一、概念:
1)、 ((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)person, sel_registerName("test"));
oc的方法的调用(消息机制)其实都是转化为objc_msgSend函数调用,给方法调用者发送消息;
消息接收者(receiver):LZHPerson 消息名称:test
2)、 objc_msgSend的执行流程可以分为3大阶段
第一阶段: 消息发送
第二阶段: 动态方法解析
第三阶段: 消息转发 将消息转发给别人去实现;
如果经历过以上3个阶段objc_msgSend 找不到合适的方法进行调用,会报错unrecognized selector sent to instance;
注:元类对象是一种特殊的类对象;
二、objc_msgSend底层实现:
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
UNWIND _objc_msgSend, NoFrame
MESSENGER_START
//寄存器:消息接收者:receiver
cmp x0, #0 // nil check and tagged pointer check
b.le LNilOrTagged // (MSB tagged pointer looks negative)
ldr x13, [x0] // x13 = isa
and x16, x13, #ISA_MASK // x16 = class
LGetIsaDone:
CacheLookup NORMAL // calls imp or objc_msgSend_uncached
LNilOrTagged:
b.eq LReturnZero // nil check
// tagged
mov x10, #0xf000000000000000
cmp x0, x10
b.hs LExtTag
adrp x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes@PAGE
add x10, x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes@PAGEOFF
ubfx x11, x0, #60, #4
ldr x16, [x10, x11, LSL #3]
b LGetIsaDone
LExtTag:
// ext tagged
adrp x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_ext_classes@PAGE
add x10, x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_ext_classes@PAGEOFF
ubfx x11, x0, #52, #8
ldr x16, [x10, x11, LSL #3]
b LGetIsaDone
LReturnZero:
// x0 is already zero
mov x1, #0
movi d0, #0
movi d1, #0
movi d2, #
从上述描述可以看出是汇编语言编写,分析其逻辑如下:
1.判断消息接收者是否为nil,如果为nil直接返回0;
movi d3, #0
MESSENGER_END_NIL
ret
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend
2.receiver通过ISA指针找到receiverClass;然后查找缓存;如果查找到了,就返回imp;
如果没有找到:就去查找方法列表;(methodtable)如果调用c的函数_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache
3.查找rw_t里面methodlist;如果排序好了使用二分查找,如果没有排序好,使用正常的遍历数组方式查找;
4.如果找到以后,把sel方法名作为key imp为vale存入cache里面的bucket里面去;
5.如果本身类里面没有找到,receiverClass通过superclass指针找到superclass;然后会再去查找superclass的查找父类的缓存和methodtable里面查找;
如果都没有找到会进行动态解析;
从汇编逻辑上看会触发C函数_class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3,下面分析一下该函数的具体实现如下:
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
IMP imp = nil;
bool triedResolver = NO;
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
1.消息发送
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
runtimeLock.read();
}
retry:
runtimeLock.assertReading();
// Try this class's cache.
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);//再去查找一下缓存;
if (imp) goto done;
// Try this class's method lists.
{
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// Try superclass caches and method lists.
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
for (Class curClass = cls->superclass;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// Superclass method list.
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
}
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.//动态解析
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.read();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding. 消息转发
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
return imp;
}
getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
assert(cls->isRealized());
// fixme nil cls?
// fixme nil sel?
for (auto mlists = cls->data()->methods.beginLists(),
end = cls->data()->methods.endLists();
mlists != end;
++mlists)
{
method_t *m = search_method_list(*mlists, sel);
if (m) return m;
}
return nil;
}
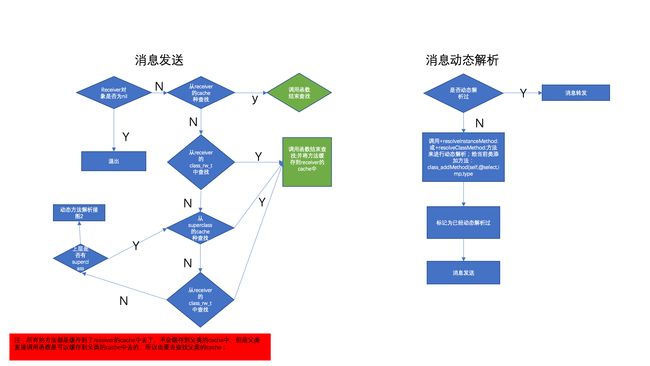
三:总结消息发送如下图:
四:动态解析
4.1从底层分析可以看出来:
1. _class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst); 实例方法消息动态解析: resolveInstanceMethod 类方法:resolveClassMethod;
2. 开发者可以实现以下方法,来动态添加方法实现;
3.动态解析过后l,会重新走“消息发送”的流程;
4.2具体的方法实现如下:
方法一:
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
if(sel ==@selector(test1)) {
Method otherMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self,@selector(other));
使用C++反编译:
// 获取其他方法 typedef struct objc_method *Method;
// struct objc_method <==> 等价于 struct method_t;
struct method_t * otherMethod = (struct method_t*)class_getInstanceMethod(self,@selector(other));
NSLog(@"%s,%s,%p",otherMethod->sel,otherMethod->type,otherMethod->imp);
// 打印结构如下:看出type类型
// 2020-12-30 17:58:52.368005+0800 objc_msgsend[5735:122677] other,UH\M^I\M-eH\M^C\M-l\^PH\M^M\^E\M-i\^B,0x100000fad
// 动态添加test方法;
class_addMethod(self, sel, otherMethod.imp, otherMethod.type);
class_addMethod(self.class, sel, (IMP)c_other,"v16@0:8");
returnYES;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}
方法二:
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
if(sel ==@selector(test1)) {
// Method otherMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(other));
// 动态添加test方法;
class_addMethod(self, sel, method_getImplementation(otherMethod),method_getTypeEncoding(otherMethod));
returnYES;
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}
4.3消息转发总结:如上述图1-1所示;
五、消息转发:
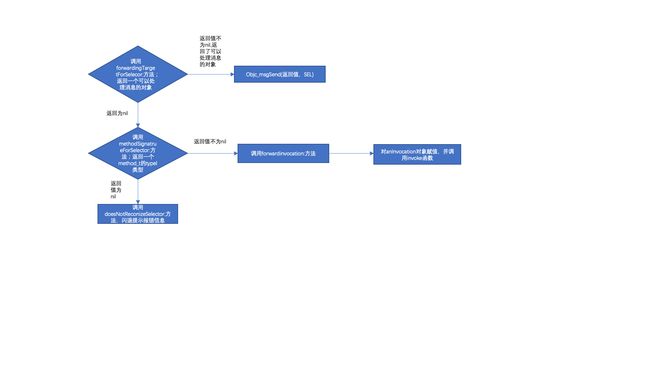
5.1:消息转发就是 返回一个可以处理这个消息的类;首先会触发forwardingTargetForSelector函数,返回一个可以处理这个消息的对象如果没有实现,会触发方法签名methodSignatureForSelector函数,返回一个方法类型type;有且只有方法返回方法type类型后,才会处理forwardInvocation函数;具体底层实现如二的底层分析代码;
5.2具体的方法实现:
5.2.1 forwardingTargetForSelector 转发给一个可以实现的类对象;
-(id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if(aSelector ==@selector(test1)) {
// 返回一个对象就是类似于调用 objc_msgSend([[lzhCat alloc]init],aSelector),给这个类发送消息
return[[lzhCatalloc]init];
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
5.2.2方法签名methodSignatureForSelector:返回值类型、参数类型,如果返回为nil,就不会调用forwardInvocation;会直接报错闪退信息;
-(NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector
{
if(aSelector ==@selector(run1)) {
// return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v16@0:8"];
// 方法一:自己写type;
// return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v20@0:8i:16"];
// 方法二: 签名决定着anInvocation的包装的参数类型和多少;
return [[[lzhCat alloc]init] methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
5.2.3如果返回签名有值,就会调用forwardInvocation来处理。
//NSInvocation 封装了一个方法调用,包括:方法调用者、方法名、方法参数;
//处理方法的实现;
-(void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation*)anInvocation{
// anInvocation.target;//方法调用者
// anInvocation.selector 方法名
// [anInvocation getArgument:NULL atIndex:0]; 获取方法参数
// 方法一:
anInvocation.target= [[lzhCatalloc]init];
int age ;
// 参数顺序:receiver、selector\_cmd、other argument
[anInvocation getArgument:&age atIndex: 2];
[anInvocation invoke];//调用这方法
// 获取函数的返回值;
[anInvocation getReturnValue:&age];
// 方法二:
[anInvocation invokeWithTarget:[[lzhCatalloc]init]];
// 初始值:
// anInvocation.target = person对象
// anInvocation.selector = test:
// anInvocation的参数: receiver、selector、15;2个隐试参数;
//}
5.3 、消息转发总结如图所示
六:类方法;
类方法是有消息发送、动态解析、消息转发机制的;只不过消息转发没有系统函数,需要手动修改这个函数;把减号改为加号即可;
具体的实现如下:
+(BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel
{
if(sel ==@selector(run1)) {
}
return [super resolveClassMethod:sel];
}
+(id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
return[[lzhCatalloc]init];
}
+(NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
if(aSelector ==@selector(run1)) {
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v20@0:8i:16"];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
+(void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation*)anInvocation{
NSLog(@"%s",anInvocation.selector);
}
七:小知识点补充:
//@dynamic
//@dynamic age;
@synthesize age = _age11;
//@synthesize age = _age; //会生成set,get函数;
//@dynamic age; //取消系统的setter,getter函数;不需要系统生成;
八:知识扩展
举例说明: 在工程目录里面声明一个LZHPerson对象;在对象里面实现一个run方法、一个成员变量name,run方法里面打印
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
id cls = [LZHPerson class];
void*obj = &cls;//类对象;
// 给类对象发送消息;
[(__bridgeid)obj print];
}
一.print为什么可以调用成功?
1.通常情况下,我们通过实例调用一个函数,就是person指针指向了person的实例对象结构体的首地址,而首地址就是isa指针,ISA指针指向了person的类对象;
2.从上面代码分析可以看出,obj 是指向cls指针的指针;cls指向类对象LzhPerson;原理类似于实例对象调用的关系;
3.cls类似于ISA指针;
4.所以可以调用成功;
二.为什么self.name变成了VierController;
1.[super viewDidLoad];
super首先是声明了一个结构体对象:{当前的消息接收者,消息接收者的superclass指针指向的对象};其实就是高地址里面有一个消息接收者对象;self。这个时候消息接收者就是VierController对象;
name在实例对象里面是一个属性,内存地址在ISA下面;正常查找会越过ISA的8个字节,继续查找高地址位的东西,当前高地址位是super声明的结构对象,高地址位是消息接收者,所以会找到VC的内存地址,打印出来VC的对象;
三、局部变量分配在栈空间;
long longa =4;
long longb =8;
long longc =12;
是由高地址到地址地址的连续一块内存空间;