalance, _amount);
// 更新目标token连接器储备量
Connector storage toConnector = connectors[_toToken];
if (toConnector.isVirtualBalanceEnabled)
toConnector.virtualBalance = safeSub(toConnector.virtualBalance, amount);
// ensure that the trade won't deplete the connector balance
uint256 toConnectorBalance = getConnectorBalance(_toToken);
assert(amount < toConnectorBalance);
// 源token目标余额减少
assert(_fromToken.transferFrom(msg.sender, this, _amount));
// 目标token钱包余额增加
assert(_toToken.transfer(msg.sender, amount));
// calculate conversion fee and dispatch the conversion event
// the fee is higher (magnitude = 2) since cross connector conversion equals 2 conversions (from / to the smart token)
uint256 feeAmount = safeSub(amount, getFinalAmount(amount, 2));
dispatchConversionEvent(_fromToken, _toToken, _amount, amount, feeAmount);
// dispatch price data updates for the smart token / both connectors
emit PriceDataUpdate(_fromToken, token.totalSupply(), getConnectorBalance(_fromToken), fromConnector.weight);
emit PriceDataUpdate(_toToken, token.totalSupply(), getConnectorBalance(_toToken), toConnector.weight);
return amount;
}
总结
到这里,bancor去中心化交易所的分析就告一段落了,这个系列只是粗线的介绍了一下这个去中心化交易所的核心流程,实际上这个交易所的合约非常多,而且十分复杂,里面使用了很多solidity的技巧,如果感兴趣的同学,可以去看看传送门。
bancor去中心化交易所解析(1)bannor协议
bancor去中心化交易所解析(2)BNT
bancor去中心化交易所解析(3)Bancor交易所上币及合约分析