DQL(data query language)数据查询语言,主要的作用是对数据库中的数据进行查询的操作,也是最重要的功能,查询的方法也是多种多样:联合查询、分组查询、内连查询、子查询等,还可以限制查询的条数等,下面一一介绍。
复习创建表
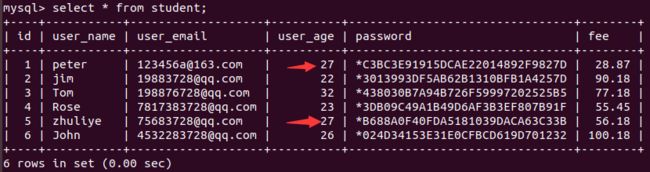
先创建两个表:student和mark表,其中student表中存储的学生姓名、年纪等信息,mark表中存储的是分数和学生学号等信息
-
student表
+----+-----------+-------------------+----------+--------------------------------+--------+
| id | user_name | user_email | user_age | password | fee |
+----+-----------+-------------------+----------+--------------------------------+--------+
| 1 | peter | [email protected] | 27 | *C3BC3E91915DCAE22014892F9827D | 28.87 |
| 2 | jim | [email protected] | 22 | *3013993DF5AB62B1310BFB1A4257D | 90.18 |
| 3 | Tom | [email protected] | 32 | *438030B7A94B726F59997202525B5 | 77.18 |
| 4 | Rose | [email protected] | 23 | *3DB09C49A1B49D6AF3B3EF807B91F | 55.45 |
| 5 | zhuliye | [email protected] | 27 | *B688A0F40FDA5181039DACA63C33B | 56.18 |
| 6 | John | [email protected] | 26 | *024D34153E31E0CFBCD619D701232 | 100.18 |
+----+-----------+-------------------+----------+--------------------------------+--------+
-
mark表
# 建表
mysql> create table mark(
> id int unsigned not null auto_increment primary key,
> mark int(20) not null comment "score",
> stu_id varchar(20) not null comment "student_id"
> );
# 查看表结构
mysql> desc mark;
+--------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+--------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(10) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| mark | int(20) | NO | | NULL | |
| stu_id | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | |
+--------+------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
# 插入数据
mysql> insert into mark values(1, 66, "2");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into mark values(2, 75, "3");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into mark values(3, 88, "4");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> insert into mark values(4, 90, "5");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into mark values(5, 82, "6");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from mark;
+----+------+--------+
| id | mark | stu_id |
+----+------+--------+
| 1 | 66 | 2 |
| 2 | 75 | 3 |
| 3 | 88 | 4 |
| 4 | 90 | 5 |
| 5 | 82 | 6 |
+----+------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
普通查询
where普通查询
带上where条件进行查询,条件可以是指定id或者其他字段。
mysql> select password, fee from student where id=3;
+--------------------------------+-------+
| password | fee |
+--------------------------------+-------+
| *438030B7A94B726F59997202525B5 | 77.18 |
+--------------------------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
mysql> select password from student where user_name="Tom";
+--------------------------------+
| password |
+--------------------------------+
| *438030B7A94B726F59997202525B5 |
+--------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
过滤查询
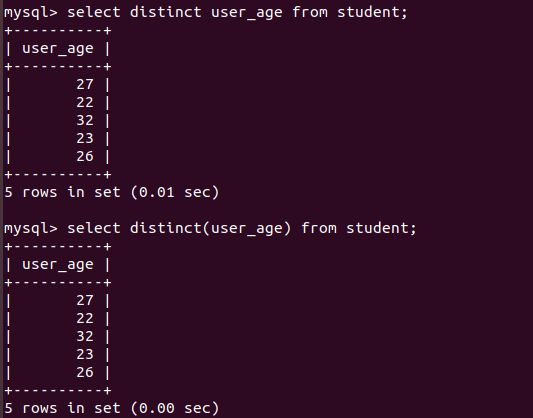
.如果某个表中,某些字段的值有重复,可以进行过滤查询。过滤重复字段的关键词是distinct。student表中的age字段有重复值:
mysql> select distinct user_age from student; # 括号有没有均可
mysql> select distinct(user_age) from student;
连接查询
连接查询的关键词是concat,有三种不同的使用情况:
- 直接使用
concat - 使用
concat....as....;显示出来的时候用as后面的别名 - 带上连接符号的查询
concat_ws("==", 列名1,列名2);其中"=="就是指定连接符
模糊查询
模糊查询的关键字是like,中文翻译成像:
mysql> select user_name from student where user_name like "peter"; # 像peter
mysql> select user_name from student where user_name like "%e"; # %表示任意,表示名字以e结尾
mysql> select user_name from student where user_name like "%e%"; # 表示名字中含有e
排列
对表中的记录进行升序asc或者降序desc的排列,默认的是升序asc:
mysql> select * from student order by user_age asc; # 年龄的升序
mysql> select * from student order by user_age desc; # 年龄的降序
聚合函数
select count(*) from student; # 总记录
select sum(列名) from student; # 总和
select avg(列名) from student; # 平均值
select max/min(列名) from student; # 最大/小值
高级查询
分组查询
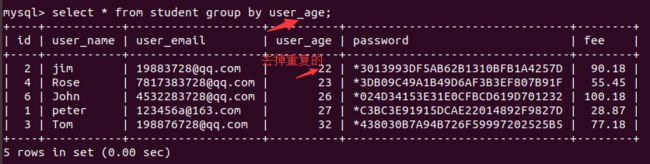
分组查询中主要使用的是group by,通过by后面的条件来筛选,同时会有一个排序(默认是升序)和去重的功能存在,从而进行查询:
mysql> select * from student group by user_age;
-
年纪中有重复的值,对比上图,进行去重显示:
-
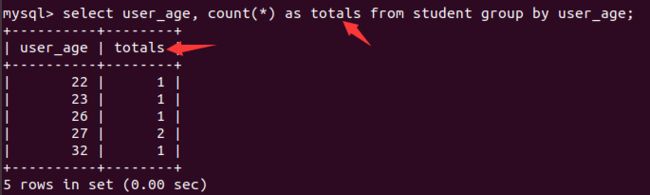
根据年龄统计个数,并且显示
user_name和别名totals:
通过
group by ...having...联合进行查询
mysql> select user_name, fee from student group by user_age having count(*)=1;
mysql> select user_name, fee from student group by user_age having count(*)=2;
内连查询
仔细看看笔者之前创建的两个表,student表中有学生的各种信息,mark表中有个分数和学生编号,请问如何通过这两个表,找到student表中对应mark表里面stu_id的成绩呢?内连查询解决的就是这个问题
mysql> select user_name, mark from student, mark where mark.stu_id = student.id; # 通过指定mark.stu_id = student.id 作为限定条件
+-----------+------+
| user_name | mark |
+-----------+------+
| jim | 66 |
| Tom | 75 |
| Rose | 88 |
| zhuliye | 90 |
| John | 82 |
+-----------+------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
- 使用别名
# 适合两个表中没有想用字段
mysql> select user_name, mark from student as s, mark as m where m.stu_id = s.id;
# 适合两个表中具有相同字段使用:一定要指明哪个字段属于那个表
mysql> select s.user_name, m.mark from student as s, mark as m where m.stu_id = s.id;
-
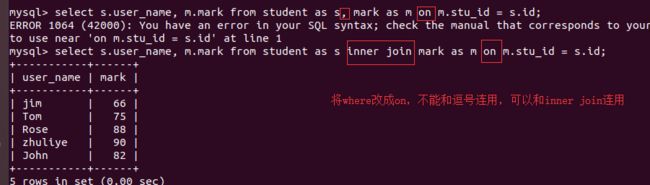
inner join查询
将上面两个表之间的逗号换成inner join
mysql> select s.user_name, m.mark from student as s inner join mark as m where m.stu_id = s.id;
where换成on
-
where可以换成on -
on不能和逗号连用 -
on只能和inner join连用
左右连接
- 左连接
mysql> select s.user_name, m.mark from student as s left join mark as m on m.stu_id = s.id;
- 右连接
mysql> select s.user_name, m.mark from student as s right join mark as m on m.stu_id = s.id;
联合查询
联合查询的关键字是union all,需要注意的是查询的时候字段需要保持一致。
-
where条件的拆分
mysql> select * from student where id in (2,4);
mysql> select * from student where id=2 union all select * from student where id=4;
子查询
mysql> select user_name, id from student where id in (select stu_id from mark);
# 结果
+-----------+----+
| user_name | id |
+-----------+----+
| jim | 2 |
| Tom | 3 |
| Rose | 4 |
| zhuliye | 5 |
| John | 6 |
+-----------+----+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
限制查询条数limit
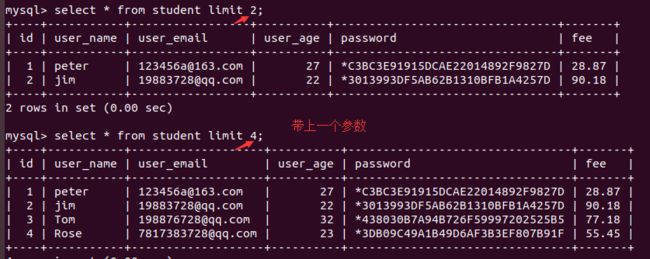
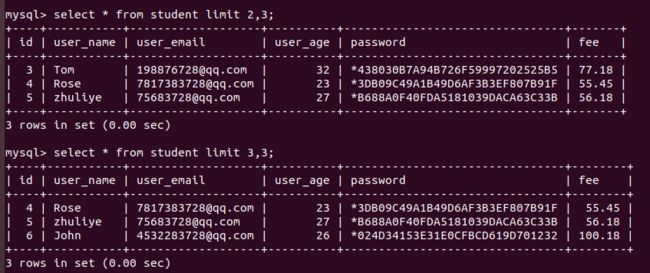
limit的作用主要是有两个:
- 如果带上一个参数,则限制每次显示的记录条数
- 如果带上两个参数,则第一个表示从哪个位置开始显示,第二个表示显示多少条记录,可以当做“分页功能”
- 以
student表为栗子:
若带上两个参数
带上两个参数形式等价于limit...offset...